|
Equine Coat Colour
Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive markings. A specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them. While most horses remain the same color throughout life, a few, over the course of several years, will develop a different coat color from that with which they were born. Most white markings are present at birth, and the underlying skin color of a healthy horse does not change. Some Equine coat colors are also related to the breed of horse, like the Friesian breed for instance. The basic outline of equine coat color genetics has largely been resolved, and DNA tests to determine the likelihood that a horse will have offspring of a given color have been developed for some colors. Discussion, research, and even controversy continues about some of the details, particularly those surrounding spotting patterns, color sub-shades such as "sooty" or " flaxen", and markings. Basic coat colors The two basic pigment colors of horse hairs are pheomelanin ("red") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustangs
The mustang is a free-roaming horse of the Western United States, descended from horses brought to the Americas by the Spanish. Mustangs are often referred to as wild horses, but because they are descended from once-domesticated animals, they are actually feral horses. The original mustangs were Colonial Spanish horses, but many other breeds and types of horses contributed to the modern mustang, now resulting in varying phenotypes. Some free-roaming horses are relatively unchanged from the original Spanish stock, most strongly represented in the most isolated populations. In 1971, the United States Congress recognized that "wild free-roaming horses and burros are living symbols of the historic and pioneer spirit of the West, which continue to contribute to the diversity of life forms within the Nation and enrich the lives of the American people". The free-roaming horse population is managed and protected by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Controversy surrounds the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grullo
Grulla or grullo, also called blue dun, gray dun or mouse dun, is a color of horses in the dun family, characterized by tan-gray or mouse-colored hairs on the body, often with shoulder and dorsal stripes and black barring on the lower legs. In this coloration, each individual hair is mouse-colored, unlike a roan, which is composed of a mixture of dark and light hairs. The several shades of grulla are informally referred to with a variety of terms, including black dun, blue dun, slate grulla, silver grulla or light grulla, silver dun, or lobo dun. Silver grulla may also refer to a grullo horse with silver dapple, regardless of shade. In the Icelandic horse, the grulla color is called gray dun, in the Highland pony it is called mouse dun, and in the Norwegian Fjord horse, ''grå'' or ''gråblakk'' (literally, "gray dun"). The word "grulla" in Spanish means crane. Because of the origin of the name, some people will refer to a mare as a grulla and a stallion or gelding as a grull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Melanoma
An equine melanoma is a tumor that results from the abnormal growth of melanocytes in horses. Unlike in humans, melanomas in horses are not thought to be caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. Melanomas are the third most common type of skin cancer in horses, with sarcoids being the first most prevalent and squamous-cell carcinoma being second. Melanomas are typically rounded black nodules that vary in size and are usually found underneath the dock of the tail, in the anal, perianal and genital regions, on the perineum, lips, eyelids, and sometimes near the throatlatch. These tumors can be either benign, meaning not cancerous, or malignant, meaning cancerous; while the benign tumors typically need little treatment to no treatment, the malignant tumors can cause serious problems and can potentially be life-threatening. Different methods are used to determine if the tumor is malignant and whether it has spread to other organs. Methods used to determine malignancy include fine ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremello
The cream gene is responsible for a number of horse coat colors. Horses that have the cream gene in addition to a base coat color that is chestnut will become palomino if they are heterozygous, having one copy of the cream gene, or cremello, if they are homozygous. Similarly, horses with a bay base coat and the cream gene will be buckskin or perlino. A black base coat with the cream gene becomes the not-always-recognized smoky black or a smoky cream. Cream horses, even those with blue eyes, are not white horses. Dilution coloring is also not related to any of the white spotting patterns. The cream gene (''CCr'') is an incomplete dominant allele with a distinct dosage effect. The DNA sequence responsible for the cream colors is the cream allele, which is at a specific locus on the solute carrier family 45 member 2 (''SLC45A2'') gene (previously known as ''MATP'' and ''OCA4'', among others). Its general effect is to lighten the coat, skin and eye colors. When one copy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominant White
Dominant white (W) is a group of genetically related coat color alleles on the KIT gene of the horse, best known for producing an all-white coat, but also able to produce various forms of white spotting, as well as bold white markings. Prior to the discovery of the W alllelic series, many of these patterns were described by the term sabino, which is still used by some breed registries. White-colored horses are born with unpigmented pink skin and white hair, usually with dark eyes. Under normal conditions, at least one parent must be dominant white to produce dominant white offspring. However, most of the currently-known alleles can be linked to a documented spontaneous mutation that began with a single ancestor born of non-dominant white parents. Horses that exhibit white spotting will have pink skin under the white markings, but usually have dark skin beneath any dark hair. There are many different alleles that produce dominant white or white spotting; they are labeled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
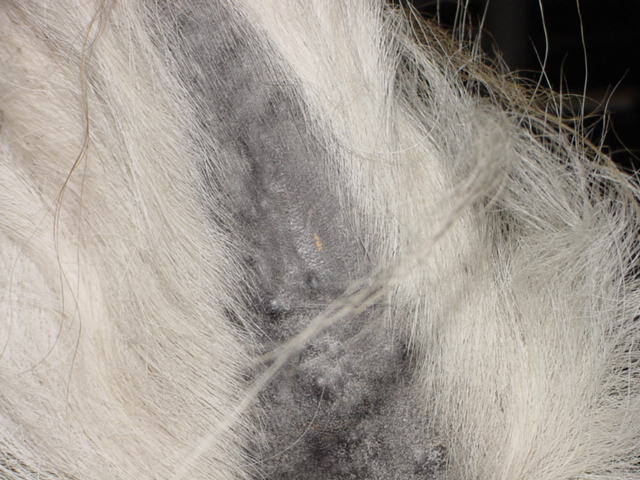
Gray Horse
A gray horse (or grey horse) has a coat color characterized by progressive depigmentation of the colored hairs of the coat. Most gray horses have black skin and dark eyes; unlike some equine dilution genes and some other genes that lead to depigmentation, gray does not affect skin or eye color. Gray horses may be born any base color, depending on other color genes present. White hairs begin to appear at or shortly after birth and become progressively more prevalent as the horse ages as white hairs become intermingled with hairs of other colors. Graying can occur at different rates—very quickly on one horse and very slowly on another. As adults, most gray horses eventually become completely white, though some retain intermixed light and dark hairs. The stages of graying vary widely. Some horses develop a dappled pattern for a period of time, others resemble a roan with more uniform intermixing of light and dark hairs. As they age, some gray horses, particularly those hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipizzaner DSC02443
The Lipizzan or Lipizzaner ( hr, Lipicanac, cz, Lipicán, hu, Lipicai, it, Lipizzano, sr, Lipicaner, sl, Lipicanec), is a European breed of riding horse developed in the Habsburg Empire in the sixteenth century. It is of Baroque type, and is powerful, slow to mature and long-lived; the coat is usually gray. The name of the breed derives from that of the village of Lipica ( it, Lipizza), now in Slovenia, one of the earliest stud farms established, then part of Austria-Hungary; the stud farm there is still active. The breed has been endangered numerous times by warfare sweeping Europe, including during the War of the First Coalition, World War I, and World War II. The rescue of the Lipizzans during World War II by American troops was made famous by the Disney movie ''Miracle of the White Stallions''. The Lipizzaner is closely associated with the Spanish Riding School of Vienna, Austria, where the horses demonstrate the '' haute école'' or "high school" movements of classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti Coloration Genetics
The agouti gene, the Agouti-signaling protein (ASIP) is responsible for variations in color in many species. ''Agouti'' works with ''extension'' to regulate the color of melanin which is produced in hairs. The agouti protein causes red to yellow pheomelanin to be produced, while the competing molecule α-MSH signals production of brown to black eumelanin. In wildtype mice, alternating cycles of agouti and α-MSH production cause agouti coloration. Each hair has bands of yellow which grew during agouti production, and black which grew during α-MSH production. Wildtype mice also have light-colored bellies. The hairs there are a creamy color the whole length because the agouti protein was produced the whole time the hairs were growing. In mice and other species, loss of function mutations generally cause a darker color, while gain of function mutations cause a yellower coat. Mice As of 1979, there were 17 known alleles of agouti in mice. *Lethal yellow ''Ay'' causes yellow color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plant. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin 1 Receptor
The melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), also known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MSHR), melanin-activating peptide receptor, or melanotropin receptor, is a G protein–coupled receptor that binds to a class of pituitary peptide hormones known as the melanocortins, which include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the different forms of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). It is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase in cells expressing this receptor. It is normally expressed in skin and melanocytes, and to a lesser degree in periaqueductal gray matter, astrocytes and leukocytes. In skin cancer, MC1R is highly expressed in melanomas but not carcinomas. MC1R is one of the key proteins involved in regulating mammalian skin color and hair color. It is located on the plasma membrane of specialized cells known as melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin through the process of melanogenesis. It works by controlling the type of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Coat Color Genetics
Equine coat color genetics determine a horse's coat color. Many colors are possible, but all variations are produced by changes in only a few genes. The "base" colors of the horse are determined by the Extension locus, which in recessive form (e) creates a solid chestnut (coat), chestnut or "red" coat. When dominant (E), a horse is black (horse), black. The next gene that strongly affects coat color, Agouti, when present on a horse dominant for E, limits the black color to the points, creating a shade known as Bay (horse), Bay that is so common and dominant in horses that it is informally grouped as a "base" coat color. Over these three "base" colors can be any number of dilution genes and patterning genes. The dilution genes include the wildtype dun gene, believed to be one of the oldest colors extant in horses and donkeys. Depending on whether it acts on a bay, black, or chestnut base coat, it produces the colors known as bay dun, grullo, and red dun. Another common dilution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sooty Gene
A horse coat color that has the sooty trait is characterized by black or darker hairs mixed into a horse's coat, typically concentrated along the topline of the horse and less prevalent on the underparts. Sootiness is presumed to be an inherited trait, though the precise genetic mechanism, or series of mechanisms, is not well understood. In most cases, sooty coats exhibit pronounced countershading; the dorsal region is darker than the ventral region. However, some forms seem to produce darker lower parts. The "false dorsal" or "countershading dorsal" can mimic the dorsal stripe associated with dun horses and is associated with the sooty trait. The most extensive expression of sooty produces a dark, often-dappled cast oriented down from the topline. Many horses with the sooty trait have a darker mask on the bony parts of the face. It was once thought that the sooty trait was responsible for turning chestnut into liver chestnut, however it is not known to evenly darken the coat. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



