|
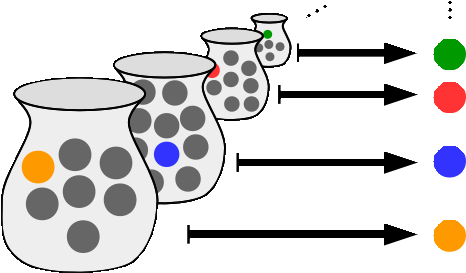
Equinumerosity
In mathematics, two sets or classes ''A'' and ''B'' are equinumerous if there exists a one-to-one correspondence (or bijection) between them, that is, if there exists a function from ''A'' to ''B'' such that for every element ''y'' of ''B'', there is exactly one element ''x'' of ''A'' with ''f''(''x'') = ''y''. Equinumerous sets are said to have the same cardinality (number of elements). The study of cardinality is often called equinumerosity (''equalness-of-number''). The terms equipollence (''equalness-of-strength'') and equipotence (''equalness-of-power'') are sometimes used instead. Equinumerosity has the characteristic properties of an equivalence relation. The statement that two sets ''A'' and ''B'' are equinumerous is usually denoted :A \approx B \, or A \sim B, or , A, =, B, . The definition of equinumerosity using bijections can be applied to both finite and infinite sets, and allows one to state whether two sets have the same size even if they are infinite. Georg Cant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinality
In mathematics, the cardinality of a set is a measure of the number of elements of the set. For example, the set A = \ contains 3 elements, and therefore A has a cardinality of 3. Beginning in the late 19th century, this concept was generalized to infinite sets, which allows one to distinguish between different types of infinity, and to perform arithmetic on them. There are two approaches to cardinality: one which compares sets directly using bijections and injections, and another which uses cardinal numbers. The cardinality of a set is also called its size, when no confusion with other notions of size is possible. The cardinality of a set A is usually denoted , A, , with a vertical bar on each side; this is the same notation as absolute value, and the meaning depends on context. The cardinality of a set A may alternatively be denoted by n(A), , \operatorname(A), or \#A. History A crude sense of cardinality, an awareness that groups of things or events compare with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Cantor
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor ( , ; – January 6, 1918) was a German mathematician. He played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between the members of two sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. In fact, Cantor's method of proof of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal and ordinal numbers and their arithmetic. Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he was well aware of. Originally, Cantor's theory of transfinite numbers was regarded as counter-intuitive – even shocking. This caused it to encounter resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré and later from Hermann Weyl and L. E. J. Brouwer, while Ludwig Wittgenstein rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Number
In mathematics, cardinal numbers, or cardinals for short, are a generalization of the natural numbers used to measure the cardinality (size) of sets. The cardinality of a finite set is a natural number: the number of elements in the set. The '' transfinite'' cardinal numbers, often denoted using the Hebrew symbol \aleph (aleph) followed by a subscript, describe the sizes of infinite sets. Cardinality is defined in terms of bijective functions. Two sets have the same cardinality if, and only if, there is a one-to-one correspondence (bijection) between the elements of the two sets. In the case of finite sets, this agrees with the intuitive notion of size. In the case of infinite sets, the behavior is more complex. A fundamental theorem due to Georg Cantor shows that it is possible for infinite sets to have different cardinalities, and in particular the cardinality of the set of real numbers is greater than the cardinality of the set of natural numbers. It is also poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-to-one Correspondence
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other set, and each element of the other set is paired with exactly one element of the first set. There are no unpaired elements. In mathematical terms, a bijective function is a one-to-one (injective) and onto (surjective) mapping of a set ''X'' to a set ''Y''. The term ''one-to-one correspondence'' must not be confused with ''one-to-one function'' (an injective function; see figures). A bijection from the set ''X'' to the set ''Y'' has an inverse function from ''Y'' to ''X''. If ''X'' and ''Y'' are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements. For infinite sets, the picture is more complicated, leading to the concept of cardinal number—a way to distinguish the various sizes of infinite sets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijection
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other set, and each element of the other set is paired with exactly one element of the first set. There are no unpaired elements. In mathematical terms, a bijective function is a one-to-one (injective) and onto (surjective) mapping of a set ''X'' to a set ''Y''. The term ''one-to-one correspondence'' must not be confused with ''one-to-one function'' (an injective function; see figures). A bijection from the set ''X'' to the set ''Y'' has an inverse function from ''Y'' to ''X''. If ''X'' and ''Y'' are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements. For infinite sets, the picture is more complicated, leading to the concept of cardinal number—a way to distinguish the various sizes of infinite set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are those numbers used for counting (as in "there are ''six'' coins on the table") and ordering (as in "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country"). Numbers used for counting are called '' cardinal numbers'', and numbers used for ordering are called '' ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are sometimes used as labels, known as ''nominal numbers'', having none of the properties of numbers in a mathematical sense (e.g. sports jersey numbers). Some definitions, including the standard ISO 80000-2, begin the natural numbers with , corresponding to the non-negative integers , whereas others start with , corresponding to the positive integers Texts that exclude zero from the natural numbers sometimes refer to the natural numbers together with zero as the whole numbers, while in other writings, that term is used instead for the integers (including negative integers). The natural numbers form a set. Many other number sets are built by succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets. A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least natural number that has not been previously used. To extend this process to various infinite sets, ordinal numbers are defined more generally as linearly ordered labels that include the natural numbers and have the property that every set of ordinals has a least element (this is needed for giving a meaning to "the least unused element"). This more general definition allows us to define an ordinal number \omega that is greater than every natural number, along with ordinal numbers \omega + 1, \omega + 2, etc., which are even greater than \omega. A linear order such that every subset has a least element is called a well-order. The axiom of choice implies that every set can be well-ordered, and given two well-ordered sets, one is isomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initial Ordinal
In a written or published work, an initial capital, also referred to as a drop capital or simply an initial cap, initial, initcapital, initcap or init or a drop cap or drop, is a letter at the beginning of a word, a chapter, or a paragraph that is larger than the rest of the text. The word is derived from the Latin ''initialis'', which means ''standing at the beginning''. An initial is often several lines in height and in older books or manuscripts are known as "inhabited" initials. Certain important initials, such as the Beatus initial or "B" of '' Beatus vir...'' at the opening of Psalm 1 at the start of a vulgate Latin. These specific initials in an illuminated manuscript were also called initiums. In the present, the word "initial" commonly refers to the first letter of any word or name, the latter normally capitalized in English usage and is generally that of a first given name or a middle one or ones. History The classical tradition was slow to use capital letters fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott's Trick
In set theory, Scott's trick is a method for giving a definition of equivalence classes for equivalence relations on a proper class (Jech 2003:65) by referring to levels of the cumulative hierarchy. The method relies on the axiom of regularity but not on the axiom of choice. It can be used to define representatives for ordinal numbers in ZF, Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory without the axiom of choice (Forster 2003:182). The method was introduced by . Beyond the problem of defining set representatives for ordinal numbers, Scott's trick can be used to obtain representatives for cardinal numbers and more generally for isomorphism types, for example, order types of linearly ordered sets (Jech 2003:65). It is credited to be indispensable (even in the presence of the axiom of choice) when taking ultrapowers of proper classes in model theory. (Kanamori 1994:47) Application to cardinalities The use of Scott's trick for cardinal numbers shows how the method is typically employed. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Relation
In mathematics, a binary relation ''R'' on a set ''X'' is reflexive if it relates every element of ''X'' to itself. An example of a reflexive relation is the relation " is equal to" on the set of real numbers, since every real number is equal to itself. A reflexive relation is said to have the reflexive property or is said to possess reflexivity. Along with symmetry and transitivity, reflexivity is one of three properties defining equivalence relations. Definitions Let R be a binary relation on a set X, which by definition is just a subset of X \times X. For any x, y \in X, the notation x R y means that (x, y) \in R while "not x R y" means that (x, y) \not\in R. The relation R is called if x R x for every x \in X or equivalently, if \operatorname_X \subseteq R where \operatorname_X := \ denotes the identity relation on X. The of R is the union R \cup \operatorname_X, which can equivalently be defined as the smallest (with respect to \subseteq) reflexive relation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, or AC, is an axiom of set theory equivalent to the statement that ''a Cartesian product of a collection of non-empty sets is non-empty''. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of sets, each containing at least one element, it is possible to construct a new set by arbitrarily choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets, there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. In many cases, a set arising from choosing elements arbitrarily can be made without invoking the axiom of choice; this is, in particular, the case if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available – some distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |