|
Foramina Of Morgagni
The sternocostal triangle (foramina of Morgagni, Larrey's space, sternocostal hiatus, etc.) are small zones lying between the costal and sternal attachments of the thoracic diaphragm. No vascular elements are present within this space. The borders of this space are: Medial: the lateral border of the sternal part of the diaphragm Lateral: the medial border of the costal part of the diaphragm Anterior: the musculoaponeurotic plane formed by a confluence of the transversus thoracis superiorly and the transversus abdominis inferiorly The superficial epigastric artery passes in front of the aponeurotic plane that forms the anterior border and enters the abdomen anterior to the diaphragm. Eponym It is named for Giovanni Battista Morgagni. Pathology It can be a site of Morgagni's hernia Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
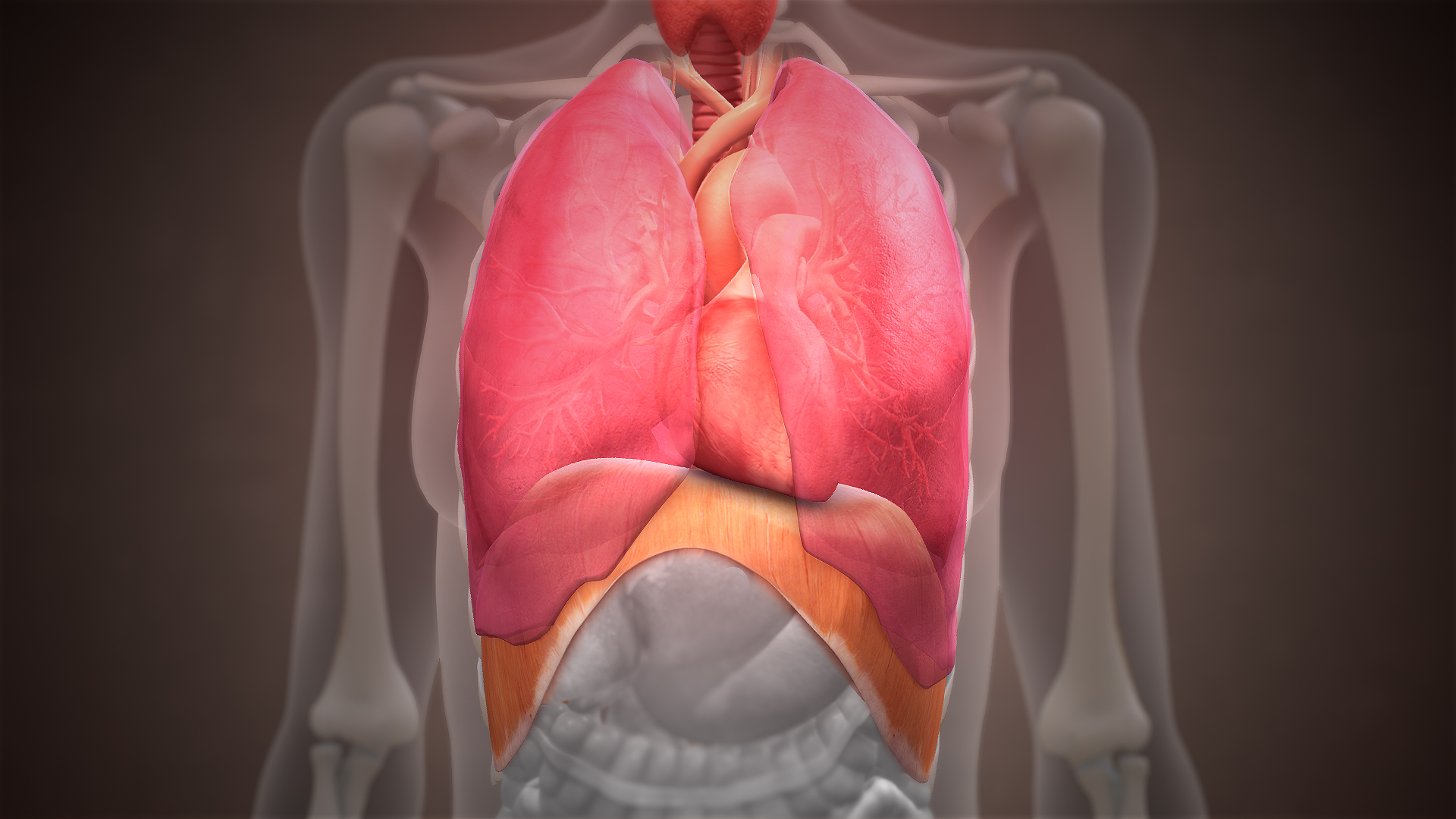
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversus Thoracis Muscle
The transversus thoracis muscle (), also known as triangularis sterni, lies internal to the thoracic cage, anteriorly. It is usually a thin plane of muscular and tendinous fibers, however on athletic individuals it can be a thick 'slab of meat', situated upon the inner surface of the front wall of the chest. It is in the same layer as the subcostal muscles and the innermost intercostal muscles. Structure It arises on either side from the lower third of the posterior surface of the body of the sternum, from the posterior surface of the xiphoid process, and from the sternal ends of the costal cartilages of the lower three or four true ribs. Its fibers diverge upward and lateralward, to be inserted by slips into the lower borders and inner surfaces of the costal cartilages of the second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth ribs. The lowest fibers of this muscle are horizontal in their direction, and are continuous with those of the transversus abdominis; the intermediate fibers are ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Abdominal Muscle
The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral (front and side) abdominal wall which is deep to (layered below) the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core. Structure The transverse abdominal, so called for the direction of its fibers, is the innermost of the flat muscles of the abdomen. It is positioned immediately inside of the internal oblique muscle. The transverse abdominal arises as fleshy fibers, from the lateral third of the inguinal ligament, from the anterior three-fourths of the inner lip of the iliac crest, from the inner surfaces of the cartilages of the lower six ribs, interdigitating with the diaphragm, and from the thoracolumbar fascia. It ends anteriorly in a broad aponeurosis (the Spigelian fascia), the lower fibers of which curve inferomedially (medially and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Epigastric Artery
The superficial epigastric artery (not to be confused with the superior epigastric artery) arises from the front of the femoral artery about 1 cm below the inguinal ligament, and, passing through the femoral sheath and the fascia cribrosa, turns upward in front of the inguinal ligament, and ascends between the two layers of the superficial fascia of the abdominal wall nearly as far as the umbilicus. It distributes branches to the superficial subinguinal lymph glands, the superficial fascia, and the integument; it anastomoses with branches of the inferior epigastric Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton *Inferior (book), ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The ..., and with its fellow of the opposite side. Additional images File:Gray393.png, The subcutaneous inguinal ring File:Gray550.png, The femoral artery File:Gray58 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Morgagni
Giovanni Battista Morgagni (25 February 1682 – 6 December 1771) was an Italian anatomist, generally regarded as the father of modern anatomical pathology, who taught thousands of medical students from many countries during his 56 years as Professor of Anatomy at the University of Padua. His most significant literary contribution, the monumental five-volume ''On the Seats and Causes of Disease'', embodied a lifetime of experience in anatomical dissection and observation, and established the fundamental principle that most diseases are not vaguely dispersed throughout the body, but originate locally, in specific organs and tissues. Education His parents were in comfortable circumstances, but not of the nobility; it appears from his letters to Giovanni Maria Lancisi that Morgagni had ambitions to improve his rank. It may be inferred that he succeeded from the fact that he is described on a memorial tablet at Padua as ''nobilis forolensis'', "noble of Forlì", apparently by right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgagni's Hernia
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of the diaphragm allows the abdominal organs to push into the chest cavity, hindering proper lung formation. CDH is a life-threatening pathology in infants and a major cause of death due to two complications: pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension. Experts disagree on the relative importance of these two conditions, with some focusing on hypoplasia, others on hypertension. Newborns with CDH often have severe respiratory distress which can be life-threatening unless treated appropriately. Classification Bochdalek hernia The Bochdalek hernia, also known as a postero-lateral diaphragmatic hernia, is the most common manifestation of CDH, accounting for more than 95% of cases. In this instance the diaphragm abnormality is character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |