|
Energy Regulator
An infinite switch, simmerstat, energy regulator or infinite controller is a type of switch that allows variable power output of a heating element of an electric stove. It is called "infinite" because its average output is infinitely variable rather than being limited to a few switched levels. It uses a bi-metallic strip conductive connection across terminals that disconnects with increased temperature. As current passes through the bimetal connection, it will heat and deform, breaking the connection and turning off the power. After a short time, the bimetal will cool and reconnect. Infinite switches vary the average power delivered to a device by switching frequently between on and off states. They may be used for situations that are not sensitive to such changes, such as the resistive heating elements in electric stoves and kilns. Disadvantages of frequently cycled mechanical contacts may include erosion of the switch contacts if the contacts move slowly by design or due to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle switch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating Element
A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is independent of the direction of current. Heating elements types Metal Resistance wire: Metallic resistance heating elements may be wire or ribbon, straight or coiled. They are used in common heating devices like toasters and hair dryers, furnaces for industrial heating, floor heating, roof heating, pathway heating to melt snow, dryers, etc. The most common classes of materials used include: * Nichrome: Most resistance wire heating elements usually use nichrome 80/20 (80% Nickel, 20% Chromium) wire, ribbon, or strip. Nichrome 80/20 is an ideal material, because it has relatively high resistance and forms an adherent layer of chromium oxide when it is heated for the first time. Material beneath this layer will not oxidize, preventing the wire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bi-metallic Strip
A bimetallic strip is used to convert a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated. The different expansions force the flat strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled. The invention of the bimetallic strip is generally credited to John Harrison, an eighteenth-century clockmaker who made it for his third marine chronometer (H3) of 1759 to compensate for temperature-induced changes in the balance spring. Harrison's invention is recognized in the memorial to him in Westminster Abbey, England. This effect is used in a range of mechanical and electrical devices. Characteristics The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joule Heating
Joule heating, also known as resistive, resistance, or Ohmic heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor (material), conductor produces heat. Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countries of former Soviet Union, USSR as the Joule–Lenz law, Assuming the element behaves as a perfect resistor and that the power is completely converted into heat, the formula can be re-written by substituting Ohm's law, V = I R , into the generalized power equation: P = IV = I^2R = V^2/R where ''R'' is the electrical resistance and conductance, resistance. Alternating current When current varies, as it does in AC circuits, P(t) = U(t) I(t) where ''t'' is time and ''P'' is the instantaneous power being converted from electrical energy to heat. Far more often, the ''average'' power is of more interest than the instantaneous power: P_ = U_\text I_\text = I_\text^2 R = U_\text^2 / R where "avg" denotes Arithmetic mean, average (mean) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Stove
An electric stove or electric range is a stove with an integrated electrical heating device to cook and bake. Electric stoves became popular as replacements for solid-fuel (wood or coal) stoves which required more labor to operate and maintain. Some modern stoves come in a unit with built-in extractor hoods. The stove's one or more "burners" (heating elements) may be controlled by a rotary switch with a finite number of positions (which may be marked out by numbers such as 1 to 10, or by settings such as Low, Medium and High), each of which engages a different combination of resistances and hence a different heating power; or may have an "infinite switch" that allows constant variability between minimum and maximum heat settings. Some stove burners and controls incorporate thermostats. History On September 20, 1859, George B. Simpson was awarded US patent #25532 for an 'electro-heater' surface heated by a platinum-wire coil powered by batteries. In his words, useful to "warm ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing—to calcinate ores, to calcinate limestone to lime for cement, and to transform many other materials. Pronunciation and etymology According to the Oxford English Dictionary, kiln was derived from the words cyline, cylene, cyln(e) in Old English, in turn derived from Latin ''culina'' ("kitchen"). In Middle English the word is attested as kulne, kyllne, kilne, kiln, kylle, kyll, kil, kill, keele, kiele. For over 600 years, the final "n" in kiln was silent. It wasn't until the late 20th century where the "n" began to be pronounced. This is due to a phenomenon known as spelling pronunciation, where the pronunciation of a word is surmised from its spelling an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
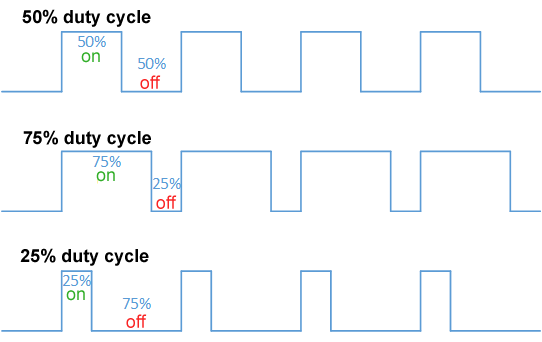
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
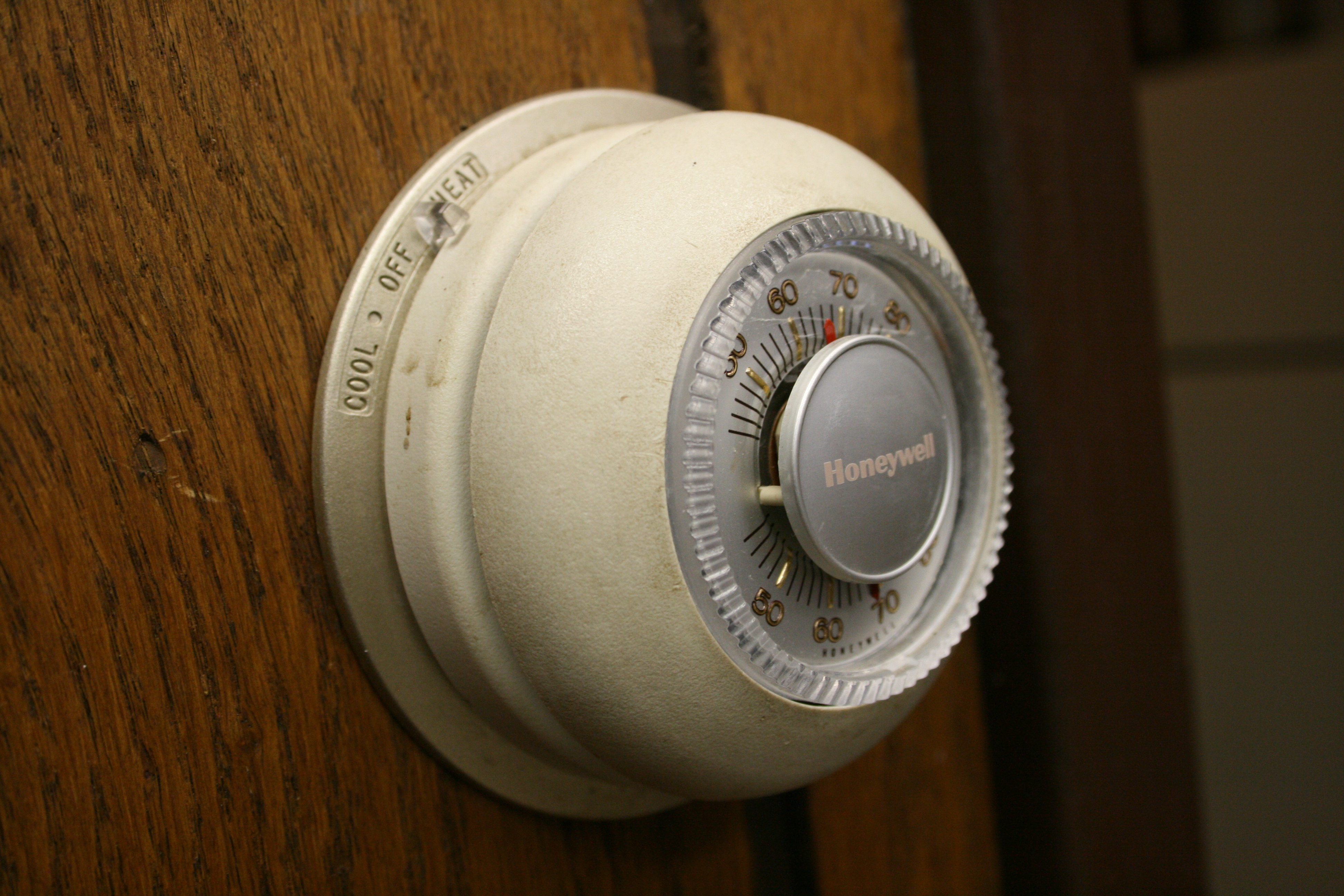
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimetallic Strip
A bimetallic strip is used to convert a temperature change into mechanical displacement. The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates as they are heated. The different expansions force the flat strip to bend one way if heated, and in the opposite direction if cooled below its initial temperature. The metal with the higher coefficient of thermal expansion is on the outer side of the curve when the strip is heated and on the inner side when cooled. The invention of the bimetallic strip is generally credited to John Harrison, an eighteenth-century clockmaker who made it for his third marine chronometer (H3) of 1759 to compensate for temperature-induced changes in the balance spring. Harrison's invention is recognized in the memorial to him in Westminster Abbey, England. This effect is used in a range of mechanical and electrical devices. Characteristics The strip consists of two strips of different metals which expand at different rates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominal Current
Nominal may refer to: Linguistics and grammar * Nominal (linguistics), one of the parts of speech * Nominal, the adjectival form of "noun", as in "nominal agreement" (= "noun agreement") * Nominal sentence, a sentence without a finite verb * Noun phrase or nominal phrase Mathematics * Nominal data, a form of categorical data in statistics * Nominal number, a number used as an identifier in mathematics Titles * Post-nominal letters, letters indicating a title, placed after the name of a person * Pre-nominal letters, letters indicating a title, placed before the name of a person Other uses * Nominal aphasia or anomic aphasia, a problem remembering words and names * Nominal category, a group of objects or ideas that can be collectively grouped on the basis of one or more shared, arbitrary characteristics * Nominal damages, a small award to compensate for technical harm * Nominal GDP, a raw gross domestic product value uncompensated for inflation or deflation * Nominal techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation Oscillator
In electronics a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation oscillators are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |