|
Flamen Quirinalis
In ancient Roman religion, the Flamen Quirinalis was the flamen or high priest of the god Quirinus. He was one of the three ''flamines maiores'', third in order of importance after the Flamen Dialis and the Flamen Martialis. Like the other two high priests, he was subject to numerous ritual taboos, such as not being allowed to touch metal, ride a horse, or spend the night outside Rome. His wife functioned as an assistant priestess with the title Flaminicia Quirinalis. The theology of Quirinus is complex and difficult to interpret. From early times, he was identified with the deified Romulus, who originally seems to have shared some common theological and mythological elements with Quirinus. Ritual functions The ''flamen Quirinalis'' presided over at least three festivals, the Consualia Aestiva on August 21, Robigalia on April 25, and Larentalia on December 23. Beside these festivals that of ''Quirinus'' himself, the Quirinalia, would almost surely require the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Ancient Rome
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule. The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, and attributed their success as a world power to their collective piety ''( pietas)'' in maintaining good relations with the gods. Their polytheistic religion is known for having honored many deities. The presence of Greeks on the Italian peninsula from the beginning of the historical period influenced Roman culture, introducing some religious practices that became fundamental, such as the '' cultus'' of Apollo. The Romans looked for common ground between their major gods and those of the Greeks ('' interpretatio graeca''), adapting Greek myths and iconography for Latin literature and Roman art, as the Etruscans had. Etruscan religion was also a major influence, particularly on the practice of augury, used by the state to seek th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
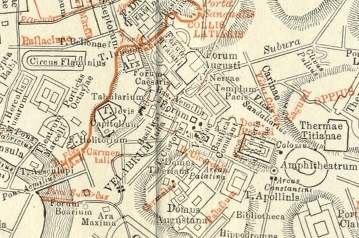
Regia
The Regia ("Royal house") was a two-part structure in Ancient Rome lying along the Via Sacra at the edge of the Roman Forum that originally served as the residence or one of the main headquarters of kings of Rome and later as the office of the '' pontifex maximus'', the highest religious official of Rome. It occupied a triangular patch of terrain between the Temple of Vesta, the Temple of Divus Julius and Temple of Antoninus and Faustina. Only the foundations of Republican/Imperial Regia remain. Like the Curia it was destroyed and rebuilt several times, as far back as the Roman monarchy. Studies have found multiple layers of similar buildings with more regular features, prompting the theory that this "Republican Regia" was to have a different use. History According to ancient tradition it was built by the second king of Rome, Numa Pompilius, as a royal palace. Indeed, the Latin term ''regia'' can be translated as ''royal residence''. It is said that he also built the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was as widespread as Greek among the elite. He is primarily known for his writings, which include the widely copied and read '' Commentarii in Somnium Scipionis'' ("Commentary on the Dream of Scipio") about ''Somnium Scipionis'', which was one of the most important sources for Neoplatonism in the Latin West during the Middle Ages; the ''Saturnalia'', a compendium of ancient Roman religious and antiquarian lore; and ''De differentiis et societatibus graeci latinique verbi'' ("On the Differences and Similarities of the Greek and Latin Verb"), which is now lost. He is the basis for the protagonist Manlius in Iain Pears' book '' The Dream of Scipio''. Name The correct order of his names is "Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius", which is how it ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gellius
Aulus Gellius (c. 125after 180 AD) was a Roman author and grammarian, who was probably born and certainly brought up in Rome. He was educated in Athens, after which he returned to Rome. He is famous for his ''Attic Nights'', a commonplace book, or compilation of notes on grammar, philosophy, history, antiquarianism, and other subjects, preserving fragments of the works of many authors who might otherwise be unknown today. Name Medieval manuscripts of the ''Noctes Atticae'' commonly gave the author's name in the form of "Agellius", which is used by Priscian; Lactantius, Servius and Saint Augustine had "A. Gellius" instead. Scholars from the Renaissance onwards hotly debated which one of the two transmitted names is correct (the other one being presumably a corruption) before settling on the latter of the two in modern times. Life The only source for the life of Aulus Gellius is the details recorded in his writings. Internal evidence points to Gellius having been born between AD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fratres Arvales
In ancient Roman religion, the Arval Brethren ( la, Fratres Arvales, "Brothers of the Fields") or Arval Brothers were a body of priests who offered annual sacrifices to the Lares and gods to guarantee good harvests. Inscriptions provide evidence of their oaths, rituals and sacrifices. Origin Roman legend held that the priestly college was originated by Romulus, first king of Rome, who took the place of a dead son of his nurse Acca Laurentia, and formed the priesthood with the remaining eleven sons. They were also connected originally with the Sabine priesthood of ''Sodales Titii'' who were probably originally their counterpart among the Sabines. Thus, it can be inferred that they existed before the founding of the city.Aulus Gellius VII 7, 7; Pliny XVII 2, 6. There is further proof of the high antiquity of the college in the verbal forms of the song with which, down to late times, a part of the ceremonies was accompanied, and which is still preserved. They persisted to the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wet Nurse
A wet nurse is a woman who breastfeeds and cares for another's child. Wet nurses are employed if the mother dies, or if she is unable or chooses not to nurse the child herself. Wet-nursed children may be known as "milk-siblings", and in some cultures, the families are linked by a special relationship of milk kinship. Wet-nursing existed in cultures around the world until the invention of reliable formula milk in the 20th century. The practice has made a small comeback in the 21st century. Reasons A wet nurse can help when a mother is unable or unwilling to breastfeed her baby. Before the development of infant formula in the 20th century, wet-nursing could save a baby's life. There are many reasons why a mother is unable to produce sufficient breast milk, or in some cases to lactate at all. For example, she may have a chronic or acute illness, and either the illness itself, or the treatment for it, reduces or stops her milk. This absence of lactation may be temporary or perma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesan
Courtesan, in modern usage, is a euphemism for a "kept" mistress or prostitute, particularly one with wealthy, powerful, or influential clients. The term historically referred to a courtier, a person who attended the court of a monarch or other powerful person. History In European feudal society, the court was the centre of government as well as the residence of the monarch, and social and political life were often completely mixed together. Prior to the Renaissance, courtesans served to convey information to visiting dignitaries, when servants could not be trusted. In Renaissance Europe, courtiers played an extremely important role in upper-class society. As it was customary during this time for royal couples to lead separate lives—commonly marrying simply to preserve bloodlines and to secure political alliances—men and women would often seek gratification and companionship from people living at court. In fact, the verb 'to court' originally meant "to be or reside at court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velabrum
The Velabrum () is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. The name Velabrum may translate to "place of mud." It was believed that before the construction of the Cloaca Maxima, which probably follows the course of an ancient stream, the area was a swamp, though this claim has been disproven by core samples taken from Velabrum in 1994. Ancient authorities state that in this marshy area the roots of a fig tree ''( Ficus Ruminalis)'' caught and stopped the basket carrying Romulus and Remus as it floated along on the Tiber current. The place therefore has a high symbolic significance. It was also used as a marketplace and a center of commerce. Even after the Cloaca was built, the area was still prone to flooding from the Tiber, until the ground level was raised after the Neronian fire. It is the site of the Arch of Janus, the Arcus Argentariorum The Arcus Argentari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acca Larentia
Acca Larentia or Acca Larentina was a mythical woman, later goddess of fertility, in Roman mythology whose festival, the Larentalia, was celebrated on December 23. Myths Foster mother In one mythological tradition (that of Licinius Macer, et al.), she was the wife of the shepherd Faustulus. And after Romulus and Remus were thrown into the Tiber river, Faustulus brought them back to his home, where Acca Larentia would raise the children. She had twelve sons, and on the death of one of them Romulus took his place. and with the remaining eleven founded the college of the Arval brothers (Fratres Arvales). She is therefore identified with the Dea Dia of that collegium. The flamen Quirinalis acted in the role of Romulus (deified as Quirinus) to perform funerary rites for his foster mother. Benefactor of Rome Another tradition holds that Larentia was a beautiful girl of notorious reputation, roughly the same age as Romulus and Remus, during the reign of Ancus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larunda
Larunda (also Larunde, Laranda, Lara) was a naiad nymph, daughter of the river Almo in Ovid's '' Fasti''. Ovid, '' Fasti 2''V. 599 Mythology The only known mythography attached to Lara is little, late and poetic, coming to us from Ovid's ''Fasti''. She was famous for both beauty and loquacity (a trait her parents attempted to curb). She was incapable of keeping secrets, and so revealed to Jupiter's wife Juno his affair with Juturna (Larunda's fellow nymph, and the wife of Janus). For betraying his trust, Jupiter cut out Lara's tongue and ordered Mercury, the psychopomp, to conduct her to Avernus, the gateway to the Underworld and realm of Pluto. Mercury, however, fell in love with Lara and prepared to force her as she pleaded with a glance, unable to speak. Lara thereby became mother to two children, referred to as the Lares, invisible household gods. However, she had to stay in a hidden cottage in the woods so that Jupiter would not find her. Larunda is likely identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
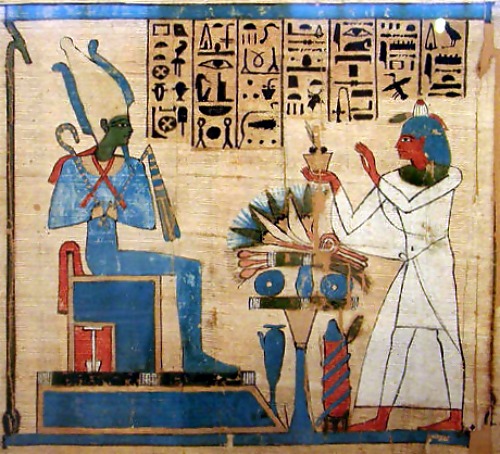
Funerary Cult
A funerary cult is a body of religious teaching and practice centered on the veneration of the dead, in which the living are thought to be able to confer benefits on the dead in the afterlife or to appease their otherwise wrathful ghosts. Rituals were carried on for the benefit of the dead, either by their relatives or by a class of priests appointed and paid to perform the rites. These rituals took place at the tombs of the dead themselves or at mortuary temples appointed to this purpose. Funerary cults are found in a wide variety of cultures. Notable cults Egypt Funerary cults are especially associated with ancient Egypt, where it was common for royalty, those associated with royalty, cats, and the wealthy to be mummified. This practice was done so as to preserve their bodies for the journey to the afterlife. The deity Osiris, who was the dying and reviving god and Lord of the Egyptian afterlife, was usually depicted as a mummy in Egyptian art. Also at Bubastis, where Bast w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |