|
Fluorosulfonic Acid
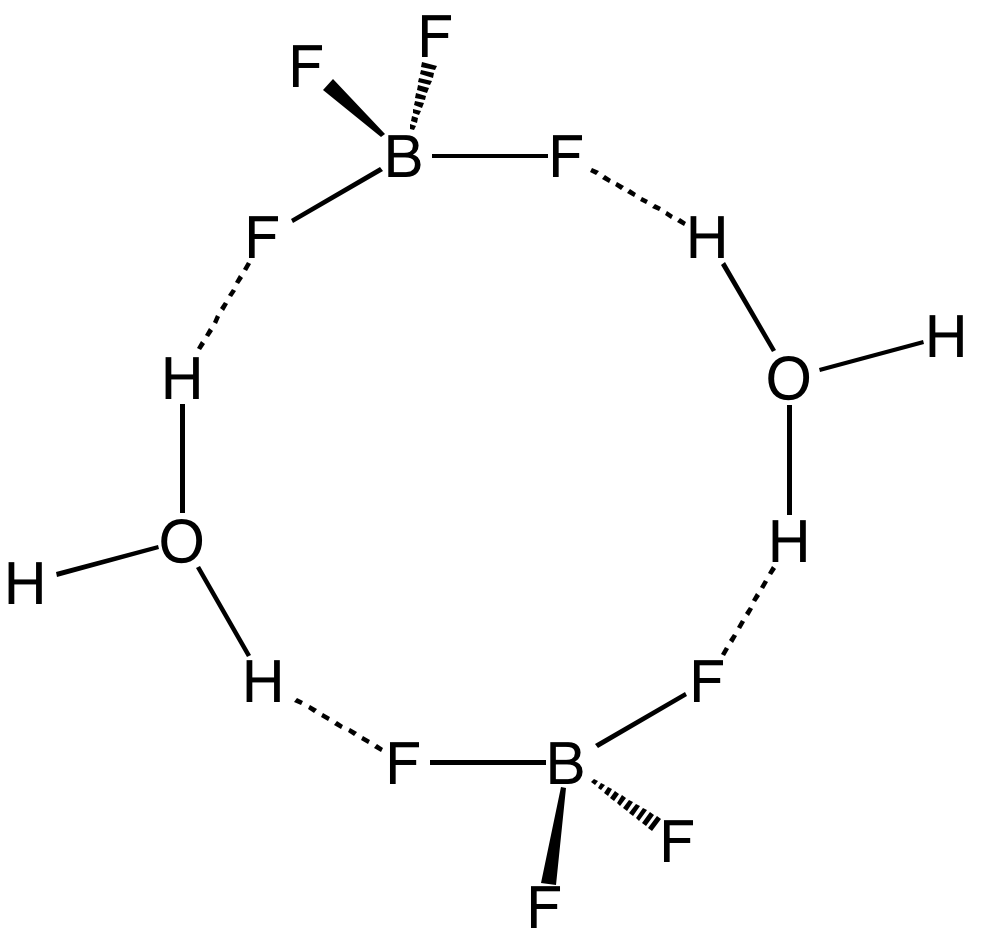
Fluorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurofluoridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available. It is a tetrahedral molecule and is closely related to sulfuric acid, H2SO4, substituting a fluorine atom for one of the hydroxyl groups. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples are often yellow.Erhardt Tabel, Eberhard Zirngiebl, Joachim Maas "Fluorosulfuric Acid" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Chemical properties Fluorosulfuric acid is a free-flowing colorless liquid. It is soluble in polar organic solvents (e.g. nitrobenzene, acetic acid, and ethyl acetate), but poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents such as alkanes. Reflecting its strong acidity, it dissolves almost all organic compounds that are even weak proton acceptors. HSO3F hydrolyzes slowly to hydrogen fluoride (HF) and sulfuric acid. The related triflic acid () retains the high acidity of HSO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorosulfate
Fluorosulfonate, in organic chemistry, is a functional group that has the chemical formula F-SO2-R, and typically is a very good leaving group. In organic chemistry, fluorosulfonate is different than fluorosulfate. In fluorosulfonates, sulfur atom is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom such as carbon. In inorganic chemistry, fluorosulfonate is another term for fluorosulfate, the anion F-SO2-O−, the conjugate base of fluorosulfonic acid. They form a series of salts with metal and organic cations called fluorosulfates. Organic (alkyl) fluorosulfonates are usually strong alkylation agents, similar to triflate esters (F3C-SO2-OR). But unlike the triflate group, the fluorosulfonate group is not stable against hydrolysis. Therefore, fluorosulfonate esters are less frequently used as alkylation agents than triflate esters. See also * Fluorosulfite * Methyl fluorosulfonate Methyl fluorosulfonate, also known as magic methyl, is the organic compound with the formula FSO2OCH3. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleum
Oleum (Latin ''oleum'', meaning oil), or fuming sulfuric acid, is a term referring to solutions of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid, or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid (also known as pyrosulfuric acid). Oleum is identified by the CAS number 8014-95-7 (EC/List number: 616-954-1 ECHA InfoCard: 100.116.872. Oleums can be described by the formula ''y''SO3·H2O where ''y'' is the total molar mass of sulfur trioxide content. The value of ''y'' can be varied, to include different oleums. They can also be described by the formula H2SO4·''x''SO3 where ''x'' is now defined as the molar free sulfur trioxide content. Oleum is generally assessed according to the free SO3 content by mass. It can also be expressed as a percentage of sulfuric acid strength; for oleum concentrations, that would be over 100%. For example, 10% oleum can also be expressed as H2SO4·''0.13611''SO3, ''1.13611''SO3·H2O or 102.25% sulfuric acid. The conversion between % acid and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Fluorosulfonate
Methyl fluorosulfonate, also known as magic methyl, is the organic compound with the formula FSO2OCH3. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a strong methylating agent in organic synthesis. Because of its extreme toxicity, it has largely been replaced by the related reagent methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. Synthesis and reactions It is prepared by distillation of an equimolar mixture of fluorosulfonic acid and dimethyl sulfate. It was originally produced by the reaction of methanol with fluorosulfonic acid. Methyl fluorosulfonate is a highly electrophilic reagent for methylation. It is ranked as less powerful than methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. Toxicity Similar to phosgene, it is acutely toxic by inhalation, with an LC50 (rat, 1 hour) of about 5 ppm. Several cases of poisoning resulting in death from pulmonary edema Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuryl Fluoride
Sulfuryl fluoride (also spelled ''sulphuryl fluoride'') is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula SO2F2. It is an easily condensed gas and has properties more similar to sulfur hexafluoride than sulfuryl chloride, being resistant to hydrolysis even up to 150 °C. It is neurotoxic and a potent greenhouse gas, but is widely used as a fumigant insecticide to control termites. Structure, preparation, reactions The molecule is tetrahedral with C2v symmetry point group, symmetry. The S-O distance is 140.5 pm, S-F is 153.0 pm. As predicted by VSEPR, the O-S-O angle is more open than the F-S-F angle, 124° and 97°, respectively. One synthesis begins with the preparation of potassium fluorosulfite: :SO2 + KF → KSO2F This salt is then chlorinated to give sulfuryl chloride fluoride: :KSO2F + Cl2 → SO2ClF + KCl Further heating at 180 °C of potassium fluorosulfite with the sulfuryl chloride fluoride gives the desired product: :SO2ClF + KSO2F → ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroantimonic Acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions (the simplest being and ). This substance is a superacid that can be over a billion times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid in terms of its protonating ability measured by Hammett function. It even protonates some hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations ( carbonium ions). Fluoroantimonic acid is corrosive. For example, it cannot be contained directly in glass carboys, as it attacks glass, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon). Chemical composition Fluoroantimonic acid is formed by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride: :SbF5 + 2 HF + H2F+ The speciation (i.e., the inventory of components) of "fluoroantimonic acid" is complex. Spectroscopic measurements show that fluoroantimonic acid consists of a mixture of HF-solvated protons, –_(such_as_)._Thus,_the_formula_""_is_a_convenient_but_overs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroboric Acid
Fluoroboric acid or tetrafluoroboric acid (archaically, fluoboric acid) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula +BF4−], where H+ represents the solvated proton. The solvent can be any suitably Lewis-basic entity. For instance, in water, it can be represented by (oxonium tetrafluoroborate), although more realistically, several water molecules solvate the proton: (H2O)''n''+BF4−]. The ethyl ether solvate is also commercially available: (Et2O)''n''+BF4−], where ''n'' is most likely 2. Unlike other strong acids like H2SO4 or HClO4, the pure unsolvated substance does not exist (see below). It is mainly produced as a precursor to other fluoroborate salts.Gregory K. Friestad, Bruce P. Branchaud "Tetrafluoroboric Acid" E-Eros Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. It is a strong acid. Fluoroboric acid is corrosive and attacks the skin. It is available commercially as a solution in water and other solvents such as diethyl ether. It is a strong acid with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorosulfuric Acid
Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator. Commercial samples usually are pale brown or straw colored. Salts and esters of chlorosulfuric acid are known as chlorosulfates. Structure and properties Chlorosulfuric acid is a tetrahedral molecule. The formula is more descriptively written SO2(OH)Cl, but HSO3Cl is traditional. It is an intermediate, chemically and conceptually, between sulfuryl chloride (SO2Cl2) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The compound is rarely obtained pure. Upon standing with excess sulfur trioxide, it decomposes to pyrosulfuryl chlorides: :2 ClSO3H + SO3 → H2SO4 + S2O5Cl2 Synthesis The industrial synthesis entails the reaction of hydrogen chloride with a solution of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid: :HCl + SO3 → ClSO3H It can al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkanes
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane () or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines alkanes as "acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula , and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms". However, some sources use the term to denote ''any'' saturated hydrocarbon, including those that are either monocyclic (i.e. the cycloalkanes) or po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Glass
Lead glass, commonly called crystal, is a variety of glass in which lead replaces the calcium content of a typical potash glass. Lead glass contains typically 18–40% (by weight) lead(II) oxide (PbO), while modern lead crystal, historically also known as flint glass due to the original silica source, contains a minimum of 24% PbO. Lead glass is often desirable for a variety of uses due to its clarity. The term ''lead crystal'' is, technically, not an accurate term to describe lead glass, because glass lacks a crystalline structure and is instead an amorphous solid. The use of the term ''lead crystal'' or just "crystal" remains popular for historical and commercial reasons, and because "lead" sounds toxic to consumers. It is retained from the Venetian word ''cristallo'' to describe the rock crystal imitated by Murano glassmakers. This naming convention has been maintained to the present day to describe decorative hollow-ware. Lead crystal glassware was formerly used to store a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superacids
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid is a medium in which the chemical potential of the proton is higher than in pure sulfuric acid. Commercially available superacids include trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (), also known as triflic acid, and fluorosulfuric acid (), both of which are about a thousand times stronger (i.e. have more negative ''H''0 values) than sulfuric acid. Most strong superacids are prepared by the combination of a strong Lewis acid and a strong Brønsted acid. A strong superacid of this kind is fluoroantimonic acid. Another group of superacids, the carborane acid group, contains some of the strongest known acids. Finally, when treated with anhydrous acid, zeolites (microporous aluminosilicate minerals) will contain superacidic sites within their pores. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Acid
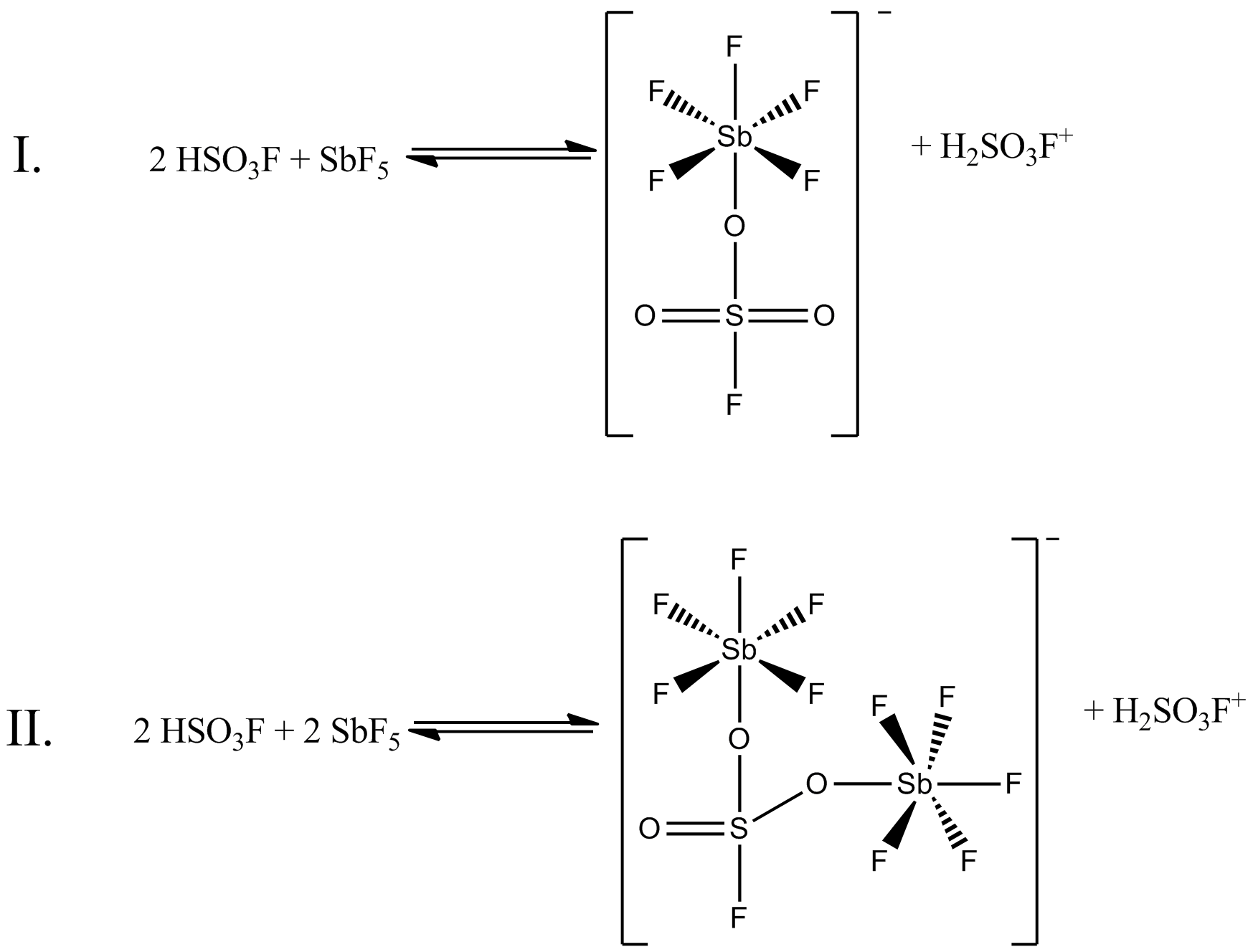
Magic acid (FSO3H·SbF5) is a superacid consisting of a mixture, most commonly in a 1:1 molar ratio, of fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5). This conjugate Brønsted–Lewis superacid system was developed in the 1960s by the George Olah lab at Case Western Reserve University, and has been used to stabilize carbocations and hypercoordinated carbonium ions in liquid media. Magic acid and other superacids are also used to catalyze isomerization of saturated hydrocarbons, and have been shown to protonate even weak bases, including methane, xenon, halogens, and molecular hydrogen. History The term "superacid" was first used in 1927 when James Bryant Conant found that perchloric acid could protonate ketones and aldehydes to form salts in nonaqueous solution. The term itself was coined by R. J. Gillespie later, after Conant combined sulfuric acid with fluorosulfuric acid, and found the solution to be several million times more acidic than sulfuric acid alone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Pentafluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. It is notable for its Lewis acidity and its ability to react with almost all known compounds. Preparation Antimony pentafluoride is prepared by the reaction of antimony pentachloride with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride:Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans J. Breunig, Hans Uwe Wolf "Antimony and Antimony Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. :SbCl5 + 5 HF → SbF5 + 5 HCl It can also be prepared from antimony trifluoride and fluorine. Structure and chemical reactions In the gas phase, SbF5 adopts a trigonal bipyramidal structure of D3h point group symmetry (see picture). The material adopts a more complicated structure in the liquid and solid states. The liquid contains polymers wherein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |