|
Eye Injuries During General Anaesthesia
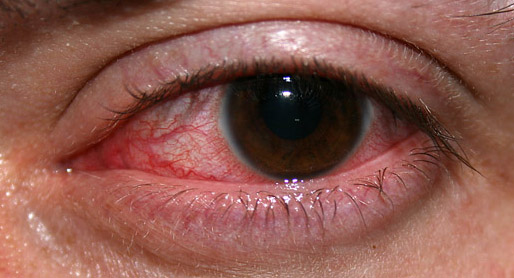
Eye injuries during general anaesthesia are reasonably common if care is not taken to prevent them. Incidence of eye injuries The incidence of eye injuries during general anaesthesia has been studied, and different methods of eye protection have been compared. When eyes are untaped during general anaesthesia, the incidence of ocular injury has been reported to be as high as 44%.C Marcucci, NA Cohen, DG Metro & JR Kirsch 2008, ''Avoiding Common Anesthesia Errors'', Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia PA USA.Kocaturk, O, Kocaturk, T, Kaan, N & Dayanir V 2012 'The Comparison of Four Different Methods of Perioperative Eye Protection under General Anesthesia in Prone Position', ''Journal of Clinical and Analytical Medicine'', vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 163-"Read Article"/ref> If tape is used to hold the eyes closed, ocular injury occurs during 0.1-0.5% of general anaesthetics, and is usually corneal in nature.S Contractor & JG Hardman 2006, 'Injury During Anaesthesia', ''Continuing E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general anaesthetic medications, which often act in combination with an analgesic and neuromuscular blocking agent. Spontaneous ventilation is often inadequate during the procedure and intervention is often necessary to protect the airway. General anaesthesia is generally performed in an operating theater to allow surgical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for a patient, or in an intensive care unit or emergency department to facilitate endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. A variety of General anesthetic, drugs may be administered, with the overall goal of achieving unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, loss of reflexes of the autonomic nervous system, and in some cases paralysis of ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iatrogenesis
Iatrogenesis is the causation of a disease, a harmful complication, or other ill effect by any medical activity, including diagnosis, intervention, error, or negligence. "Iatrogenic", ''Merriam-Webster.com'', Merriam-Webster, Inc., accessed 27 Jun 2020. First used in this sense in 1924, the term was introduced to sociology in 1976 by Ivan Illich, alleging that industrialized societies impair quality of life by overmedicalizing life."iatrogenesis" ''A Dictionary of Sociology'', . updated 31 May 2020. Iatrogenesis may thus include mental suffering via medical beliefs or a practitioner's statements. Some iatrogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctival Hyperemia
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The affected eye may have increased tears or be "stuck shut" in the morning. Swelling of the white part of the eye may also occur. Itching is more common in cases due to allergies. Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes. The most common infectious causes are viral followed by bacterial. The viral infection may occur along with other symptoms of a common cold. Both viral and bacterial cases are easily spread between people. Allergies to pollen or animal hair are also a common cause. Diagnosis is often based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally, a sample of the discharge is sent for culture. Prevention is partly by handwashing. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. In the majority of viral cases, there is no specific treatment. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
Vancomycin-resistant ''Enterococcus'', or vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), are bacterial strains of the genus ''Enterococcus'' that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin. Mechanism of acquired resistance Six different types of vancomycin resistance are shown by enterococcus: Van-A, Van-B, Van-C, Van-D, Van-E and Van-G. The significance is that Van-A VRE is resistant to both vancomycin and teicoplanin, Van-B VRE is resistant to vancomycin but susceptible to teicoplanin, and Van-C is only partly resistant to vancomycin. The mechanism of resistance to vancomycin found in enterococcus involves the alteration of the peptidoglycan synthesis pathway. The D-alanyl-D-lactate variation results in the loss of one hydrogen-bonding interaction (four, as opposed to five for D-alanyl-D-alanine) being possible between vancomycin and the peptide. The D-alanyl-D-serine variation causes a six-fold loss of affinity between vancomycin and the peptide, likely due to steric hindrance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospital-acquired Infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is sometimes instead called a healthcare–associated infection. Such an infection can be acquired in hospital, nursing home, rehabilitation facility, outpatient clinic, diagnostic laboratory or other clinical settings. Infection is spread to the susceptible patient in the clinical setting by various means. Health care staff also spread infection, in addition to contaminated equipment, bed linens, or air droplets. The infection can originate from the outside environment, another infected patient, staff that may be infected, or in some cases, the source of the infection cannot be determined. In some cases the microorganism originates from the patient's own skin microbiota, becoming opportunistic after surgery or other procedures that compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape On Scrubs
Tape or Tapes may refer to: Material A long, narrow, thin strip of material (see also Ribbon (other): Adhesive tapes * Adhesive tape, any of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive *Athletic tape, pressure-sensitive tape that holds muscles or bones in certain positions * Box-sealing tape, a pressure-sensitive tape used for closing or sealing corrugated fiberboard boxes * Copper tape (or slug tape), adhesive-backed copper tape used to keep slugs and snails out of certain areas * Double-sided tape, any pressure-sensitive tape that is coated with adhesive on both sides * Duct tape, cloth- or scrim-backed pressure-sensitive tape often coated with polyethylene * Elastic therapeutic tape * Electrical tape, a type of pressure-sensitive tape used to insulate electrical wires and other materials that conduct electricity * Filament tape, a pressure-sensitive tape used for several packaging functions * Gaffer tape, a strong, tough, cotton cloth pressure- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape Removal
Tape or Tapes may refer to: Material A long, narrow, thin strip of material (see also Ribbon (other): Adhesive tapes * Adhesive tape, any of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive *Athletic tape, pressure-sensitive tape that holds muscles or bones in certain positions * Box-sealing tape, a pressure-sensitive tape used for closing or sealing corrugated fiberboard boxes * Copper tape (or slug tape), adhesive-backed copper tape used to keep slugs and snails out of certain areas * Double-sided tape, any pressure-sensitive tape that is coated with adhesive on both sides * Duct tape, cloth- or scrim-backed pressure-sensitive tape often coated with polyethylene * Elastic therapeutic tape * Electrical tape, a type of pressure-sensitive tape used to insulate electrical wires and other materials that conduct electricity * Filament tape, a pressure-sensitive tape used for several packaging functions * Gaffer tape, a strong, tough, cotton cloth pressure- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |