|
Exertional Rhabdomyolysis
Exertional rhabdomyolysis (ER) is the breakdown of muscle from extreme physical exertion. It is one of many types of rhabdomyolysis that can occur, and because of this, the exact prevalence and incidence are unclear. Cause ER is more likely to occur when strenuous exercise is performed under high temperatures and humidity. Poor hydration levels before, during, and after strenuous bouts of exercise have also been reported to lead to ER.Clarkson, Priscilla M. "Exertional Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Renal Failure in Marathon Runners." Sports Medicine 37.4 (2007): 361-63. Print. This condition and its signs and symptoms are not well known amongst the sport and fitness community and because of this it is believed that the incidence is greater but highly underreported. Risks that lead to ER include exercise in hot and humid conditions, improper hydration, inadequate recovery between bouts of exercise, intense physical training, and inadequate fitness levels for beginning high-intensity wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
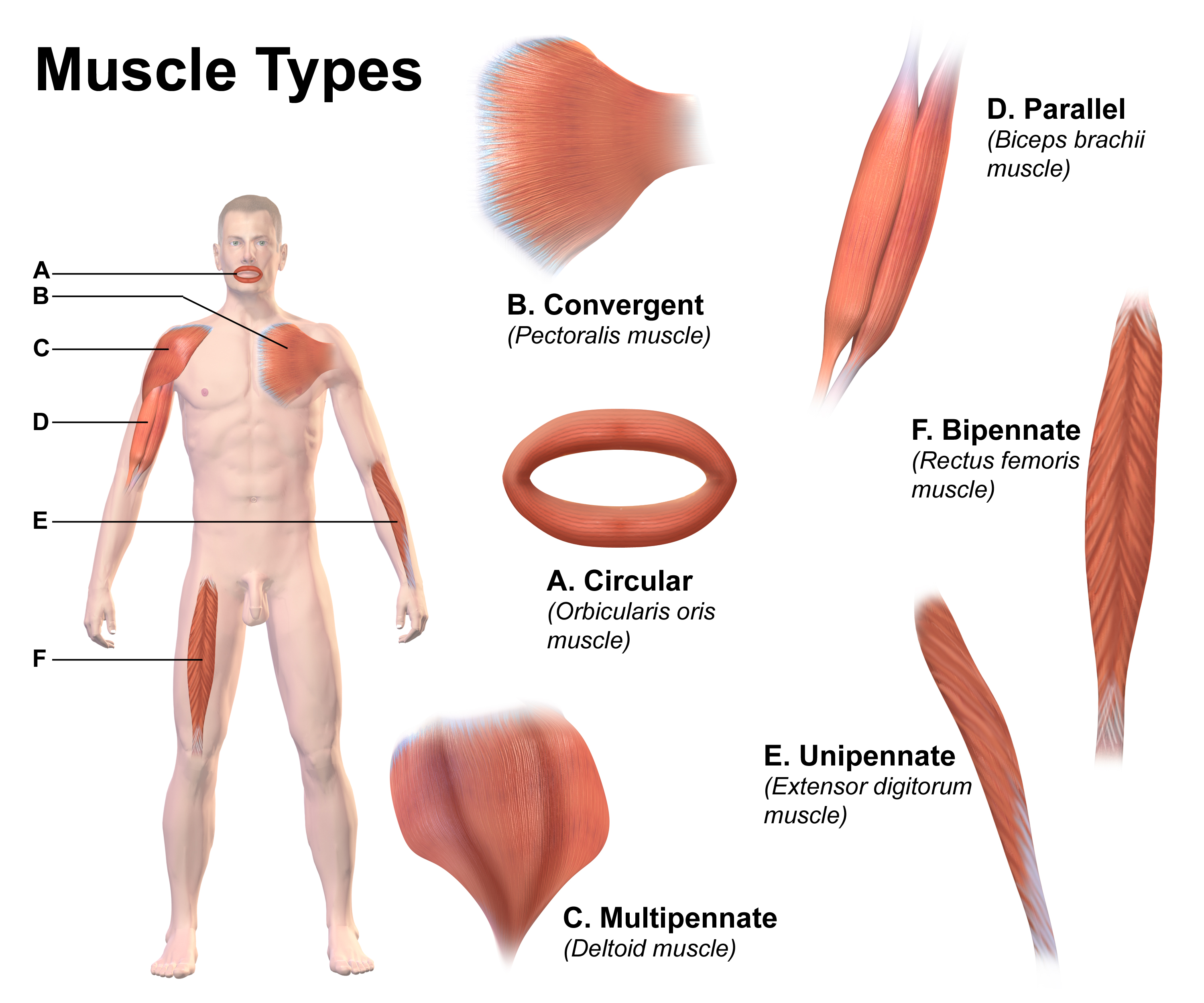
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatine Kinase
Creatine kinase (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phosphocreatine kinase, is an enzyme () expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme reaction is reversible and thus ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP. In tissues and cells that consume ATP rapidly, especially skeletal muscle, but also brain, photoreceptor cells of the retina, hair cells of the inner ear, spermatozoa and smooth muscle, PCr serves as an energy reservoir for the rapid buffering and regeneration of ATP ''in situ'', as well as for intracellular energy transport by the PCr shuttle or circuit. Thus creatine kinase is an important enzyme in such tissues. Clinically, creatine kinase is assayed in blood tests as a marker of damage of CK-rich tissue such as in myocardial infarction (heart attack), rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle breakdown), muscular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at , but only 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at . Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: absolute, relative, and specific. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body. Glycogen functions as one of two forms of energy reserves, glycogen being for short-term and the other form being triglyceride stores in adipose tissue (i.e., body fat) for long-term storage. In humans, glycogen is made and stored primarily in the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle. In the liver, glycogen can make up 5–6% of the organ's fresh weight, and the liver of an adult, weighing 1.5 kg, can store roughly 100–120 grams of glycogen. In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass) and the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 kg stores roughly 400 grams of glycogen. The amount of glycogen stored in the body—particularly within the muscles and liver—mostly depends on physical training, bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries. Treatment of a major injury is typically carried out by a health professional and varies greatly depending on the nature of the injury. Traffic collisions are the most common cause of accidental injury and injury-related death among humans. Injuries are distinct from chronic conditions, psychological trauma, infections, or medical procedures, though injury can be a contributing factor to any of these. Several major health organizations have established systems for the classification and description of human injuries. Occurrence Injuries may be intentional or unintentional. Intentional injuries may be acts of viole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excretion, excreted from the body through the urethra. Cell (biology), Cellular metabolism generates many by-products that are rich in nitrogen and must be clearance (medicine), cleared from the Circulatory system, bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. These by-products are expelled from the body during urination, which is the primary method for excreting water-soluble chemicals from the body. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, Reuse of excreta, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to territory (animal)#Scent marking, mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. In humans, myoglobin is only found in the bloodstream after muscle injury. (Google books link is the 2008 edition) High concentrations of myoglobin in muscle cells allow organisms to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Diving mammals such as whales and seals have muscles with particularly high abundance of myoglobin. Myoglobin is found in Type I muscle, Type II A, and Type II B; although many texts consider myoglobin not to be found in smooth muscle, this has proved erroneous: there is also myoglobin in smooth muscle cells. Myoglobin was the first protein to have its three-dimensional structure revealed by X-ray crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compartment Syndrome In Muscle (cleaned Up) (annotated)
Compartment may refer to: Biology * Compartment (anatomy), a space of connective tissue between muscles * Compartment (chemistry), in which different parts of the same protein serves different functions * Compartment (development), fields of cells of distinct cell lineage, cell affinity, and genetic identity * Compartment (pharmacokinetics), a defined and distinct volume of body fluids * Cellular compartment, a closed part within a cell, surrounded by a membrane Other uses * Compartment coach, a railway car divided into separate areas or compartments, with no means of moving between them * Compartment (ship), subdivision of the space within a ship * Compartment (heraldry), the part of a coat of arms design which appears immediately below the shield * Multi-compartment model, a type of mathematical model * "Compartments", a song and album by José Feliciano * Hidden compartment See also * * * Compartmentalization (other) * Apartment * Division (other) * Section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the leg or arm are most commonly involved. Symptoms of acute compartment syndrome (ACS) can include severe pain, poor pulses, decreased ability to move, numbness, or a pale color of the affected limb. It is most commonly due to physical trauma such as a bone fracture (up to 75% of cases) or crush injury, but it can also be caused by acute exertion during sport. It can also occur after blood flow returns following a period of poor blood flow. Diagnosis is generally based upon a person's symptoms and may be supported by measurement of intracompartmental pressure before, during, and after activity. Normal compartment pressure should be within 12-18 mmHg; anything greater than that is considered abnormal and would need treatment. Treatment i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time (blood flow) per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb "perfuser" meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions. Tests verifying that adequate perfusion exists are a part of a patient's assessment process that are performed by medical or emergency personnel. The most common methods include evalua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |