|
Fire Ant
Fire ants are several species of ants in the genus ''Solenopsis'', which includes over 200 species. ''Solenopsis'' are stinging ants, and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many of the names shared by this genus are often used interchangeably to refer to other species of ant, such as the term red ant, mostly because of their similar coloration despite not being in the genus ''Solenopsis''. Both '' Myrmica rubra'' and '' Pogonomyrmex barbatus'' are common examples of non-Solenopsis ants being termed red ants. None of these common names apply to all species of ''Solenopsis'' nor exclusively to species of ''Solenopsis''; for example, several species of weaver ants of the genus '' Oecophylla'' in Southeast Asia are colloquially called "fire ants" because of their similar coloration and painful bites, but the two genera are not closely related. '' Wasmannia auropunctata'' is another unrelated ant more commonly called the "littl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Obadiah Westwood
John Obadiah Westwood (22 December 1805 – 2 January 1893) was an English people , English entomologist and archaeologist noted for his artistic talents. He published several illustrated works on insects and antiquities. He was among the first entomologists with an academic position at University of Oxford , Oxford University. He was a natural theologian, staunchly anti-Darwinian, and sometimes adopted a Quinarian system , quinarian viewpoint. Although he never travelled widely, he described species from around the world on the basis of specimens, especially of the larger, curious, and colourful species obtained by naturalists and collectors in England. Life and work John Obadiah Westwood was born into a Quakers , Quaker family in Sheffield, the son of medal and die maker, John Westwood (1774–1850) and Mary, daughter of Edward Betts. He went to school at the Friends' School, Sheffield and later at Lichfield when the family moved there. He apprenticed briefly to become a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formic Acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts, and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol. Natural occurrence Formic acid, which has a pungent, penetrating odor, is found naturally in insects, weeds, fruits and vegetables, and forest emissions. It appears in most ants and in stingless bees of the genus '' Oxytrigona''. Wood ants from the genus ''Formica'' can spray formic acid on their prey or to defend the nest. The puss moth caterpillar (''Cerura vinula'') will spray it as well when threatened by predators. It is also found in the trichomes of stinging nettle (''Urtica dioica''). Apart from that, this acid is incorporated in many fruits such as pineapple (0.21 mg per 100 g), apple (2 mg per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological Biological interaction, interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of Ecology, ecological interaction. Prominent examples are: * the nutrient exchange between vascular plants and mycorrhizal fungi, * the Fertilisation, fertilization of flowering plants by pollinators, * the ways plants use fruits and edible seeds to encourage animal aid in seed dispersal, and * the way corals become photosynthetic with the help of the microorganism zooxanthellae. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and Cheating (biology), exploitation, and with parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. However, mutualism may evolve from interactions that began with imbalanced benefits, such as parasitism. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belknap Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is an academic publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University. It is a member of the Association of University Presses. Its director since 2017 is George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint (trade name), imprint, which it inaugurated in May 1954 with the publication of the ''Harvard Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglossa Imperialis
''Euglossa imperialis'' is a bee species in the family Apidae. It is considered to be one of the most important pollinators to many Neotropical orchid species in mainland tropical America. It is also one of the most common non-parasitic Euglossini, euglossine species in lowland Panama.Ackerman, James D., et al.Food-foraging behavior of male Euglossini (Hymenoptera: Apidae): vagabonds or trapliners?" Biotropica (1982): 241-248. ''E. imperialis'', unlike many other bee species, is not a social bee in the sense that there is no apparent morphological or physiological division within the species to distinguish individual bees to be part of a worker or reproductive caste.Roberts, R. B., and Calaway H. Dodson.Nesting biology of two communal bees, Euglossa imperialis and Euglossa ignita (Hymenoptera: Apidae), including description of larvae" Annals of the Entomological Society of America 60.5 (1967): 1007-1014. Taxonomy and phylogenetics ''Euglossa imperialis'' is a bee species of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, TA&M, or TAMU) is a public university, public, Land-grant university, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas, United States. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. Since 2021, Texas A&M has enrolled the List of United States university campuses by enrollment, largest student body in the United States. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity" and since 2001 a member of the Association of American Universities. The university was the first public higher education institution in Texas; it opened for classes on October 4, 1876, as the History of Texas A&M University, Agricultural and Mechanical College of Texas (A.M.C.) under the provisions of the 1862 Morrill Land-Grant Acts, Morrill Land-Grant Act. In the following decades, the college grew in size and scope, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products. Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion reaction when the fuel reaches its ignition point temperature. Flames from hydrocarbon fuels consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce Plasma (physics), plasma. The color and Intensity (heat transfer), intensity of the flame depend on the type of fuel and composition of the surrounding gases. Fire, in its most common form, has the potential to result in conflagration, which can lead to permanent physical damage. It directly impacts land-based ecological systems worldwide. The positive effects of fire include stimulating plant growth and maintaining ecological balance. Its negative effects include hazards to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidines
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name ''Piper (genus), Piper'', which is the Latin word for Black pepper, pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring Solenopsin, solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson (chemist), Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste André Thomas Cahours, Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
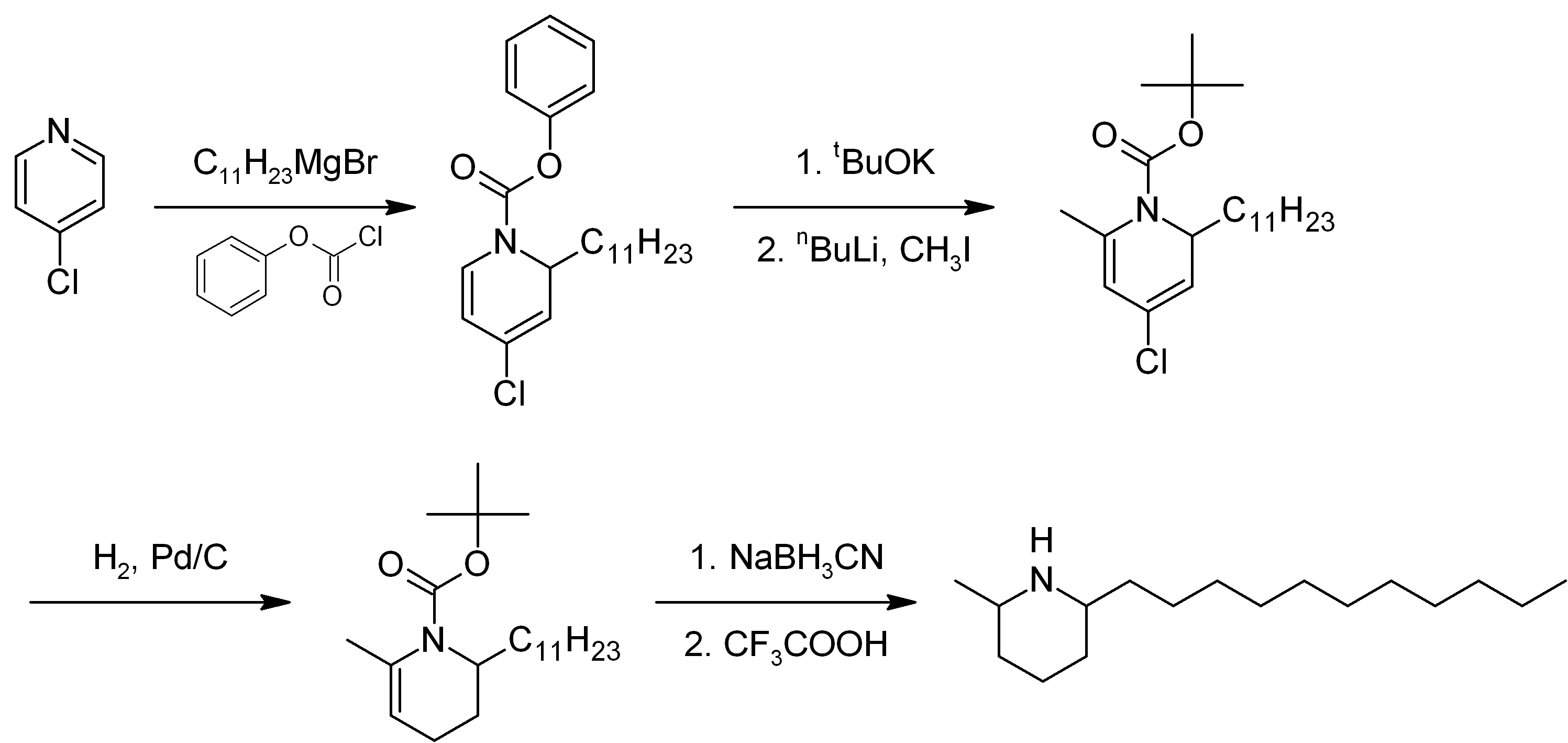
Solenopsin
Solenopsin is a lipophilic alkaloid with the molecular formula C17H35N found in the venom of fire ants (''Solenopsis''). It is considered the primary toxin in the venom and may be the component responsible for the cardiorespiratory failure in people who experience excessive fire ant stings. Structurally solenopsins are a piperidine ring with a methyl group substitution at position 2 and a long hydrophobic chain at position 6. They are typically oily at room temperature, water-insoluble, and present an absorbance peak at 232 nanometers. Fire ant venom contains other chemically related piperidines which make purification of solenopsin from ants difficult. Therefore, solenopsin and related compounds have been the target of organic synthesis from which pure compounds can be produced for individual study. Originally synthesized in 1993, several groups have designed novel and creative methods of synthesizing enantiopure solenopsin and other alkaloidal components of ant venom. To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called ''envenomation''. Venom is often distinguished from ''poison'', which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and ''toxungen'', which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrosis, necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and Hemotoxin, haemotoxins, which disrupt Thrombus, blood clotti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including bacteria, fungus, fungi, Medicinal plant, plants, and animals. They can be purified from crude extracts of these organisms by acid-base extraction, or solvent extractions followed by silica-gel column chromatography. Alkaloids have a wide range of pharmacology, pharmacological activities including antimalarial medication, antimalarial (e.g. quinine), asthma, antiasthma (e.g. ephedrine), chemotherapy, anticancer (e.g. omacetaxine mepesuccinate, homoharringtonine), cholinomimetic (e.g. galantamine), vasodilation, vasodilatory (e.g. vincamine), Antiarrhythmic agent, antiarrhythmic (e.g. quinidine), analgesic (e.g. morphine), antibacterial (e.g. chelerythrine), and anti-diabetic, antihyperglycemic activities (e.g. berb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |