|
Fascioliasis
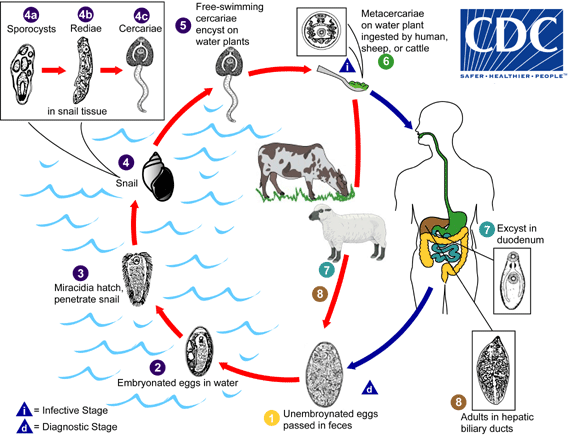
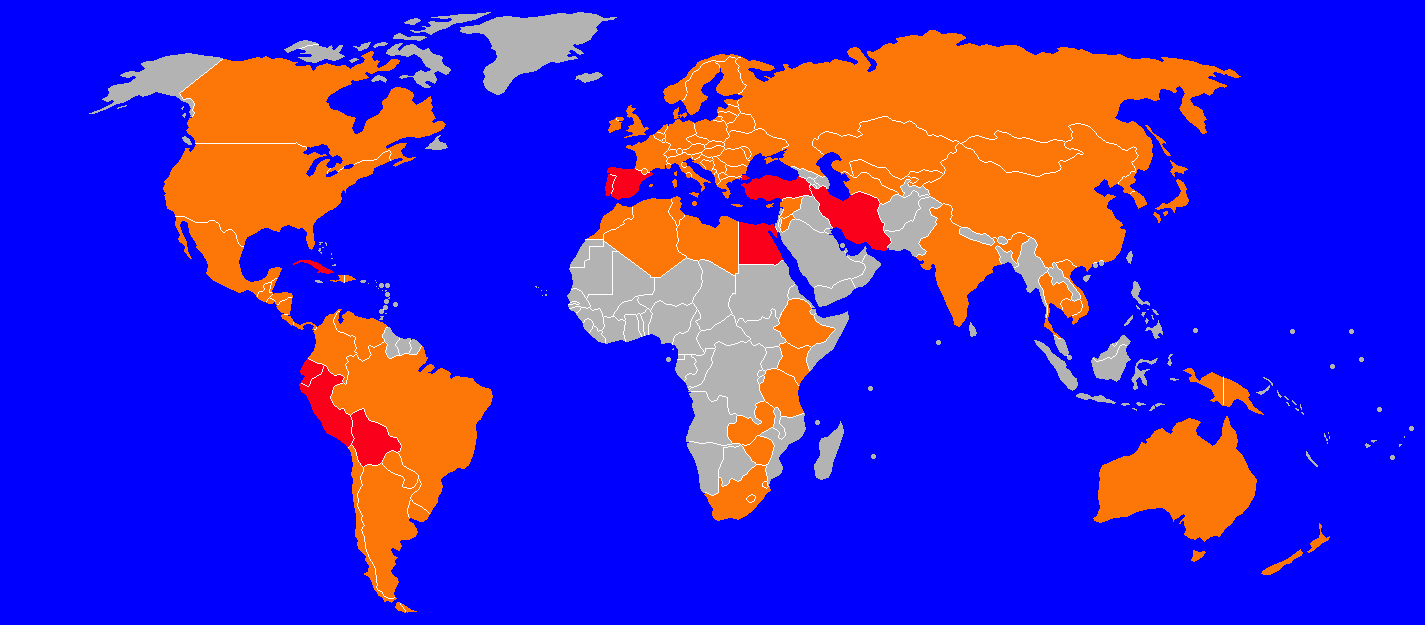
Fasciolosis is a parasitic worm infection caused by the common liver fluke ''Fasciola hepatica'' as well as by '' Fasciola gigantica''. The disease is a plant-borne trematode zoonosis, and is classified as a neglected tropical disease (NTD). It affects humans, but its main host is ruminants such as cattle and sheep. The disease progresses through four distinct phases; an initial incubation phase of between a few days up to three months with little or no symptoms; an invasive or acute phase which may manifest with: fever, malaise, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, urticaria, anemia, jaundice, and respiratory symptoms. The disease later progresses to a latent phase with fewer symptoms and ultimately into a chronic or obstructive phase months to years later. In the chronic state the disease causes inflammation of the bile ducts, gall bladder and may cause gall stones as well as fibrosis. While chronic inflammation is connected to increased cancer rates, it is unclear wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Hepatica
''Fasciola hepatica'', also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitism, parasitic trematode (fluke (flatworm), fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class (biology), class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans, and is transmitted by sheep and cattle to humans all over the world. The disease caused by the fluke (flatworm), fluke is called fasciolosis or fascioliasis, which is a type of helminthiasis and has been classified as a neglected tropical disease. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant/food-borne trematode infection, often acquired through eating the parasite's Trematode life cycle stages, metacercariae encysted on plants. ''F. hepatica'', which is distributed worldwide, has been known as an important parasite of sheep and cattle for decades and causes significant economic losses in these livestock species, up to £23'' ''million in the UK alone. Because of its relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola
''Fasciola'', commonly known as the liver fluke, is a genus of parasitic trematodes. There are three species within the genus ''Fasciola'': ''Fasciola nyanzae,'' ''Fasciola'' ''hepatica'' and ''Fasciola'' ''gigantica''. ''Fasciola hepatica'' and ''F. gigantica'' are known to form hybrids. Both ''F. hepatica'' and ''F. gigantica'' and their hybrids infect the liver tissue of a wide variety of mammals, including humans, in a condition known as fascioliasis. ''F. hepatica'' measures up to 30 mm by 15 mm, while ''F. gigantica'' measures up to 75 mm by 15 mm. ''Fasciola nyanzae'' is thought to exclusively infect the common hippopotamus, ''Hippopotamus amphibius''. Species *''Fasciola nyanzae'' Leiper, 1910 *''Fasciola hepatica'' Linnaeus, 1758 *'' Fasciola gigantica'' Cobbold, 1855Also published separately as: Abstract published as: * Hybrid or introgressed populations of ''Fasciola gigantica'' × ''Fasciola hepatica'' Life cycle ''Fasciola'' pass through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciolopsis
''Fasciolopsis'' () is a genus of trematodes. They are also known as giant intestinal flukes. Only one species is recognised: ''Fasciolopsis buski''. It is a notable parasite of medical importance in humans and veterinary importance in pigs. It is prevalent in Southern and Eastern Asia. The term for infestation with ''Fasciolopsis'' is fasciolopsiasis. ''Fasciolopsis buski'' ''Fasciolopsis buski'' is commonly called the giant intestinal fluke, because it is an exceptionally large parasitic fluke, and the largest known to parasitise humans. Its size is variable and a mature specimen might be as little as 2 cm long, but the body may grow to a length of 7.5 cm and a width of 2.5 cm. It is a common parasite of humans and pigs and is most prevalent in Southern and Southeastern Asia. It is a member of the family Fasciolidae in the order Plagiorchiida. The Echinostomida are members of the class Trematoda, the flukes. The fluke differs from most species that parasiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watercress
Watercress or yellowcress (''Nasturtium officinale'') is a species of aquatic flowering plant in the cabbage family, Brassicaceae. Watercress is a rapidly growing perennial plant native to Eurasia. It is one of the oldest known leaf vegetables consumed by humans. Watercress and many of its relatives, such as garden cress, mustard, radish, and wasabi, are noteworthy for their piquant flavors. Description Watercress can grow up to in length. The stems are hollow and float in water. The leaf structure is pinnately compound. Small, white, and green inflorescences are produced in clusters and are frequently visited by insects, especially hoverflies, such as '' Eristalis'' flies. Taxonomy Watercress is listed in some sources as belonging to the genus ''Rorippa'', although molecular evidence shows those aquatic species with hollow stems are more closely related to ''Cardamine'' than ''Rorippa''. Despite the Latin name, watercress is not particularly closely related to the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praziquantel
Praziquantel, sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections in mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. In humans specifically, it is used to treat schistosomiasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, tapeworm infections, cysticercosis, echinococcosis, paragonimiasis, fasciolopsiasis, and fasciolosis. It should not be used for worm infections of the eye. It is taken by mouth. Side effects in humans may include poor coordination, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, and allergic reactions. While it may be used during pregnancy, it is not recommended for use during breastfeeding. Praziquantel is in the anthelmintic class of medications. It works partly by affecting the function of the worm's sucker. Praziquantel was approved for medical use in the United States in 1982, and in the European Union in April 2025. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, disease burden, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, praziquantel for schistosomiasis costs about US $0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 billion over the subsequent five to sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Gigantica
''Fasciola gigantica'' is a parasitic flatworm of the Class (biology), class Trematoda, which causes tropical fascioliasis. It is regarded as one of the most important single platyhelminth infections of ruminants in Asia and Africa. The infection is commonly called fasciolosis. The prevalence of ''F. gigantica'' often overlaps with that of ''Fasciola hepatica'', and the two species are so closely related in terms of genetics, behaviour, and morphology (biology), morphological and anatomy, anatomical structures that distinguishing them is notoriously difficult. Therefore, sophisticated molecular techniques are required to correctly identify and diagnose the infection. Distribution ''Fasciola gigantica'' causes outbreaks in tropical areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The geographical distribution of ''F. gigantica'' overlaps with ''F. hepatica'' in many African and Asian countries and sometimes in the same country, although in such cases, the ecological requirement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatobiliary Diseases
Hepato-biliary diseases include liver diseases and biliary diseases. Their study is known as hepatology. Liver diseases Viral hepatitis * Acute hepatitis A * Acute hepatitis B * Acute hepatitis C * Acute hepatitis D – this is a superinfection with the delta-agent in a patient already infected with hepatitis B * Acute hepatitis E * Chronic viral hepatitis * Other viral hepatitis viruses may exist but their relation to the disease is not firmly established like the previous ones ( hepatitis F, GB virus C, hepatitis X) Other infectious diseases * Hepatitis: ** cytomegalovirus infection ** herpesviral: herpes simplex infection * Toxoplasmosis * Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis * Portal hypertension in schistosomiasis * Liver disease in syphilis * Epstein–Barr virus infection * yellow fever virus infection * rubella virus infection * leptospirosis * Echinococcosis * Amoebiasis Other inflammatory diseases * liver abscess * autoimmune hepatitis * primary biliary cholangitis (primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a surgical incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as a celiotomy. Origins and history The first successful laparotomy was performed without anesthesia by Ephraim McDowell in 1809 in Danville, Kentucky. On July 13, 1881, George E. Goodfellow treated a miner outside Tombstone, Arizona Territory, who had been shot in the abdomen with a .32-caliber Colt revolver. Goodfellow was able to operate on the man nine days after he was shot, when he performed the first laparotomy to treat a bullet wound. Terminology The term comes from the Greek word λᾰπάρᾱ (lapara) 'the soft part of the body between the ribs and hip, flank' and the suffix ''-tomy'', from the Greek word τομή (tome) '(surgical) cut'. In diagnostic laparotomy (most often referred to as an exploratory laparotomy and abbreviated ex-lap), the nature of the disease is unknown, and laparotomy is deemed the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinostoma
''Echinostoma'' is a genus of Trematoda, trematodes (flukes), which can infect both humans and other animals. These intestinal trematoda, flukes have a three-host life cycle with snails or other aquatic organisms as intermediate hosts, and a variety of animals, including humans, as their host (biology), definitive hosts. ''Echinostoma'' infect the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract of humans, and can cause a disease known as echinostomiasis. The parasites are spread when humans or animals eat infected raw or undercooked food, such as bivalvia, bivalve molluscs or fish. Taxonomy There has been debate about the number of species in this group, with estimates as high as 120 unique species of ''Echinostoma'', however, currently 16 species have been accepted as valid species with another 10 to be validated ''Echinostoma'' are difficult to biological classification, classify based on morphology alone. Many species look alike and can be considered cryptic species com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an Disease#Terminology, illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an Innate immune system, innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an Adaptive immune system, adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |