|
Extraordinary Mode
In plasma physics, an electromagnetic electron wave is a wave in a plasma which has a magnetic field component and in which primarily the electrons oscillate. In an unmagnetized plasma, an electromagnetic electron wave is simply a light wave modified by the plasma. In a magnetized plasma, there are two modes perpendicular to the field, the O and X modes, and two modes parallel to the field, the R and L waves. Waves in an unmagnetized plasma Langmuir Wave The Langmuir wave is a purely longitudinal wave, that is, the wave vector is in the same direction as the E-field. It is an electrostatic wave, thus it doesn't have an oscillating magnetic field. A plasma consists of charged particles which react to electric fields, in contrast with dielectric matter. When electrons in a uniform, homogeneous plasma are perturbed from their equilibrium position, a charge separation occurs creating an electric field which acts as restoring force on the electrons. Since electrons have inertia t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the . It contains a significant portion of charged particles – s and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of |
Cut-off Frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than passing through. Typically in electronic systems such as filters and communication channels, cutoff frequency applies to an edge in a lowpass, highpass, bandpass, or band-stop characteristic – a frequency characterizing a boundary between a passband and a stopband. It is sometimes taken to be the point in the filter response where a transition band and passband meet, for example, as defined by a half-power point (a frequency for which the output of the circuit is −3 dB of the nominal passband value). Alternatively, a stopband corner frequency may be specified as a point where a transition band and a stopband meet: a frequency for which the attenuation is larger than the required stopband attenuation, which for example may be 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
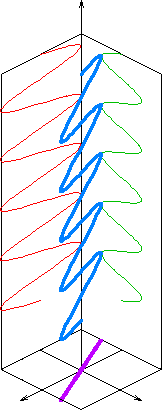
Polarization (waves)
Polarization (also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string ''(see image)''; for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''λ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Cyclotron Resonance
Electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) is a phenomenon observed in plasma physics, condensed matter physics, and accelerator physics. It happens when the frequency of incident radiation coincides with the natural frequency of rotation of electrons in magnetic fields. A free electron in a static and uniform magnetic field will move in a circle due to the Lorentz force. The circular motion may be superimposed with a uniform axial motion, resulting in a helix, or with a uniform motion perpendicular to the field (e.g., in the presence of an electrical or gravitational field) resulting in a cycloid. The angular frequency (ω = 2π ''f'' ) of this ''cyclotron'' motion for a given magnetic field strength ''B'' is given (in SI units) by :\omega_\text = \frac. where e is the elementary charge and m is the mass of the electron. For the commonly used microwave frequency 2.45 GHz and the bare electron charge and mass, the resonance condition is met when ''B'' = 875 G = 0.0875 T. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Frequency
Plasma oscillations, also known as Langmuir waves (after Irving Langmuir), are rapid oscillations of the electron density in conducting media such as plasmas or metals in the ultraviolet region. The oscillations can be described as an instability in the dielectric function of a free electron gas. The frequency only depends weakly on the wavelength of the oscillation. The quasiparticle resulting from the quantization of these oscillations is the plasmon. Langmuir waves were discovered by American physicists Irving Langmuir and Lewi Tonks in the 1920s. They are parallel in form to Jeans instability waves, which are caused by gravitational instabilities in a static medium. Mechanism Consider an electrically neutral plasma in equilibrium, consisting of a gas of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. If one displaces by a tiny amount an electron or a group of electrons with respect to the ions, the Coulomb force pulls the electrons back, acting as a restoring fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See ''polarization'' and '' plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion Relation
In the physical sciences and electrical engineering, dispersion relations describe the effect of dispersion on the properties of waves in a medium. A dispersion relation relates the wavelength or wavenumber of a wave to its frequency. Given the dispersion relation, one can calculate the phase velocity and group velocity of waves in the medium, as a function of frequency. In addition to the geometry-dependent and material-dependent dispersion relations, the overarching Kramers–Kronig relations describe the frequency dependence of wave propagation and attenuation. Dispersion may be caused either by geometric boundary conditions (waveguides, shallow water) or by interaction of the waves with the transmitting medium. Elementary particles, considered as matter waves, have a nontrivial dispersion relation even in the absence of geometric constraints and other media. In the presence of dispersion, wave velocity is no longer uniquely defined, giving rise to the distinction of phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Frequency
In physics, angular frequency "''ω''" (also referred to by the terms angular speed, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function. Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.(UP1) One turn is equal to 2''π'' radians, hence \omega = \frac = , where: *''ω'' is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second), *''T'' is the period (unit: seconds), *''f'' is the ordinary frequency (unit: hertz) (sometimes ''ν''). Units In SI units, angular frequency is normally presented in radians per second, even when it does not express a rotational value. The unit hertz (Hz) is dimensionally equivalent, but by convention it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Velocity
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall envelope shape of the wave's amplitudes—known as the ''modulation'' or ''envelope'' of the wave—propagates through space. For example, if a stone is thrown into the middle of a very still pond, a circular pattern of waves with a quiescent center appears in the water, also known as a capillary wave. The expanding ring of waves is the wave group, within which one can discern individual waves that travel faster than the group as a whole. The amplitudes of the individual waves grow as they emerge from the trailing edge of the group and diminish as they approach the leading edge of the group. Definition and interpretation Definition The group velocity is defined by the equation: :v_ \ \equiv\ \frac\, where is the wave's angular frequency (usually expressed in radians per second), and is the angular wavenumber (usually expressed in radians per meter). The phase velocity is: . The function , which gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.gif)