|
Fatty Aldehyde
Fatty aldehydes are aliphatic, long-chain aldehydes which may be mono- or polyunsaturated. The fatty aldehydes include compounds such as octanal, nonanal, decanal or dodecanal. The nomenclature is derived from the nomenclature of the alkanes, the ending ''-al'' is added to indicate the aldehyde group. Occurrence Fatty aldehydes are a natural component of many natural ingredients such as the essential oils of various citrus fruits. Decanal, for example, is a component of orange peel. The pheromone cocktails of various insect pheromones contain fatty aldehydes. Fat aldehydes were also detected in the heart muscle of mammals. Preparation Fatty aldehydes can be prepared by dehydrogenation of fatty alcohols on copper-zinc catalysts. By the hydroformylation of alkenes, fatty aldehydes are produced on a large industrial scale. Use A large proportion of the fatty aldehydes prepared by hydroformylation is directly processed further to fatty alcohols. Many fatty aldehydes find use a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecanal
Dodecanal, also known as lauraldehyde or dodecyl aldehyde, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)10CHO. This colourless liquid is a component of many fragrances. It occurs naturally in citrus oils, but commercial samples are usually produced from dodecanol by dehydrogenation. References Fatty aldehydes Alkanals {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Alcohol
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies with the source. Some commercially important fatty alcohols are lauryl, stearyl, and oleyl alcohols. They are colourless oily liquids (for smaller carbon numbers) or waxy solids, although impure samples may appear yellow. Fatty alcohols usually have an even number of carbon atoms and a single alcohol group (–OH) attached to the terminal carbon. Some are unsaturated and some are branched. They are widely used in industry. As with fatty acids, they are often referred to generically by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule, such as "a C12 alcohol", that is an alcohol having 12 carbons, for example dodecanol. Production and occurrence Most fatty alcohols in nature are found as waxes which are esters of fatty acids and fatty alcohols. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Alcohol
Fatty alcohols (or long-chain alcohols) are usually high-molecular-weight, straight-chain primary alcohols, but can also range from as few as 4–6 carbons to as many as 22–26, derived from natural fats and oils. The precise chain length varies with the source. Some commercially important fatty alcohols are lauryl, stearyl, and oleyl alcohols. They are colourless oily liquids (for smaller carbon numbers) or waxy solids, although impure samples may appear yellow. Fatty alcohols usually have an even number of carbon atoms and a single alcohol group (–OH) attached to the terminal carbon. Some are unsaturated and some are branched. They are widely used in industry. As with fatty acids, they are often referred to generically by the number of carbon atoms in the molecule, such as "a C12 alcohol", that is an alcohol having 12 carbons, for example dodecanol. Production and occurrence Most fatty alcohols in nature are found as waxes which are esters of fatty acids and fatty alcohols. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfume Industry
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. The 1939 Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory." Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin or coumarin, which allowed for the composition of perfumes with smells previously unattainable solely from natural aromatics. History The word ''perfume'' derives from the Latin ''perfumare'', meaning "to smoke through". Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, family-run activities that are highly labor-intensive, to large, capital-intensive and highly mechanized industrial processes. Many food industries depend almost entirely on local agriculture, produce, or fishing. It is challenging to find an inclusive way to cover all aspects of food production and sale. The UK Food Standards Agency describes it as "the whole food industry – from farming and food production, packaging and distribution, to retail and catering." The Economic Research Service of the USDA uses the term ''food system'' to describe the same thing, stating: "The U.S. food system is a complex network of farmers and the industries that link to them. Those links include makers of farm equipment and chemicals as well as firms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavoring Agent
A flavoring (or flavouring), also known as flavor (or flavour) or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptors of the gustatory and olfactory systems. Along with additives, other components like sugars determine the taste of food. A flavoring is defined as a substance that gives another substance taste, altering the characteristics of the solute, causing it to become sweet, sour, tangy, etc. Although the term, in common language, denotes the combined chemical sensations of taste and smell, the same term is used in the fragrance and flavors industry to refer to edible chemicals and extracts that alter the flavor of food and food products through the sense of smell. Owing to the high cost, or unavailability of natural flavor extracts, most commercial flavorings are "nature-identical", which means that they are the chemical equivalent of natural flavors, but c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanel No
Chanel No. 5 was the first perfume launched by French couturier Gabrielle "Coco" Chanel in 1921. The scent formula for the fragrance was compounded by French-Russian chemist and perfumer Ernest Beaux. The design of its bottle has been an important part of the product's branding. Coco Chanel was the first face of the fragrance, appearing in the advertisement published by Harper's Bazaar in 1937. Inspiration Traditionally, fragrances worn by women fell into two basic categories. "Respectable women" favored the essence of a single garden flower while sexually provocative indolic perfumes heavy with animal musk or jasmine were associated with women of the demi-monde, prostitutes, or courtesans. Chanel sought a new scent that would appeal to the flapper and celebrate the seemingly liberated feminine spirit of the 1920s. The No. 5 name At the age of twelve, Chanel was handed over to the care of nuns, and for the next six years spent a stark, disciplined existence in a conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
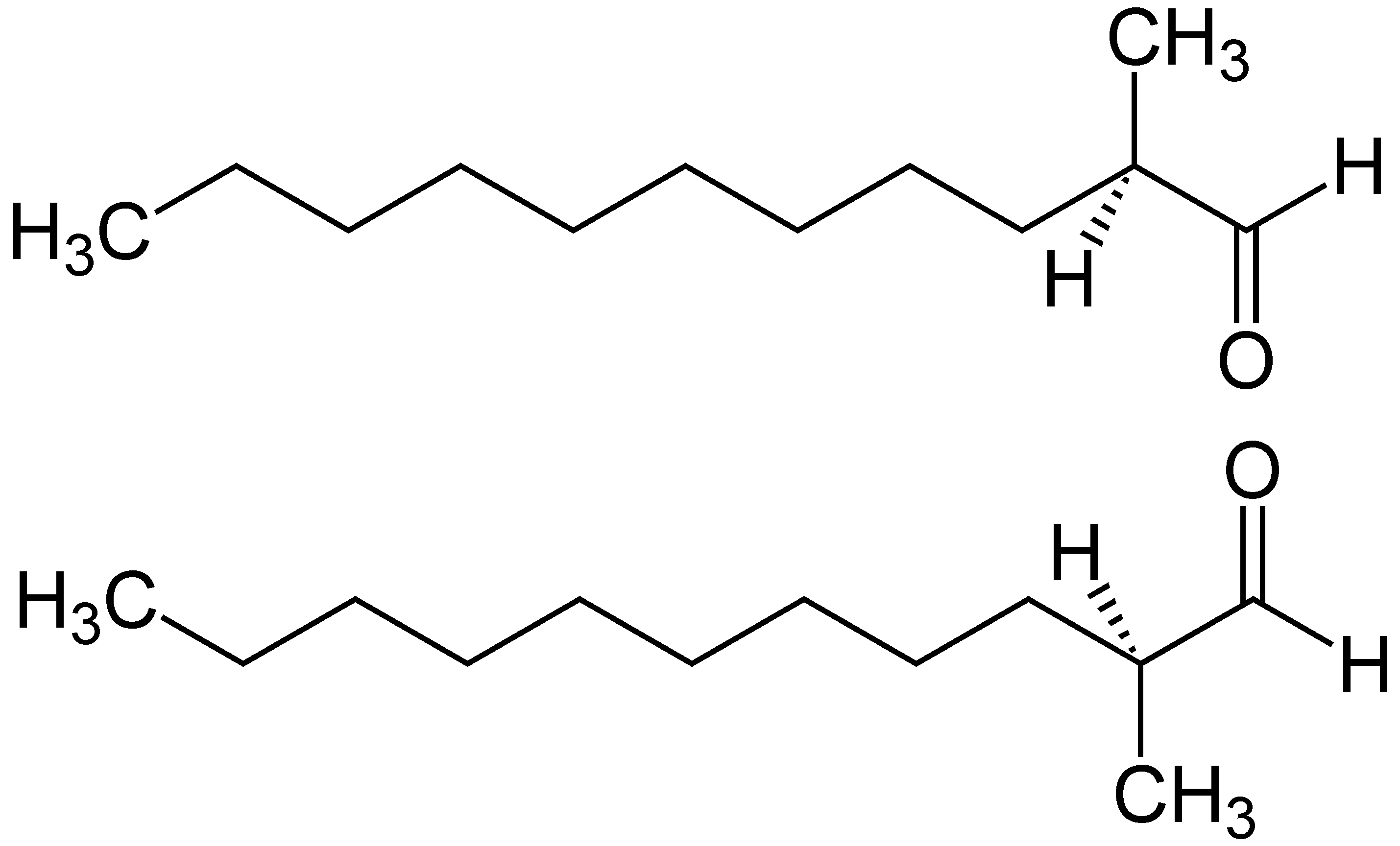
2-Methylundecanal
2-Methylundecanal is an organic compound that is found naturally in kumquat peel oil. This compound smells herbaceous, orange, and ambergris-like. At high dilution it has a flavor similar to honey and nuts. It is a colorless or pale yellow liquid that is soluble in organic solvents such as ether and ethanol. It is used as a fragrance component in soaps, detergents, and perfumes. Preparation The first synthesis of 2-methylundecanal was recorded by Georges Darzens in 1904 from methyl nonyl ketone and ethyl chloroacetate. This method of synthesis can be used to produce a variety of aldehydes and became known as the Darzens reaction and is still used today. 2-Methylundecanal is synthesized in industry by two main routes. The first route, like Darzens, involves converting methyl nonyl ketone to its glycidate by allowing it to react with alkyl chloroacetate. The glycidate then undergoes saponification followed by decarboxylation. :CH3(CH2)8C(O)CH3 + ClCH2CO2CH3 → CH3(CH2)8CH(CH3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragrance
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds, particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds. Generally, molecules meeting this specification have molecular weights of less than 310. Flavors affect both the sense of taste and smell, whereas fragrances affect only smell. Flavors tend to be naturally occurring, and the term ''fragrances'' may also apply to synthetic compounds, such as those used in cosmetics. Aroma compounds can naturally be found in various foods, such as fruits and their peels, wine, spices, floral scent, perfumes, fragrance oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroformylation
Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and drugs. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry. The process entails treatment of an alkene typically with high pressures (between 10 and 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. In one variation, formaldehyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |