|
Acca Larentia
Acca Larentia or Acca Larentina was a mythical woman, later goddess of fertility, in Roman mythology whose festival, the Larentalia, was celebrated on December 23. Myths Foster mother In one mythological tradition (that of Licinius Macer, et al.), she was the wife of the shepherd Faustulus. And after Romulus and Remus were thrown into the Tiber river, Faustulus brought them back to his home, where Acca Larentia would raise the children. She had twelve sons, and on the death of one of them Romulus took his place. and with the remaining eleven founded the college of the Arval brothers (Fratres Arvales). She is therefore identified with the Dea Dia of that collegium. The flamen Quirinalis acted in the role of Romulus (deified as Quirinus) to perform funerary rites for his foster mother. Benefactor of Rome Another tradition holds that Larentia was a beautiful girl of notorious reputation, roughly the same age as Romulus and Remus, during the reign of Ancus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacopo Della Quercia, Acca Larentia 01
Jacopo (also Iacopo) is a masculine Italian language, Italian given name, derivant from Latin language, Latin ''Iacōbus''. It is an Italian variant of Giacomo. * Jacopo Aconcio (), Italian religious reformer * Jacopo Bassano (1592), Italian painter * Iacopo Barsotti (1921–1987), Italian mathematician * Jacopo da Bologna (), Italian composer * Tintoretto, Jacopo Comin (1518–1594), Italian painter otherwise known as Tintoretto * Pontormo, Jacopo Carucci (1494–1557), Italian painter otherwise known as Pontormo * Jacopo Corsi (1561–1602), Italian composer * Jacopo da Leona (died 1277), Italian poet * Jacopo Peri (1561–1633), Italian composer * Jacopo della Quercia (1438), Italian sculptor * Jacopo Riccati (1676–1754), Italian mathematician * Jacopo Sadoleto (1477–1547), Italian Catholic cardinal * Jacopo M. (1989), Italian Communicator, upholder of the European Commission Fictional characters: * Jacopo, a key character in the 2002 film version of ''The Count of Monte Cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancus Marcius
Ancus Marcius was the legendary fourth king of Rome, who traditionally reigned 24 years. Upon the death of the previous king, Tullus Hostilius, the Roman Senate appointed an interrex, who in turn called a session of the assembly of the people who elected the new king. Ancus is said to have ruled by waging war as Romulus did, while also promoting peace and religion as Numa did. Ancus Marcius was believed by the Romans to have been the namesake of the Marcii, a plebeian family. Background Ancus was the son of Marcius (whose father, also named Marcius, had been a close friend of Numa Pompilius, who may be identified with Numa Marcius, and Pompilia, daughter of Numa Pompilius.Livy, ''Ab Urbe Condita'', 1:32 Ancus Marcius was thus the grandson of Numa and therefore a Sabine. According to Festus, Marcius had the surname of Ancus from his crooked arm (''ancus'' signifying "bent" in Latin). First acts as King According to Livy, Ancus's first act as king was to order the Pontifex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostitute
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, non-penetrative sex, oral sex, etc.) with the customer. The requirement of physical contact also creates the risk of transferring diseases. Prostitution is sometimes described as sexual services, commercial sex or, colloquially, hooking. It is sometimes referred to euphemistically as "the world's oldest profession" in the English-speaking world. A person who works in this field is called a prostitute, or more inclusively, a sex worker. Prostitution occurs in a variety of forms, and its legal status varies from country to country (sometimes from region to region within a given country), ranging from being an enforced or unenforced crime, to unregulated, to a regulated profession. It is one branch of the sex industry, along with pornography, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
She-wolf (Roman Mythology)
In the Founding of Rome, Roman foundation myth, it was a she-Italian wolf, wolf (lupa) that nursed and sheltered the twins Romulus and Remus after they were abandoned in the wild by order of Amulius, King Amulius of Alba Longa. She cared for the infants at her den, a cave known as the Lupercal, until they were discovered by a shepherd, Faustulus. Romulus would later become the founder and first king of Rome. The image of the she-wolf suckling the twins has been a symbol of Rome since ancient times and is one of the most recognizable icons of ancient mythology. Origins There is evidence that the wolf held a special place in the world of the ancient peoples of Italy. One legend claims that the Hirpini people were so-called because, when they set out to find their first colony, they were led to its location by a wolf (from the Osco-Umbrian word for wolf: ''hirpus''). The tale of the Lupercal is central to that of the twins, and probably predates theirs. To the Roman god Mars (myt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oxford Classical Dictionary
The ''Oxford Classical Dictionary'' (''OCD'') is generally considered "the best one-volume dictionary on antiquity," an encyclopædic work in English consisting of articles relating to classical antiquity and its civilizations. It was first published in 1949 (''OCD''1 or ''OCD''), edited by Max Cary with the assistance of H. J. Rose, H. P. Harvey, and Alexander Souter. A second edition followed in 1970 (''OCD''2), edited by Nicholas G. L. Hammond and H. H. Scullard, and a third edition in 1996 (''OCD''3), edited by Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth. A revised third edition was released in 2003, which is nearly identical to the previous third edition. A fourth edition was published in 2012 (''OCD''4), edited by Simon Hornblower, Antony Spawforth, and Esther Eidinow. In 2016, a fully digital edition launched online, edited by Sander Goldberg (2013–2017) and Tim Whitmarsh (2018–present). Continuously updated on a monthly basis, this edition incorporates all 6,300 ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerius Antias
Valerius Antias ( century BC) was an ancient Roman annalist whom Livy mentions as a source. No complete works of his survive but from the sixty-five fragments said to be his in the works of other authors it has been deduced that he wrote a chronicle of ancient Rome in at least seventy-five books. The latest dateable event in the fragments is mention of the heirs of the orator, Lucius Licinius Crassus, who died in 91 BC. Of the seventy references to Antias in classical (Greek and Latin) literature sixty-one mention him as an authority on Roman legendary history. Life Not much is known about the life of Valerius Antias. His family were the Valerii Antiates, a branch of the Valeria gens residing at least from early republican times in the vicinity of Antium. He may have been descended from Lucius Valerius Antias. He was probably a younger contemporary of Quintus Claudius Quadrigarius and lived in the times of Sulla, although some scholars believe that he was a contemporary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturnalia (Macrobius)
''Saturnalia'' ( la, Saturnaliorum Libri Septem, "Seven Books of the Saturnalia") is a work written after 431 CE by the Roman provincial Macrobius Theodosius (b. 390 CE - d. ?). The ''Saturnalia'' consists of an account of the discussions held at the house of Vettius Agorius Praetextatus during the holiday of the Saturnalia. It contains a great variety of curious historical, mythological, critical, antiquarian and grammatical discussions. "The work takes the form of a series of dialogues among learned men at a fictional banquet." There is little attempt to give any dramatic character to the dialogue; in each book some one of the personages takes the leading part, and the remarks of the others serve only as occasions for calling forth fresh displays of erudition. Contents The first book is devoted to an inquiry as to the origin of the Saturnalia and the festivals of Janus, which leads to a history and discussion of the Roman calendar, and to an attempt to derive all forms of wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was as widespread as Greek among the elite. He is primarily known for his writings, which include the widely copied and read '' Commentarii in Somnium Scipionis'' ("Commentary on the Dream of Scipio") about ''Somnium Scipionis'', which was one of the most important sources for Neoplatonism in the Latin West during the Middle Ages; the ''Saturnalia'', a compendium of ancient Roman religious and antiquarian lore; and ''De differentiis et societatibus graeci latinique verbi'' ("On the Differences and Similarities of the Greek and Latin Verb"), which is now lost. He is the basis for the protagonist Manlius in Iain Pears' book '' The Dream of Scipio''. Name The correct order of his names is "Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius", which is how it ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Terentius Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes called Varro Reatinus to distinguish him from his younger contemporary Varro Atacinus. Biography Varro was born in or near Reate (now Rieti) to a family thought to be of equites, equestrian rank, and always remained close to his roots in the area, owning a large farm in the Reatine plain, reported as near Lago di Ripasottile, until his old age. He supported Pompey, reaching the office of praetor, after having been tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people, ''quaestor'' and ''curule aedile''. It is probable that Varro was discontented with the course on which Pompey entered when the First Triumvirate was formed, and he may thus have lost his chance of rising to the consulate. He actually ridiculed the coalition in a work entitled the ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lares (Roman Deities)
Lares ( , ; archaic , singular ''Lar'') were guardian deities in ancient Roman religion. Their origin is uncertain; they may have been hero-ancestors, guardians of the hearth, fields, boundaries, or fruitfulness, or an amalgam of these. Lares were believed to observe, protect, and influence all that happened within the boundaries of their location or function. The statues of domestic Lares were placed at the table during family meals; their presence, cult, and blessing seem to have been required at all important family events. Roman writers sometimes identify or conflate them with ancestor-deities, domestic Penates, and the hearth. Because of these associations, Lares are sometimes categorised as household gods, but some had much broader domains. Roadways, seaways, agriculture, livestock, towns, cities, the state, and its military were all under the protection of their particular Lar or Lares. Those who protected local neighbourhoods ('' vici'') were housed in the crossroad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
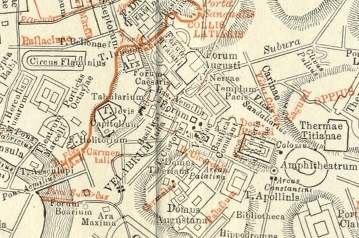
Velabrum
The Velabrum () is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. The name Velabrum may translate to "place of mud." It was believed that before the construction of the Cloaca Maxima, which probably follows the course of an ancient stream, the area was a swamp, though this claim has been disproven by core samples taken from Velabrum in 1994. Ancient authorities state that in this marshy area the roots of a fig tree ''( Ficus Ruminalis)'' caught and stopped the basket carrying Romulus and Remus as it floated along on the Tiber current. The place therefore has a high symbolic significance. It was also used as a marketplace and a center of commerce. Even after the Cloaca was built, the area was still prone to flooding from the Tiber, until the ground level was raised after the Neronian fire. It is the site of the Arch of Janus, the Arcus Argentariorum The Arcus Argentari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_01.jpg)