|
Egocentric Bias
Egocentric bias is the tendency to rely too heavily on one's own perspective and/or have a higher opinion of oneself than reality. It appears to be the result of the psychological need to satisfy one's ego and to be advantageous for memory consolidation. Research has shown that experiences, ideas, and beliefs are more easily recalled when they match one's own, causing an egocentric outlook. Michael Ross and Fiore Sicoly first identified this cognitive bias in their 1979 paper, "Egocentric biases in availability and attribution". Egocentric bias is referred to by most psychologists as a general umbrella term under which other related phenomena fall. The effects of egocentric bias can differ based on personal characteristics, such as age and the number of languages one speaks. Thus far, there have been many studies focusing on specific implications of egocentric bias in different contexts. Research on collaborative group tasks have emphasized that people view their own contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
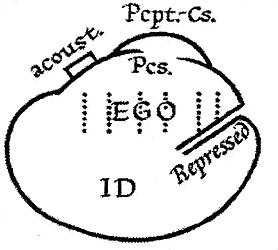
Ego (Freudian)
The id, ego, and super-ego are a set of three concepts in psychoanalytic theory describing distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus (defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche). The three agents are theoretical constructs that describe the activities and interactions of the mental life of a person. In the ego psychology model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual desires; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic agent that mediates between the instinctual desires of the id and the critical super-ego; Freud explained that: The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that, normally, control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus, in its relation to the id, he egois like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength, while the ego us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Load
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load refers to the amount of working memory resources used. There are three types of cognitive load: ''intrinsic'' cognitive load is the effort associated with a specific topic; ''extraneous'' cognitive load refers to the way information or tasks are presented to a learner; and ''germane'' cognitive load refers to the work put into creating a permanent store of knowledge (a schema). Cognitive load theory was developed in the late 1980s out of a study of problem solving by John Sweller. Sweller argued that instructional design can be used to reduce cognitive load in learners. Much later, other researchers developed a way to measure perceived mental effort which is indicative of cognitive load. Task-invoked pupillary response is a reliable and sensitive measurement of cognitive load that is directly related to working memory. Information may only be stored in long term memory after first being attended to, and processed by, working memory. Workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Inference
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derived from a statistical model for the observed data. Bayesian inference computes the posterior probability according to Bayes' theorem: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayes' Rule
In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, Bayes' theorem allows the risk to an individual of a known age to be assessed more accurately (by conditioning it on their age) than simply assuming that the individual is typical of the population as a whole. One of the many applications of Bayes' theorem is Bayesian inference, a particular approach to statistical inference. When applied, the probabilities involved in the theorem may have different probability interpretations. With Bayesian probability interpretation, the theorem expresses how a degree of belief, expressed as a probability, should rationally change to account for the availability of related evidence. Bayesian inference is fundamental to Bayesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Reasoning
Bayesian probability is an interpretation of the concept of probability, in which, instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon, probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of propositional logic that enables reasoning with hypotheses; that is, with propositions whose truth or falsity is unknown. In the Bayesian view, a probability is assigned to a hypothesis, whereas under frequentist inference, a hypothesis is typically tested without being assigned a probability. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the Bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability. This, in turn, is then updated to a posterior probability in the light of new, relevant data (evidence). The Bayesian interpretation provides a standard set of procedures and formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam Glucksberg
Sam Glucksberg (February 6, 1933 – August 29, 2022) was a Canadian professor in the Psychology Department at Princeton University in New Jersey, known for his works on figurative language: metaphors, irony, sarcasm, and idioms. He is particularly known for manipulating the Candle Problem experiment which had participants figure out the best way to erect a candle on a wall. Along with performing experiments, Glucksberg has also written ''Understanding Figurative Language: From Metaphors to Idioms'', published by Oxford University Press in 2001. Biography Glucksberg was born February 6, 1933, in Montreal, Quebec. He received his B.S. in psychology in 1956 at City College of New York, magna cum laude. He then received his Ph.D in experimental psychology with distinction at New York University in 1960. After a period of three years as a research psychologist at the U.S. Army Human Engineering Laboratories, he came to Princeton as an instructor in 1963, and rose progressively throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all Europeans claim to speak at least one language other than their mother tongue; but many read and write in one language. Multilingualism is advantageous for people wanting to participate in trade, globalization and cultural openness. Owing to the ease of access to information facilitated by the Internet, individuals' exposure to multiple languages has become increasingly possible. People who speak several languages are also called polyglots. Multilingual speakers have acquired and maintained at least one language during childhood, the so-called first language (L1). The first language (sometimes also referred to as the mother tongue) is usually acquired without formal education, by mechanisms about which scholars disagree. Children acquirin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (touch, temperature, and pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "little man") in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them. The superior parietal lobule and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supramarginal Gyrus
The supramarginal gyrus is a portion of the parietal lobe. This area of the brain is also known as Brodmann area 40 based on the brain map created by Korbinian Brodmann to define the structures in the cerebral cortex. It is probably involved with language perception and processing, and lesions in it may cause receptive aphasia. Important functions The supramarginal gyrus is part of the somatosensory association cortex, which interprets tactile sensory data and is involved in perception of space and limbs location. It is also involved in identifying postures and gestures of other people and is thus a part of the mirror neuron system. The right-hemisphere supramarginal gyrus appears to play a central role in controlling empathy towards other people. When this structure is not working properly or when individuals have to make very quick judgements, empathy becomes severely limited. Research has shown that disrupting the neurons in the right supramarginal gyrus causes humans to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |