|
Ethoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a derivative o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Methoxide
Sodium methoxide is the simplest sodium alkoxide. With the formula , it is a white solid, which is formed by the deprotonation of methanol. Itis a widely used reagent in industry and the laboratory. It is also a dangerously caustic base. Preparation and structure Sodium methoxide is prepared by treating methanol with sodium: : The reaction is so exothermic that ignition is possible. The resulting solution, which is colorless, is often used as a source of sodium methoxide, but the pure material can be isolated by evaporation followed by heating to remove residual methanol. As a solid, sodium methoxide is polymeric, with sheet-like arrays of centers, each bonded to four oxygen centers. The structure, and hence the basicity, of sodium methoxide in solution depends on the solvent. It is a significantly stronger base in DMSO where it is more fully ionized and free of hydrogen bonding. Applications Organic synthesis Sodium methoxide is a routinely used base in organic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cationoid' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williamson Ether Synthesis
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol ( alkoxide). This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction. This reaction is important in the history of organic chemistry because it helped prove the structure of ethers. The general reaction mechanism is as follows: An example is the reaction of sodium ethoxide with chloroethane to form diethyl ether and sodium chloride: :C2H5Cl + C2H5ONa -> C2H5OC2H5 + NaCl Mechanism The Williamson ether reaction follows an SN2 bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism. In an SN2 reaction mechanism there is a backside attack of an electrophile by a nucleophile and it occurs in a concerted mechanism (happens all at once). In order for the SN2 reaction to take place there must be a good leaving group which is strongly electronegative, commonly a hali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica .... A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as Sodium hydroxide, NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ynolate
Ynolates are chemical compounds with a negatively charged oxygen attached to an alkyne functionality. They were first synthesized in 1975 by Schöllkopf and Hoppe via the ''n''-butyllithium fragmentation of 3,4-diphenylisoxazole. Synthetically, they behave as ketene precursors or synthons. See also *Enolate In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds. Bonding and structure Enolate anions are electr ... References Functional groups {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenoxides
Phenolates (also called phenoxides) are anions, salts, and esters of phenols. They may be formed by reaction of phenols with strong base. Properties Alkali metal phenolates, such as sodium phenolate hydrolyze in aqueous solution to form basic solutions. At pH = 10, phenol and phenolate are in approximately 1:1 proportions. Phenolate anions are enolates. As such, they react as nucleophiles at both oxygen and carbon positions. In general, reaction at oxygen occurs under kinetic control, whereas reaction at carbon occurs under thermodynamic control. Uses Alkyl aryl ethers can be synthesized through the Williamson ether synthesis by treating sodium phenolate with an alkyl halide: :C6H5ONa + CH3I → C6H5OCH3 + NaI :C6H5ONa + (CH3O)2SO2 → C6H5OCH3 + (CH3O)SO3Na Production of salicylic acid Salicylic acid is produced in the Kolbe–Schmitt reaction between carbon dioxide and sodium phenolate. : See also * Sodium phenolate Sodium phenoxide (sodium phenolate) is an organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major industrial chemical, it finds limited use in consumer items because of its toxicity. History Discovery The word "''benzene''" derives from "''gum benzoin''" (benzoin res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
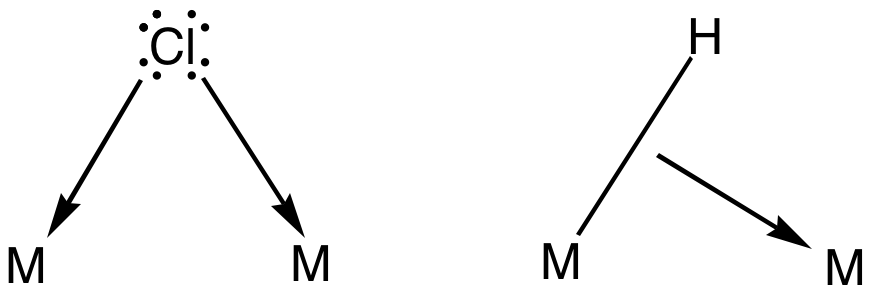
Bridging Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually restricted to small ligands such as pseudohalides or to ligands that are specifically designed to link two metals. In naming a complex wherein a single atom bridges two metals, the bridging ligand is preceded by the Greek letter mu, μ, with a subscript number denoting the number of metals bound to the bridging ligand. μ2 is often denoted simply as μ. When describing coordination complexes care should be taken not to confuse μ with η ('eta'), which relates to hapticity. Ligands that are not bridging are called terminal ligands. List of bridging ligands Virtually all ligands are known to bridge, with the exception of amines and ammonia. Common bridging ligands include most of the common anions. Many simple organic ligands form str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




2.png)