|
Equine Massage
Equine massage is the practice of massage on horses. Beginning in the early 1990s, it has been a growing field of equine therapy, used for both day-to-day riding and post-trauma rehabilitation. Proponents list a number of positive effects, including the improvement of movement and the reduction of pain and stress responses. Practice Hands-on therapies, including massage, acupressure, and joint mobilization, were some of the fastest growing equine therapy categories in the early 1990s. Equine massage uses the hands, fingers, and elbows of the therapist, and other tools, including tennis balls and vibrating tools. During the massage, the soft tissue is manipulated with the goal of loosening tight muscles, joints, tendons, scar tissue, and edema; increasing blood flow and lymphatic activity; and reducing stress. Equine massage is used in exercise warm-up and after injury or for surgery rehabilitation. Scientific study Massage in horses uses many techniques first used for human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50mile-massage
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digits on each hand. In mathematics 5 is the third smallest prime number, and the second super-prime. It is the first safe prime, the first good prime, the first balanced prime, and the first of three known Wilson primes. Five is the second Fermat prime and the third Mersenne prime exponent, as well as the third Catalan number, and the third Sophie Germain prime. Notably, 5 is equal to the sum of the ''only'' consecutive primes, 2 + 3, and is the only number that is part of more than one pair of twin primes, ( 3, 5) and (5, 7). It is also a sexy prime with the fifth prime number and first prime repunit, 11. Five is the third factorial prime, an alternating factorial, and an Eisenstein prime with no imaginary part and real part of the form 3p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include Chronic venous insufficiency, venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, hypoalbuminemia, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves Hypernatremia, sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiologic
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascial
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and ''visceral'' or ''parietal'' fascia, or by its function and anatomical location. Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia. Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular System Of The Horse
Types of muscle There are 3 types of muscle, all found within the equine: * Skeletal muscle: Contraction of these muscles leads to the muscle pulling a tendon, which in turn pulls a bone. Moving a bone results in either flexing or extending a joint. Skeletal muscles are usually arranged in pairs so that they oppose each other (they are "antagonists" irror image, with one flexing the joint (a flexor muscle) and the other extending it (extensor muscle). Therefore, one muscle of the pair must be relaxed in order for the other muscle in the pair to contract and bend the joint properly. A muscle or muscles and its/their tendon(s) that operate together to cause flexion or extension of a joint are referred to respectively as a flexor unit and an extensor unit. * Smooth: muscle which makes up automatic systems (digestive system, for example) * Cardiac: involuntary muscle the keeps the heart pumping and able to carry round oxygen to the muscles. Build of skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Riding
Pleasure riding is a form of equestrianism that encompasses many forms of recreational riding for personal enjoyment, absent elements of competition. In horse show competition, a wide variety of classes are labeled pleasure classes with judging standards based on the concept that horses or ponies exhibited should be well-mannered and thus a “pleasure” to ride. Pleasure riding is called hacking in British English, and in parts of the eastern United States and Canada. In the United States, particularly the American west, the term trail riding is used to describe recreational pleasure riding, particularly on public lands. Pleasure riding Many horses are suitable for pleasure riding, including grade horses and other animals of ordinary quality and good disposition. Such horses are sometimes called "hacks," particularly in areas where pleasure riding is known as hacking. Statistics provided by the American Horse Council (AHC) in a 2005 study indicated that out of 9.2 million h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
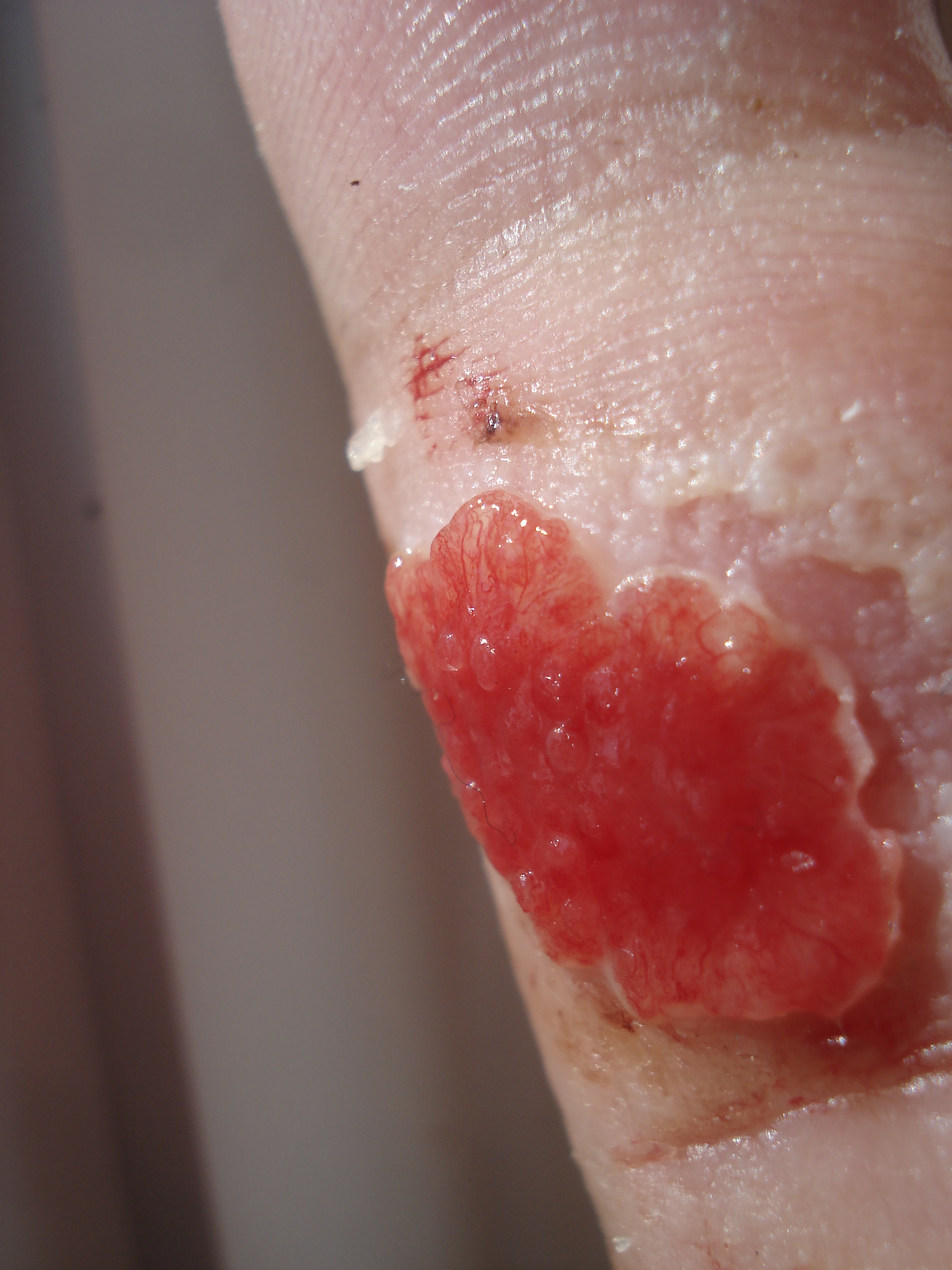
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Massge
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, which have lived worldwide (except Indonesia and Australia) from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They are thought to be a monophyletic grouping.B. J. MacFadden. 1998. Equidae. In C. M. Janis, K. M. Scott, and L. L. Jacobs (eds.), Evolution of Tertiary Mammals of North America Members of the subfamily are referred to as equines; the only extant equines are the horses, asses, and zebras of the genus ''Equus''. The subfamily contains two tribes, the Equini and the Hipparionini, as well as two unplaced genera, ''Merychippus'' and ''Scaphohippus''. Sister taxa * Anchitheriinae * Hyracotheriinae ''Hyracotherium'' ( ; " hyrax-like beast") is an extinct genus of very small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal was once considered to be the earliest kn ... References Miocene horses Pliocene odd-toed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligaments, fat, fibrous tissue, lymph and blood vessels, fasciae, and synovial membranes. with :q=a_E_E_ \qquad Q=b_E_E_ quadratic forms of Green-Lagrange strains E_ and a_, b_ and c material constants. W is the strain energy function per volume unit, which is the mechanical strain energy for a given temperature. Isotropic simplification The Fung-model, simplified with isotropic hypothesis (same mechanical properties in all directions). This written in respect of the principal stretches (\lambda_i): :W = \frac\left (\lambda_1^2 + \lambda_2^2 + \lambda_3^2 - 3) + b\left( e^ -1 \right) \right/math> , where a, b and c are constants. Simplification for small and big stretches For small strains, the exponential term is very small, thus neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrating
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |