|
Exhaust Silencer
A muffler (North American and Australian English) or silencer (British English) is a device for reducing the noise emitted by the exhaust of an internal combustion engine—especially a noise-deadening device forming part of the exhaust system of an automobile. Description Mufflers are installed within the exhaust system of most internal combustion engines. The muffler is engineered as an acoustic device to reduce the loudness of the sound pressure created by the engine by acoustic quieting. The noise of the burning-hot exhaust gas exiting the engine at high speed is abated by a series of passages and chambers lined with roving fiberglass insulation and/or resonating chambers harmonically tuned to cause destructive interference, wherein opposite sound waves cancel each other out. An unavoidable side effect of this noise reduction is the restriction of the exhaust gas flow, which creates back pressure, which can decrease engine efficiency. This is because the engine exha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducati Muffler
Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A. () is the motorcycle-manufacturing division of Italian company Ducati, headquartered in Bologna, Italy. The company is directly owned by Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini, whose German parent company is Audi, itself owned by the Volkswagen Group. History In 1926 Antonio Cavalieri Ducati and his three sons, Adriano, Marcello, and Bruno, founded ''Società Scientifica Radiobrevetti Ducati'' (SSR Ducati) in Bologna to produce vacuum tubes, condensers and other radio components. In 1935 they had become successful enough to enable construction of a new factory in the Borgo Panigale area of the city. Production was maintained during World War II, despite the Ducati factory being a repeated target of Allied bombing. It was finally destroyed by around 40 Consolidated B-24 Liberators on 12 October 1944 as part of the United States Army Air Forces's Operation Pancake, which involved some 700 aircraft flying from airfields in the Province of Foggia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Pressure
Back pressure (or backpressure) is a resistance or force opposing the desired flow of fluid through pipes, leading to friction loss and pressure drop. The term ''back pressure'' is a misnomer, as pressure is a scalar quantity, so it has a magnitude but no direction. The fluid is what is directed, tending to flow away from high-pressure regions and toward low-pressure regions. If the low-pressure space is more high-pressure than intended (e.g. due to obstructions or tight bends in an exhaust pipe) or the high-pressure space is more low-pressure than intended, this opposes the desired flow and reduces the discharge. Similarly, bending or other operations on a pipe (such as a stock car exhaust system with a particularly high number of twists and bends) can reduce flow rate. Explanation A common example of backpressure is that caused by the exhaust system (consisting of the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler and connecting pipes) of an automotive four-stroke engine, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
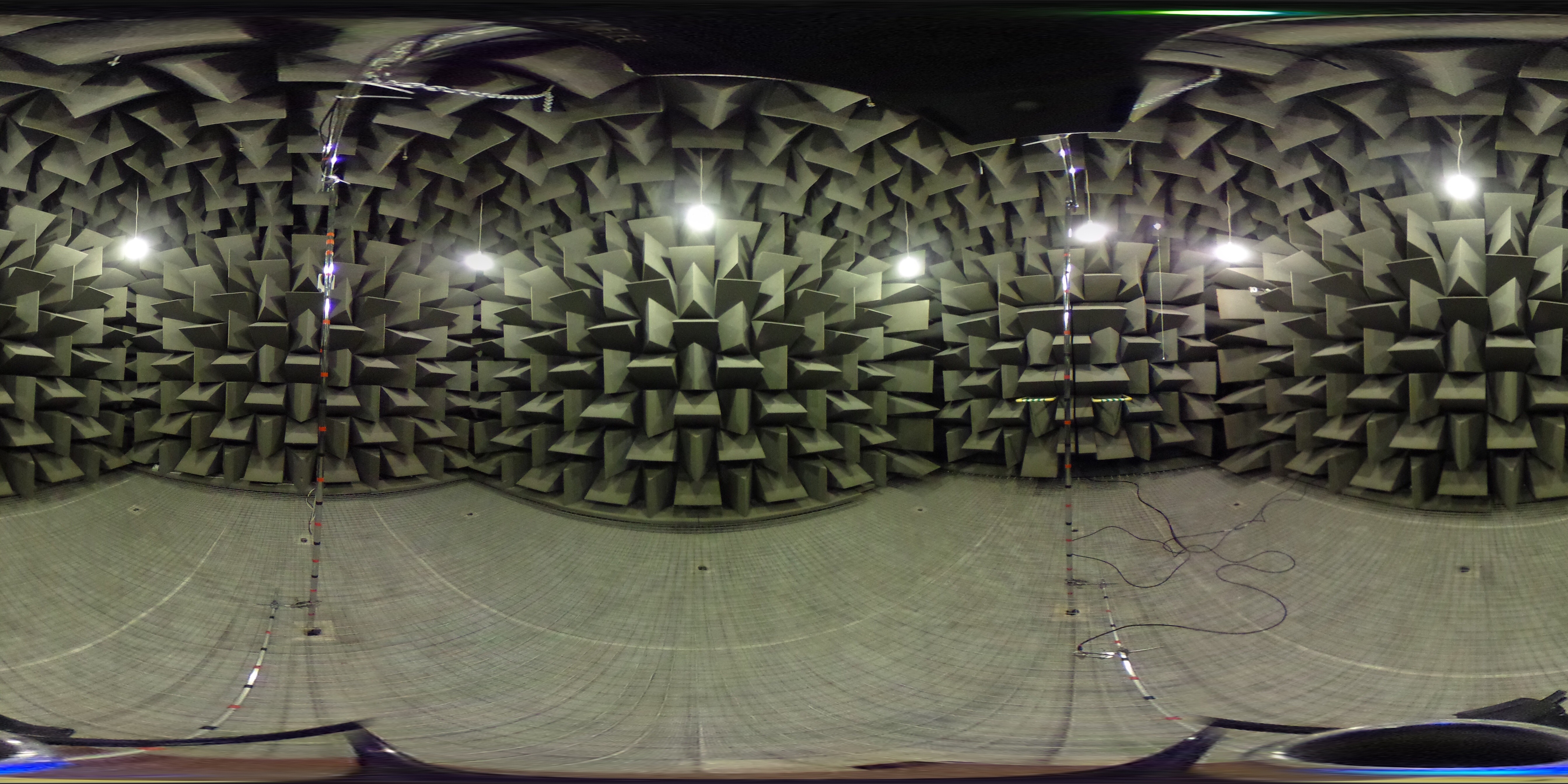
Anechoic Chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective") is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reflected sounds), in effect simulating being outside in a free field. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to other RF and Sonar anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges being tested. Acoustic anechoic chambers The requirement for what was subsequently called an anechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soundproofing
Soundproofing is any means of impeding sound propagation. There are several basic approaches to reducing sound: increasing the distance between source and receiver, decoupling, using noise barriers to reflect or absorb the energy of the sound waves, using damping structures such as sound baffles for absorption, or using active antinoise sound generators. Acoustic quieting and noise control can be used to limit unwanted noise. Soundproofing can reduce the transmission of unwanted direct sound waves from the source to an involuntary listener through the use of distance and intervening objects in the sound path (see sound transmission class and sound reduction index). Soundproofing can suppress unwanted indirect sound waves such as reflections that cause echoes and resonances that cause reverberation. Absorption Sound-absorbing material controls reverberant sound pressure levels within a cavity, enclosure or room. Synthetic absorption materials are porous, referring to open ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Control
Noise control or noise mitigation is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution or to reduce the impact of that noise, whether outdoors or indoors. Overview The main areas of noise mitigation or abatement are: transportation noise control, architectural design, urban planning through zoning codes, and occupational noise control. Roadway noise and aircraft noise are the most pervasive sources oenvironmental noise Social activities may generate noise levels that consistently affect the health of populations residing in or occupying areas, both indoor and outdoor, near entertainment venues that feature amplified sounds and music that present significant challenges for effective noise mitigation strategies. Multiple techniques have been developed to address interior sound levels, many of which are encouraged by local building codes. In the best case of project designs, planners are encouraged to work with design engineers to examine trade-offs of roadway design and architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silencer 001
Silencer may refer to: * Silencer (firearms), a muzzle device that reduces acoustic intensity * Muffler, or silencer in British English, a device to reduce the noise of an engine's exhaust * Sound trap, or silencer, a device to reduce mechanical equipment noise Fictional characters * Silencer (comics), the name of different characters in Marvel Comics * Silencers, in the '' Crusader: No Remorse'' game * Silencer, a nickname given to another character in the film ''3 Idiots'' * Silencer, a supporting ''Arrow'' character * The Silencer, in ''The New Age of DC Heroes'' Film and television * ''The Silencers'' (novel), a 1962 Matt Helm novel by Donald Hamilton * ''The Silencers'' (film), a 1966 Matt Helm film * "Silencer", an episode of ''CSI: Miami'' (season 4) * "Silencer", an episode of ''Law & Order: Criminal Intent'' (season 6) * ''The Silencer'' (film), a 2000 action film Music * Silencer (band), a Swedish black metal band * ''Silencer'' (Blake Morgan album), 2006 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developed Country
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. A point of reference of US$20,000 in 2021 USD nominal GDP per capita for the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a good point of departure, it is a similar level of development to the United States in 1960. Developed countries have generally more advanced post-industrial society, post-industrial economies, meaning the terti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
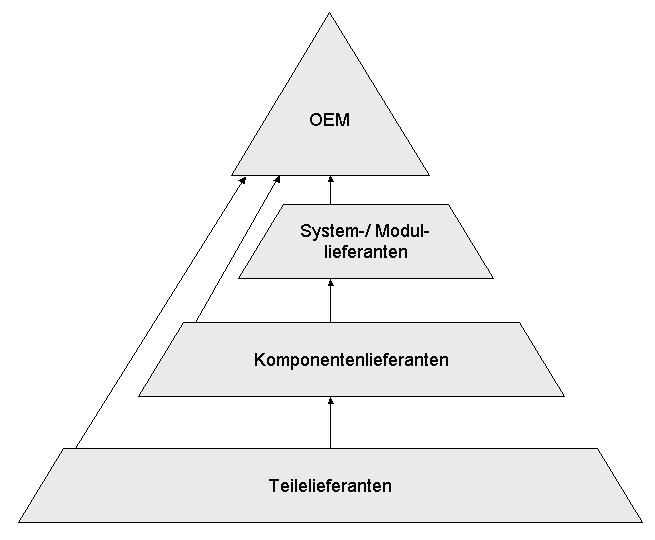
Original Equipment Manufacturer
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is generally perceived as a company that produces non-aftermarket parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. It is a common industry term recognized and used by many professional organizations such as SAE International, ISO, and others. However, the term is also used in several other ways, which causes ambiguity. It sometimes means the maker of a system that includes other companies' subsystems, an end-product producer, an automotive part that is manufactured by the same company that produced the original part used in the automobile's assembly, or a value-added reseller.Ken Olsen: PDP-1 and PDP-8 (page 3) , economicadventure.com Automotive parts When referring to auto parts, OEM refers to the manufactur ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Economy In Automobiles
The fuel economy of an automobile relates distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance traveled per unit volume of fuel consumed. Since fuel consumption of vehicles is a significant factor in air pollution, and since importation of motor fuel can be a large part of a nation's foreign trade, many countries impose requirements for fuel economy. Different methods are used to approximate the actual performance of the vehicle. The energy in fuel is required to overcome various losses (wind resistance, tire drag, and others) encountered while propelling the vehicle, and in providing power to vehicle systems such as ignition or air conditioning. Various strategies can be employed to reduce losses at each of the conversions between the chemical energy in the fuel and the kinetic energy of the vehicle. Driver behavior can affect fuel economy; maneuvers such as sudden accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |