|
Equal Channel Angular Extrusion
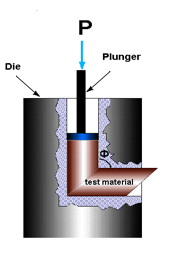
Equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) called also equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) is one technique from the Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) group, aimed at producing Ultra Fine Grained (UFG) material. Developed in the Soviet Union in 1973 by Segal. However, the dates are not always consistent. In industrial metalworking, it is an extrusion process, The technique is able to refine the microstructure of metals and alloys, thereby improving their strength according to the Hall-Petch relationship. This process improves not only the strength but also other properties such as corrosion and wear resistance of alloys and compounds. ECAE is unique because significant cold work can be accomplished without reduction in the cross sectional area of the deformed workpiece. In conventional deformation processes like rolling, forging, extrusion, and drawing, strain is introduced by reduction in the cross sectional area. ECAE produces significant deformation strain without redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Plastic Deformation
Severe plastic deformation (SPD) is a generic term describing a group of metalworking techniques involving very large strains typically involving a complex stress state or high shear, resulting in a high defect density and equiaxed "ultrafine" grain (UFG) size ( d < 500 nm) or (NC) structure (d < 100 nm). History The significance of SPD was known from the ancient times, at least during the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age, when repeated hammering and folding was employed for processing strategic tools such as swords. The development of the principles underlying SPD techniques goes back to the pioneering work of P.W. Bridgman at |
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process. Drawing is a similar process, using the tensile strength of the material to pull it through the die. It limits the amount of change that can be performed in one step, so it is limited to simpler shapes, and multiple stages are usually needed. Drawing is the main way to produce wire. Metal bars and tubes are also often drawn. Extrusion may be continuous (theoretically producing indefinitely long material) or semi-continuous (producing many pieces). It can be done with hot or cold material. Commonly extruded ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Nanotechnology Corporation
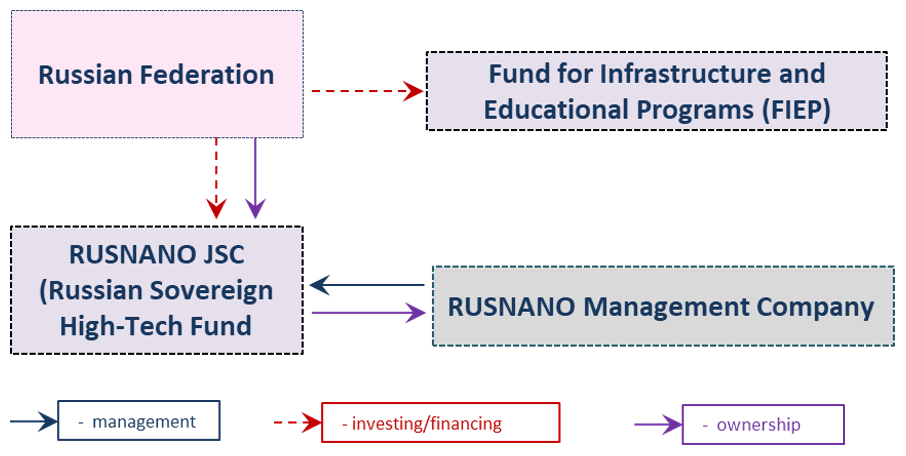
Rusnano Group (russian: Роснано АО, lit=Rosnano plc.) is a Russian state-established and funded company. The Rusnano Group's mission is to create competitive nanotechnology-based industry in Russia. Rusnano invests directly and through indirect funds into all major knowledge-based areas where nanotechnology is widely implemented: electronics, optics, telecom, classic and renewable energy, healthcare and biotechnology, materials and metallurgy, engineering and chemistry. In 2020 the government of Russia has merged it with VEB.RF. As of 2017 100 % shares of Rusnano were owned by the Russian government. In 2015 Rusnano had 16 investment projects. It invested into about 97 plants and R&D companies in 37 regions of Russia. In 2016 many such enterprises were either dissolved, bankrupted or repurposed (see. below). In 2016 the company was on the verge of bankruptcy significantly devaluating below the equity levels but managed to recover. In November 2021 trade of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers, ceramics or composites) can strongly influence physical properties such as strength, toughness, ductility, hardness, corrosion resistance, high/low temperature behaviour or wear resistance. These properties in turn govern the application of these materials in industrial practice. Microstructure at scales smaller than can be viewed with optical microscopes is often called nanostructure, while the structure in which individual atoms are arranged is known as crystal structure. The nanostructure of biological specimens is referred to as ultrastructure. A microstructure’s influence on the mechanical and physical properties of a material is primarily governed by the different defects present or absent of the structure. These defects can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall-Petch Relationship
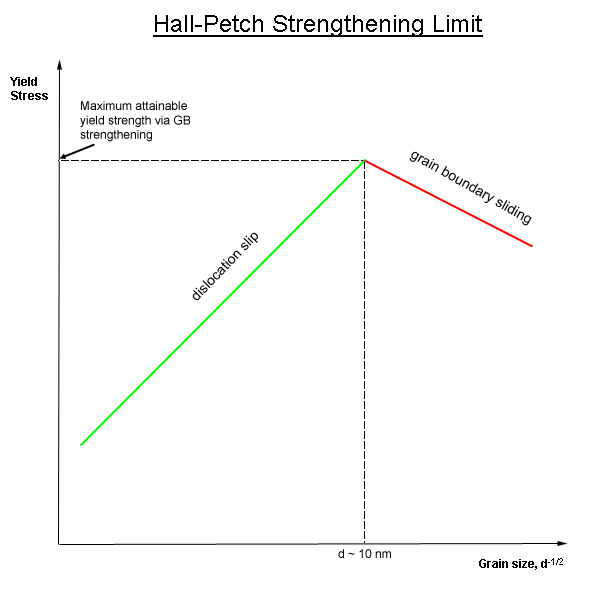
In materials science, grain-boundary strengthening (or Hall–Petch strengthening) is a method of strengthening materials by changing their average crystallite (grain) size. It is based on the observation that grain boundaries are insurmountable borders for dislocations and that the number of dislocations within a grain has an effect on how stress builds up in the adjacent grain, which will eventually activate dislocation sources and thus enabling deformation in the neighbouring grain as well. So, by changing grain size, one can influence the number of dislocations piled up at the grain boundary and yield strength. For example, heat treatment after plastic deformation and changing the rate of solidification are ways to alter grain size.W.D. Callister. Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering, 2nd ed. Wiley & Sons. pp. 252. Theory In grain-boundary strengthening, the grain boundaries act as pinning points impeding further dislocation propagation. Since the lattice stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling (metalworking)
In metalworking, rolling is a metal forming process in which metal stock is passed through one or more pairs of rolls to reduce the thickness, to make the thickness uniform, and/or to impart a desired mechanical property. The concept is similar to the rolling of dough. Rolling is classified according to the temperature of the metal rolled. If the temperature of the metal is above its recrystallization temperature, then the process is known as hot rolling. If the temperature of the metal is below its recrystallization temperature, the process is known as cold rolling. In terms of usage, hot rolling processes more tonnage than any other manufacturing process, and cold rolling processes the most tonnage out of all cold working processes... Roll stands holding pairs of rolls are grouped together into rolling mills that can quickly process metal, typically steel, into products such as structural steel (I-beams, angle stock, channel stock), bar stock, and rails. Most steel mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons.Degarmo, p. 389 Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry. History Forging is one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing (manufacturing)
Drawing is a metalworking process that uses tensile forces to stretch (elongate) metal, glass, or plastic. As the metal is drawn (pulled), it stretches to become thinner, to achieve a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at elevated temperatures to hot work large wires, rods or hollow sections in order to reduce forces.Degarmo, p. 432.Kalpakjian, pp. 415–419. Drawing differs from rolling in that the pressure of drawing is not transmitted through the turning action of the mill but instead depends on force applied locally near the area of compression. This means the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large scale (300 kton/year, in 1989) for uses in pencils, lubricants, and electrodes. Under high pressures and temperatures it converts to diamond. It is a weak conductor of heat and electricity. Types and varieties Natural graphite The principal types of natural graphite, each occurring in different types of ore deposits, are * Crystalline small flakes of graphite (or flake graphite) occurs as isolated, flat, plate-like particles with hexagonal edges if unbroken. When broken the edges can be irregular or angular; * Amorphous graphite: very fine flake graphite is sometimes called amorphous; * Lump graphite (or vein graphite) occurs in fissure veins or fractures and appears as massive platy intergrowths of fibrous or acicular cryst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (metallurgy)
In materials science, recrystallization is a process by which deformed grains are replaced by a new set of defect-free grains that nucleate and grow until the original grains have been entirely consumed. Recrystallization is usually accompanied by a reduction in the strength and hardness of a material and a simultaneous increase in the ductility.Thus, the process may be introduced as a deliberate step in metals processing or may be an undesirable byproduct of another processing step. The most important industrial uses are softening of metals previously hardened or rendered brittle by cold work, and control of the grain structure in the final product. Recrystallization temperature is typically 0.3–0.4 times the melting point for pure metals and 0.5 times for alloys. Definition Recrystallization is defined as the process in which grains of a crystal structure come in a new structure or new crystal shape. A precise definition of recrystallization is difficult to state as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strengthening Mechanisms Of Materials
Methods have been devised to modify the yield strength, ductility, and toughness of both crystalline and amorphous materials. These strengthening mechanisms give engineers the ability to tailor the mechanical properties of materials to suit a variety of different applications. For example, the favorable properties of steel result from interstitial incorporation of carbon into the iron lattice. Brass, a binary alloy of copper and zinc, has superior mechanical properties compared to its constituent metals due to solution strengthening. Work hardening (such as beating a red-hot piece of metal on anvil) has also been used for centuries by blacksmiths to introduce dislocations into materials, increasing their yield strengths. Basic description Plastic deformation occurs when large numbers of dislocations move and multiply so as to result in macroscopic deformation. In other words, it is the movement of dislocations in the material which allows for deformation. If we want to enhance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |