|
Euctenochasmatia
Euctenochasmatia is an extinct group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs. It was named by David Unwin in 2003 as the group that contains the most recent common ancestor of ''Pterodactylus'' and ''Ctenochasma'', and all their descendants. Euctenochasmatians were specialized pterosaurs that had elongated necks as well as specialized teeth. A peculiar family within this group is the Ctenochasmatidae, which most of the members had very distinguishing teeth that were lined within their elongated snouts. A genus called ''Pterofiltrus'' only had 112 teeth, but these teeth cover about 55.8% of the total skull, and the skull itself measured about in length. Description Euctenochasmatians had very distinctive features in comparison to other pterosaurs, including the shape of their jaws, as well as their highly specialized teeth. These teeth are thought to have been used for filter-feeding, the genus ''Pterodaustro'' for example, had a long snout and its lower jaws curve strongly upwards, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
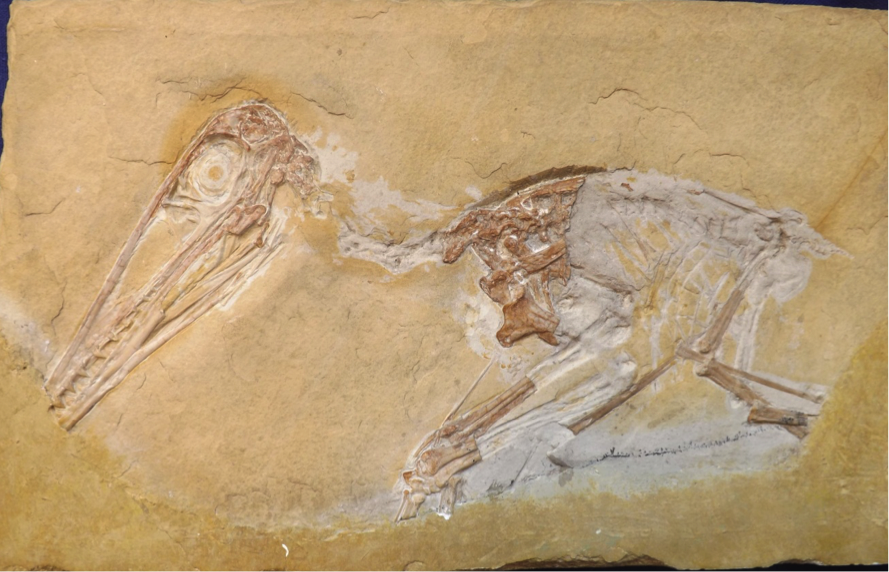
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
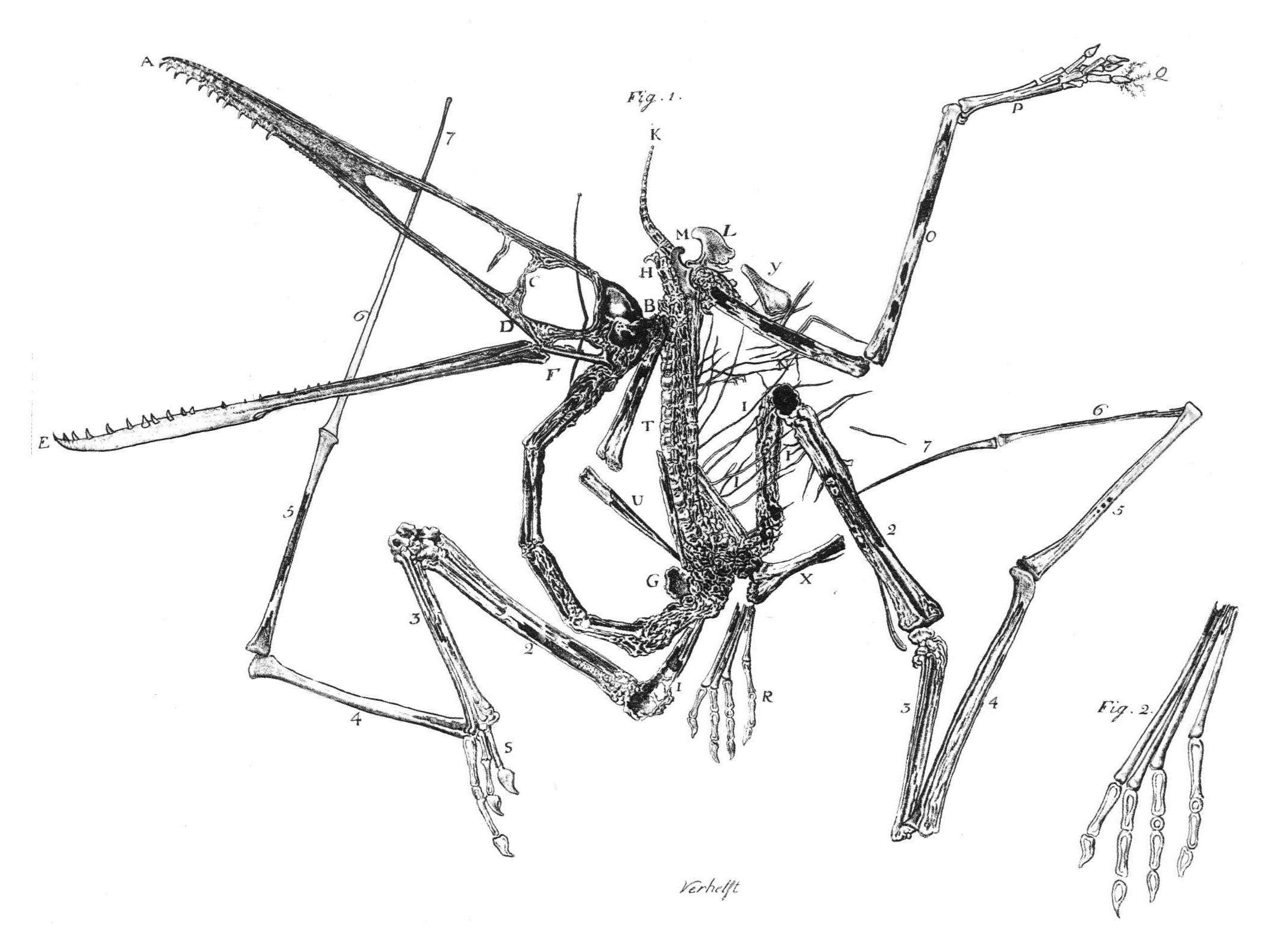
Pterodactylus Antiquus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloid
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenochasmatoidea
Ctenochasmatoidea is a group of early pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Their remains are usually found in what were once coastal or lake environments. They generally had long wings, long necks, and highly specialized teeth. Evolutionary history The earliest known ctenochasmatoid remains date to the Late Jurassic Kimmeridgian age. Previously, a fossil jaw recovered from the Middle Jurassic Stonesfield Slate formation in the United Kingdom, was considered the oldest known. This specimen supposedly represented a member of the family Ctenochasmatidae,Buffetaut, E. and Jeffrey, P. (2012). "A ctenochasmatid pterosaur from the Stonesfield Slate (Bathonian, Middle Jurassic) of Oxfordshire, England." ''Geological Magazine'', (advance online publication) though further examination suggested it belonged to a teleosaurid stem-crocodilian instead of a pterosaur. Ecology Most ctenochasmatoids were aquatic or semi-aquatic pterosaurs, possessing large webbed hindfeet and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloidea
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylidae
Pterodactylidae is a controversial group of pterosaurs. During the 2000s and 2010s, several competing definitions for the various Jurassic pterodactyloid groups were proposed. Pereda-Suberbiola ''et al.'' (2012) used Fabien Knoll's (2000) definition of the name Pterodactylidae. Knoll had defined Pterodactylidae as a clade containing "''Pterodactylus antiquus'', ''Ctenochasma elegans'', their most recent common ancestor and all its descendants". Using this definition with the analysis conducted by Pereda-Suberbiola ''et al.'' (2012) meant that Ctenochasmatoidea was nested inside Pterodactylidae. Classification Below is the majority-rule consensus tree found by Pereda-Suberbiola ''et al.'' (2012), showing their preferred definitions of Pterodactylidae and Ctenochasmatoidea. Other researchers, such as David Unwin, have traditionally defined Pterodactylidae in such a way to ensure it is nested within Ctenochasmatoidea instead. In 2003, Unwin defined the same clade (''Pterodactylus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diopecephalus
''Diopecephalus'' is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Lower Tithonian (Upper Jurassic) of the Lithographic Limestone, Bavaria, Germany. The type and only species is ''D. kochi'', although the name has been applied to ''Pterodactylus longicollum'', with ''longicollum'' erroneously listed as the type species. Assigned species Like many pterosaurs, it has had a confusing taxonomic history, being given names by various authorities which identify it with four other genera: *''Pterodactylus longicollum'' (von Meyer 1854) *''Pterodactylus vulturinus'' (Wagner 1857) *''Pterodactylus longicollis'' (Wagner 1858) *''Pterodactylus suevicus'' (Fraas 1878) *''Cycnorhamphus fraasii'' (Seeley 1891) *''Pterodactylus frassi'' (Seeley 1901) *''Gallodactylus longicollum'' (Fabre 1974) *''Ornithocephalus longipes'' (Olshevsky 1978) (''Ornithocephalus'' is an obsolete name for ''Pterodactylus'') *''Ornithocephalus vulturinus'' (Olshevsky 1978) In 2017, Steven U. Vidovic and David M. Mart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to 66 million years ago). Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger. There were two major types of pterosaurs. Basal pterosaurs (also called 'non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs' or 'rhamphorhynchoids') were smaller animals with fully toothed jaws and, typically, long tails. Their wide wing membranes probably included and connected the hind legs. On the ground, they would have had an awkward sprawling posture, but the anatomy of their joints and strong claws would have made them effective climbers, and some may have even lived in trees. Basal pterosaurs were insectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kryptodrakon
''Kryptodrakon'' is an extinct genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Middle to Late Jurassic with an age of approximately 162.7 million years. It is known from a single type species, ''Kryptodrakon progenitor''. The age of its fossil remains made ''Kryptodrakon'' the basalmost and oldest pterodactyloid known to date. Discovery and naming In 2001, pterosaur bones were discovered in Xinjiang by Chris Sloan. The bones were first identified as those of a theropod; paleontologist James Clark later recognized their pterosaurian nature. In 2014, Brian Andres, Clark and Xu Xing named and described the type species ''Kryptodrakon progenitor''. The generic name means ''hidden dragon'' from Greek κρυπτός, ''kryptos'' (''hidden''), and δράκων, ''drakon'' (''dragon''). The name alludes to the film ''Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon,'' which included some scenes filmed near the type locality. The specific name ''progenitor'' means ''ancestor'' or ''founder of a family'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moganopterus
''Moganopterus'' is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous of western Liaoning Province, China. Discovery and naming The fossil of ''Moganopterus'' was discovered at the village of Xiaosanjiazi near the town of Lamadong in Liaoning Province. In 2012 it was named and described by Lü Junchang, Pu Hanyong, Xu Li, Wu Yanhua and Wei Xuefang as the type species ''Moganopterus zhuiana''. The generic name is derived from the legendary sword couple Gan Jiang and Mo Ye, in reference to the blade-like jaws, and a Latinized Greek πτερόν, ''pteron'', "wing". The specific name honors Ms. Zhu Haifen, who made the specimen available to science. The holotype, 41HIII0419, was uncovered in a layer of the Yixian Formation, dating from the Aptian, about 125 million years old. It consists of an almost complete skull with lower jaws and the second to fourth neck vertebrae. The fossil is compressed on a slab and counterslab, the splitting of the two plates havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle
Needle may refer to: Crafting * Crochet needle, a tool for making loops in thread or yarn * Knitting needle, a tool for knitting, not as sharp as a sewing needle * Sewing needle, a long slender tool with a pointed tip * Trussing needle, a long slender tool, sometimes with a flattened point, to tie poultry for cooking * Upholstery needle, a tool for upholstery, generally thick and curved Science and technology Botany * Needle (botany), of conifers Medicine * Hypodermic needle, a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject fluid into or extract fluid from the body * Surgical needle, several types of needles used for surgical suture * Tuohy needle, a needle used to administer epidural catheters Technology * Acupuncture needle, in alternative medicine * Gramophone needle, used for playing records * Indicator needle, of a measuring instrument * Needle valve Places * Needle Rocks, Tasmania, Australia * Needle (stack), a sea stack on the island of Hoy, Orkney, Scotland * Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |