|
Ebolaviruses
The genus ''Ebolavirus'' (- or ; - or ) is a International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, virological taxon included in the family ''Filoviridae'' (filament-shaped viruses), order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of this genus are called ebolaviruses, and encode their genome in the form of RNA virus#Group V—negative-sense ssRNA viruses, single-stranded negative-sense RNA. The six known virus International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, species are named for the region where each was originally identified: ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'', ''Reston ebolavirus'', ''Sudan ebolavirus'', ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' (originally ''Côte d'Ivoire ebolavirus''), ''Zaire ebolavirus'', and ''Bombali ebolavirus''. The last is the most recent species to be named and was isolated from Angolan free-tailed bats in Sierra Leone. Each species of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' has one member virus, and four of these cause Ebola virus disease (EVD) in humans, a type of Viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundibugyo Ebolavirus
The species ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of one virus, Bundibugyo virus (BDBV), that forms filamentous virions and is closely related to the infamous Ebola virus (EBOV). The virus causes severe disease in humans in the form of viral hemorrhagic fever and is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and is listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The species ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'' is a virological taxon (i.e. a man-made concept) that was suggested in 2008 to be included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Bundibugyo virus (BDBV). The members of the species are called Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaire Ebolavirus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taï Forest Ebolavirus
The species ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' () is a virological taxon included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Taï Forest virus (TAFV). The members of the species are called Taï Forest ebolaviruses. ''Tai Forest ebolavirus'' has been seen in a single human infection due to contact with chimpanzees from the Tai Forest in Côte d'Ivoire. Nomenclature The name ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' is derived from '' Parc National de Taï'' (the name of a national park in Côte d'Ivoire, where Taï Forest virus was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''ebolavirus'' (which denotes an ebolavirus species). According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, never abbreviated, and to be preceded by the word "species". The names of its members (Taï Forest ebolavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan Ebolavirus
The species ''Sudan ebolavirus'' is a virological taxon included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Sudan virus (SUDV). The members of the species are called Sudan ebolaviruses. It was discovered in 1977 and causes Ebola clinically indistinguishable from the ebola Zaire strain, but is less transmissible than it. Unlike with ebola Zaire there is no vaccine available. Nomenclature The name ''Sudan ebolavirus'' is derived from '' Sudan'' (the country in which Sudan virus was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''ebolavirus'' (which denotes an ebolavirus species). The species was introduced in 1998 as ''Sudan Ebola virus''. In 2002, the name was changed to ''Sudan ebolavirus''. A virus of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' is a member of the species ''Sudan ebolavirus'' if: * it is endemic in Sudan and/or Uganda * it has a genome with three gene overlaps (''VP35''/''VP40'', ''GP''/''VP30'', ''VP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
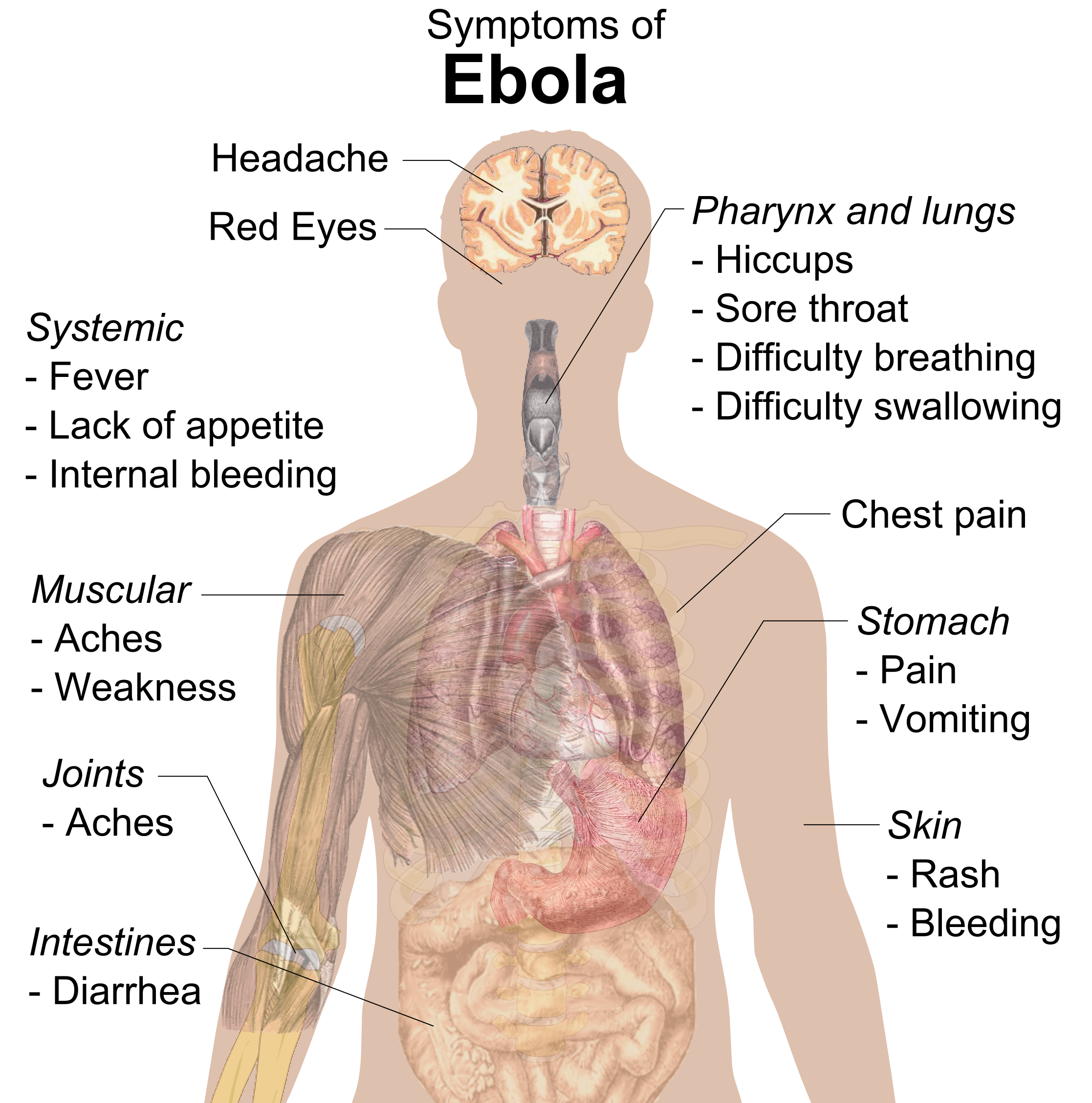
Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014 West Africa Ebola Virus Outbreak
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease, centered in Western Africa, was the most widespread outbreak of the disease in history. It caused major loss of life and socioeconomic disruption in the region, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013; later, the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone, with minor outbreaks occurring in Ebola virus disease in Nigeria, Nigeria and Mali. Secondary infections of medical workers occurred in the United States and Spain. In addition, isolated cases were recorded in Senegal, the United Kingdom and Italy. The number of cases peaked in October 2014 and then began to decline gradually, following the commitment of substantial international resources. It caused significant mortality, with a considerable case fatality rate. By the end of the epidemic, 28,616 people had been infected; of these, 11,310 had died, for a case-fatality rate of 40%. , the World Health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marburgvirus
The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is the taxonomic home of ''Marburg marburgvirus'', whose members are the two known marburgviruses, Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Both viruses cause Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. Both are Select agents, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogens (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogens, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agents, and are listed as Biological Agents for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The genus ''Marburgvirus'' is a virological taxon included in the family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The genus currently includes a single virus species, '' Marburg marburgvirus''. The members of the genus (i.e. the actual physical entities) are called marburgviruses. The name ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ebola Outbreaks
This list of Ebola outbreaks records the known occurrences of Ebola virus disease, a highly infectious and acutely lethal viral disease that has afflicted humans and animals primarily in equatorial Africa. The pathogens responsible for the disease are the five ebolaviruses recognized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses: Ebola virus (EBOV), Sudan virus (SUDV), Reston virus (RESTV), Taï Forest virus (TAFV), and Bundibugyo virus (BDBV). Four of the five variants have caused the disease in humans as well as other animals; RESTV has caused clinical symptoms only in non-human primates. RESTV has caused subclinical infections in humans, producing an antibody response but no visual symptoms or disease state manifestations. Transmission of the ''ebolaviruses'' between natural reservoirs and humans is rare, and outbreaks of Ebola virus disease are often traceable to a single case where an individual has handled the carcass of a gorilla, chimpanzee, bats, or duiker. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypsignathus Monstrosus
The hammer-headed bat ('), also known as hammer-headed fruit bat and big-lipped bat, is a megabat widely distributed in West and Central Africa. It is the only member of the genus ''Hypsignathus'', which is part of the tribe Epomophorini along with four other genera. It is the largest bat in continental Africa, with wingspans approaching , and males almost twice as heavy as females. Males and females also greatly differ in appearance, making it the most sexually dimorphic bat species in the world. These differences include several adaptations that help males produce and amplify vocalizations: the males' larynges (vocal cords) are about three times as large as those of females, and they have large resonating chambers on their faces. Females appear more like a typical megabat, with foxlike faces. The hammer-headed bat is frugivorous, consuming a variety of fruits such as figs, bananas, and mangoes, though a few instances of carnivory have been noted. Females tend to travel a consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filoviridae
''Filoviridae'' () is a family of single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Both viruses, and some of their lesser known relatives, cause severe disease in humans and nonhuman primates in the form of viral hemorrhagic fevers. All filoviruses are classified by the US as select agents, by the World Health Organization as Risk Group 4 Pathogens (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases as Category A Priority Pathogens, and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as Category A Bioterrorism Agents, and are listed as Biological Agents for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The family ''Filoviridae'' is a virological taxon that was defined in 1982 and emended in 1991, 1998, 2000, 2005, 2010 and 2011. The family currently includes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reston Ebolavirus
Reston virus (RESTV) is one of six known viruses within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Reston virus causes Ebola virus disease in non-human primates; unlike the other five ebolaviruses, it is not known to cause disease in humans, but has caused asymptomatic infections. Reston virus was first described in 1990 as a new "strain" of Ebola virus (EBOV). It is the single member of the species ''Reston ebolavirus'', which is included into the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. Reston virus is named after Reston, Virginia, US, where the virus was first discovered. RESTV was discovered in crab-eating macaques from Hazleton Laboratories (now Labcorp Drug Development) in 1989. This attracted significant media attention due to Reston's location in the Washington, DC metro area and the lethality of a closely related Ebola virus. Despite its status as a level-4 organism, Reston virus is non-pathogenic to humans, though hazardous to monkeys; the perception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)

