|
Ericoid Mycorrhiza
The ericoid mycorrhiza is a mutualistic relationship formed between members of the plant family Ericaceae and several lineages of mycorrhizal fungi. This symbiosis represents an important adaptation to acidic and nutrient poor soils that species in the Ericaceae typically inhabit, including boreal forests, bogs, and heathlands. Molecular clock estimates suggest that the symbiosis originated approximately 140 million years ago. Structure and function Ericoid mycorrhizas are characterized by fungal coils that form in the epidermal cells of the fine hair roots of ericaceous species.Smith, S. E. and D. J. Read. 2008. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, Third Edition. Academic Press. Ericoid mycorrhizal fungi establish loose hyphal networks around the outside of hair roots, from which they penetrate the walls of cortical cells to form intercellular coils that can densely pack individual plant cells. However, the fungi do not penetrate plasma membranes of plant cells. Evidence suggests that coils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epacris Pulchella
''Epacris pulchella'', commonly known as wallum heath or coral heath is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a slender, erect shrub with egg-shaped, pointed leaves and white or pinkish, tube-shaped flowers. Description ''Epacris longiflora'' is a slender, erect shrub that typically grows to a height of and has only a few woolly-hairy branches, the stems with inconspicuous leaf scars. The leaves are egg-shaped, with a heart-shaped base and long, tapering tip, long and wide on a petiole long. The flowers are arranged in leaf axils extending down the branches and are white or pinkish and wide, each flower on a peduncle long. The sepals are long and the petals are joined at the base to form a tube long with lobes long. The anthers protrude beyond the end of the petal tube. Flowering occurs from January to May with a peak in March, and the fruit is a capsule long. This species is similar to '' E. microphylla'' but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairneyella
''Cairneyella'' is a genus of at least two ericoid mycorrhizal and root-associated fungi that is, to date, endemic to Australian plants, mostly from the family Ericaceae. It has been demonstrated to form typical ericoid mycorrhizal coils in hair roots and is known to enhance the growth of ericaceous seedlings. The genus is named in honour of John Cairney John Cairney (born 16 February 1930) is a Scottish film and television actor who is well known to audiences in Scotland and internationally through his one-man shows on Robert Burns, Robert Louis Stevenson, Robert Service, Charles Rennie Macki ..., an Australian-Scottish mycologist. Species *'' Cairneyella variabilis'' *''Cairneyella'' sp. 2. References External links * Helotiales {{leotiomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
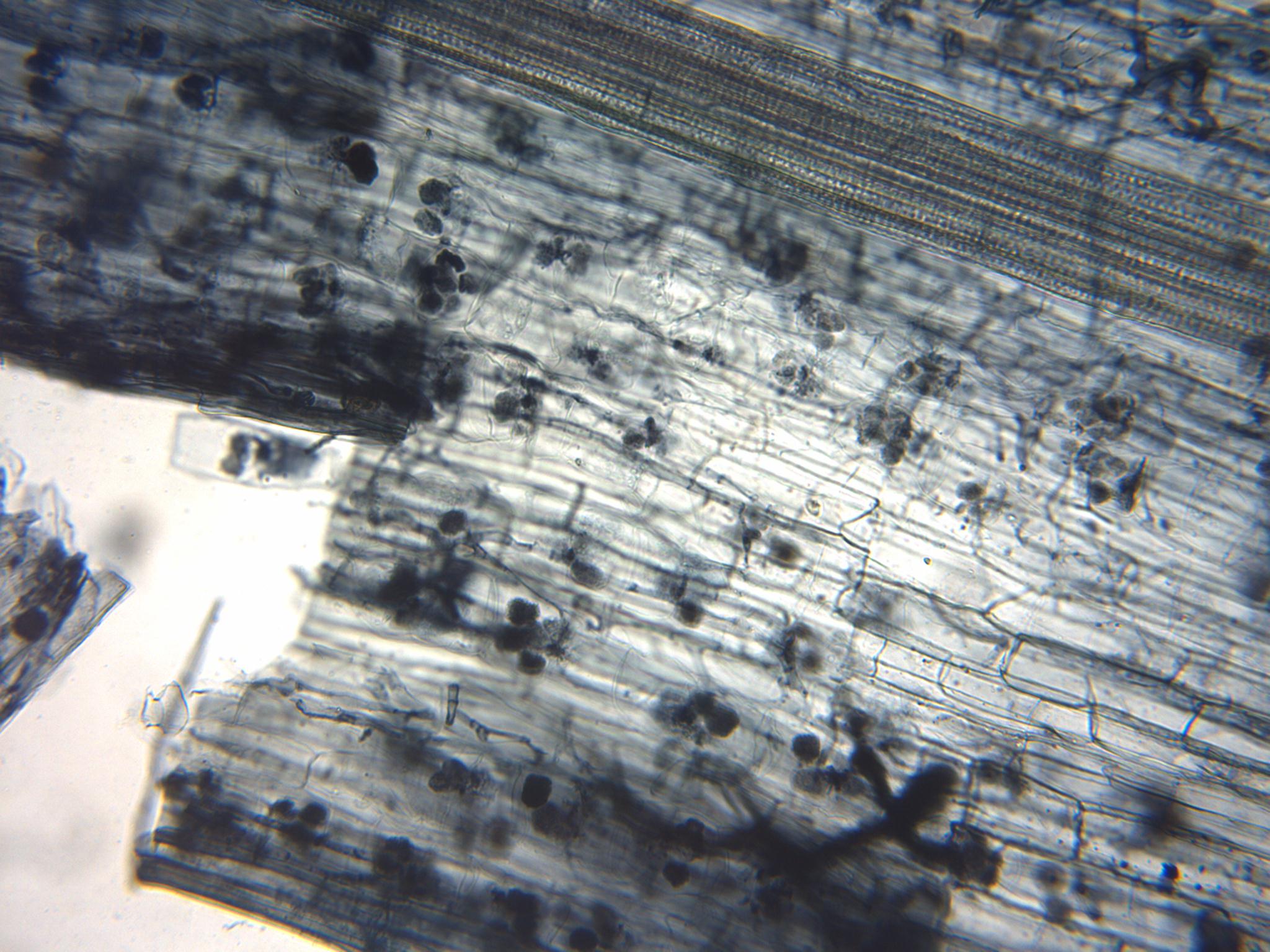
Fungal Morphology And Anatomy
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectomycorrhizal
An ectomycorrhiza (from Greek ἐκτός ', "outside", μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. ectomycorrhizas or ectomycorrhizae, abbreviated EcM) is a form of symbiotic relationship that occurs between a fungal symbiont, or mycobiont, and the roots of various plant species. The mycobiont is often from the phyla Basidiomycota and Ascomycota, and more rarely from the Zygomycota. Ectomycorrhizas form on the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pine and rose families. Research on ectomycorrhizas is increasingly important in areas such as ecosystem management and restoration, forestry and agriculture. Unlike other mycorrhizal relationships, such as arbuscular mycorrhiza and ericoid mycorrhiza, ectomycorrhizal fungi do not penetrate their host's cell walls. Instead they form an entirely intercellular interface known as the Hartig net, consisting of highly branched hyphae formi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are characterized by the formation of unique structures, arbuscules and vesicles, by Glomeromycota and Mucoromycota, sister clades of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi (all three are together called "symbiomycota"). AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a crucial role in the initial colonisation of land by plants and in the evolution of the vascular plants. It has been said that it is quicker to list the plants that do not form endomycorrhizae than those that do. This symbiosis is a hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrone
''Arbutus'' is a genus of 12 accepted speciesAct. Bot. Mex no.99 Pátzcuaro abr. 2012.''Arbutus bicolor''/ref> of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae, native to warm temperate regions of the Mediterranean, western Europe, the Canary Islands and North America. The name ''Arbutus'' was taken from Latin, where it referred to ''Arbutus unedo''. Description ''Arbutus'' are small trees or shrubs with red flaking bark and edible red berries.Mabberley, D. J. 1997. ''The plant book: A portable dictionary of the vascular plants''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Fruit development is delayed for about five months after pollination, so that flowers appear while the previous year's fruit are ripening. Peak flowering for the genus is in April with peak fruiting in October. History The smooth wood of the tree is mentioned by Theophrastus in his ''Enquiry into Plants'' (''Historia Plantarum'') as formerly being used to make weaving spindles. An article on Arbutus tree cultivatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manzanita
Manzanita is a common name for many species of the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. They are evergreen shrubs or small trees present in the chaparral biome of western North America, where they occur from Southern British Columbia and Washington to Oregon, California, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas in the United States, and throughout Mexico. Manzanitas can live in places with poor soil and little water. They are characterized by smooth orange or red bark and stiff, twisting branches. There are 105 species and subspecies of manzanita, 95 of which are found in the Mediterranean climate and colder mountainous regions of California, ranging from ground-hugging coastal and mountain species to small trees up to 20 feet (6m) tall. Manzanitas bloom in the winter to early spring and carry berries in spring and summer. The berries and flowers of most species are edible. The word ''manzanita'' is the Spanish diminutive of ''manzana'' (apple). A literal translation would be ''little apple' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenochaetales
The Hymenochaetales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. The order in its current sense is based on molecular research and not on any unifying morphological characteristics. According to one 2008 estimate, the Hymenochaetales contain around 600 species worldwide, mostly corticioid fungi and poroid fungi, but also including several clavarioid fungi and agarics. Species of economic importance include wood decay fungi in the genera '' Phellinus'' and ''Inonotus'' sensu lato, some of which may cause losses in forestry. Therapeutic properties are claimed for ''Inonotus obliquus'' ("chaga") and ''Phellinus linteus'', both of which are now commercially marketed. Taxonomy History The order was proposed in 1977 to recognize the family Hymenochaetaceae at a higher taxonomic rank. As originally conceived, species within the Hymenochaetales had several morphological features in common, notably brown or brownish basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that turn black in alkali, hyphae l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and ''Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebacina
''Sebacina'' is a genus of fungi in the family Sebacinaceae. Its species are mycorrhizal, forming a range of associations with trees and other plants. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are produced on soil and litter, sometimes partly encrusting stems of living plants. The fruit bodies are cartilaginous to rubbery-gelatinous and variously effused (corticioid) to coral-shaped ( clavarioid). The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Taxonomy History The genus was first published in 1871 by Louis and Charles Tulasne who had discovered that two species (''Sebacina incrustans'' and ''Sebacina epigaea'') previously referred to '' Corticium'' or ''Thelephora'' possessed septate basidia, similar to those found in the genus ''Tremella''. Although it was unusual at that time to separate fungal genera on purely microscopic characters, ''Sebacina'' was erected for effused, ''Corticium''-like fungi with tremelloid basidia. Subsequent authors added many additional species of corticioid fungi with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)