|
End Of The British Mandate For Palestine
The end of the British Mandate for Palestine was formally made by way of the Palestine bill of 29 April 1948. A public statement prepared by the Colonial and Foreign offices confirmed termination of British responsibility for the administration of Palestine from midnight on 14 May 1948. Background Mandatory Palestine was created at the end of the First World War out of the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire. In 1920 Britain was awarded the mandate for Palestine by the League of Nations, to administer until such time as the territory was "able to stand alone". The 1939 White Paper provided for the establishment of an independent Palestinian state within 10 years. As explained by Malcolm MacDonald to the 1939 meeting of the Permanent Mandates Commission it was not clear at that stage what form such a state would take. The February 1945 Yalta Conference agreed that arrangements would be made to provide for UN trusteeships for existing League Mandates. In July 1945, the Harrison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Termination Of The Mandate 15th May 1948
__NOTOC__ Palestine may refer to: * State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia * Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia * Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip * Palestinian enclaves, the areas designated for Palestinians under a variety of US and Israeli-led proposals * Mandatory Palestine (1920–1948), a geopolitical entity under British administration * Timeline of the name Palestine, Timeline of the name ''Palestine'' lists other historic uses Other places Canada * Palestine, Ontario Iraq * Palestine Hotel, in Baghdad * Palestine Street, in Baghdad Saudi Arabia * Palestine Street, Jeddah United Kingdom * Palestine, Hampshire, England * Palestine Place, headquarters in London of the Church of England's organization Church's Ministry Among Jewish People United States * Palestine, Arkansas * Palestine, a community of Newtown, Connecticut * Palestine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Conference Of 1946–1947
The London Conference of 1946–1947, which took place between September 1946 and February 1947, was called by the British Government of Clement Attlee to resolve the future governance of Palestine and negotiate an end of the Mandate. It was scheduled following an Arab request after the April 1946 Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry report. A press statement made by President Truman on October 4 advocating for the Jewish Agency proposal effectively "torpedoed" British plans for the conference. Bevin blamed Truman for the failure of the conference in a speech a week after he announced its failure; according to Professor Arieh Kochavi, "Bevin was furious at what he regarded as the President's bowing to American Jewish political pressure." Bevin's speech was widely attacked in the United States. Truman commented on the matter in detail in his memoirs. Background The Council of the Arab League had met at the Bloudan Conference of 1946 to consider the Anglo-American Committee of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloudan Conference Of 1946
The Bloudan Conference of 1946 (Arabic transliteration: ''al-Mu'tamar al-'Arabi al-Qawmi fi Bludan'') was the second pan-Arab summit held in Bloudan, Syria in 1946, following the first conference in 1937. It was called to for the Council of the Arab League to consider the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry The Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry was a joint British and American committee assembled in Washington, D.C. on 4 January 1946. The committee was tasked to examine political, economic and social conditions in Mandatory Palestine Mandat ... report which had been published on 20 April 1946. References Bibliography * * * {{Authority control 1946 in politics 20th-century diplomatic conferences Arab nationalism in Mandatory Palestine Diplomatic conferences in Syria History of Mandatory Palestine 1946 in Syria 1946 conferences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inshas
Inshas ( ar, أنشاص الرمل) is a village located in Bilbeis, Sharqia Governorate, 60 kilometers east of Cairo, Egypt. It holds the first experimental nuclear reactor to be operated in Egypt ETRR-1 as well as the second experimental reactor ETRR-2, the ''Egyptian Atomic Energy Authority Experimental Farm'', unauthorized IAEA The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 .... Following the creation of the Arab League in March 1945, Inshas held the first Arab League Summit in May 1946. References {{egypt-geo-stub Arab League Sharqia Governorate Populated places in Sharqia Governorate Villages in Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Higher Committee
The Arab Higher Committee ( ar, اللجنة العربية العليا) or the Higher National Committee was the central political organ of the Arab Palestinians in Mandatory Palestine. It was established on 25 April 1936, on the initiative of Haj Amin al-Husayni, the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, and comprised the leaders of Palestinian Arab clans and political parties under the mufti's chairmanship. The committee was outlawed by the British Mandatory administration in September 1937 after the assassination of a British official. A committee of the same name was reconstituted by the Arab League in 1945, but went to abeyance after it proved ineffective during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. It was sidestepped by Egypt and the Arab League with the formation of the All-Palestine Government in 1948 and both were banned by Jordan. Formation, 1936–37 The first Arab Higher Committee was formed on 25 April 1936, following the outbreak of the Great Arab revolt, and national committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, Eastern Africa, and Western Asia. The Arab League was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945, initially with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (renamed Jordan in 1949), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. Yemen joined as a member on 5 May 1945. Currently, the League has 22 members, but Syria's participation has been suspended since November 2011. The League's main goal is to "draw closer the relations between member states and co-ordinate collaboration between them, to safeguard their independence and sovereignty, and to consider in a general way the affairs and interests of the Arab countries". The organization has received a relatively low level of cooperation throughout its history. Through institutions, notably the Arab League ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Gurney
Sir Henry Lovell Goldsworthy Gurney (27 June 1898 – 6 October 1951) was a British colonial administrator who served in various posts throughout the British Empire. Gurney was killed by communist insurgents during the Malayan Emergency, while serving as high commissioner in the Federation of Malaya. Career As a boy, Gurney was educated at Winchester College. During World War I, he joined the British Army, and served with the King's Royal Rifle Corps from 1917 to 1920. After a brief spell at University College, Oxford, he joined the British Colonial Service in 1921, and was posted to Kenya as an assistant district commissioner. In 1935, after fourteen years in Kenya, he was appointed Assistant Colonial Secretary to Jamaica. After a brief stint working at the Colonial Office in London, Gurney served as Chief Secretary to the Conference of East Africa Governors from 1938 to 1944, and Colonial Secretary in the Gold Coast from 1944 to 1946. In 1946, he was appointed Chief S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Arab–Israeli War
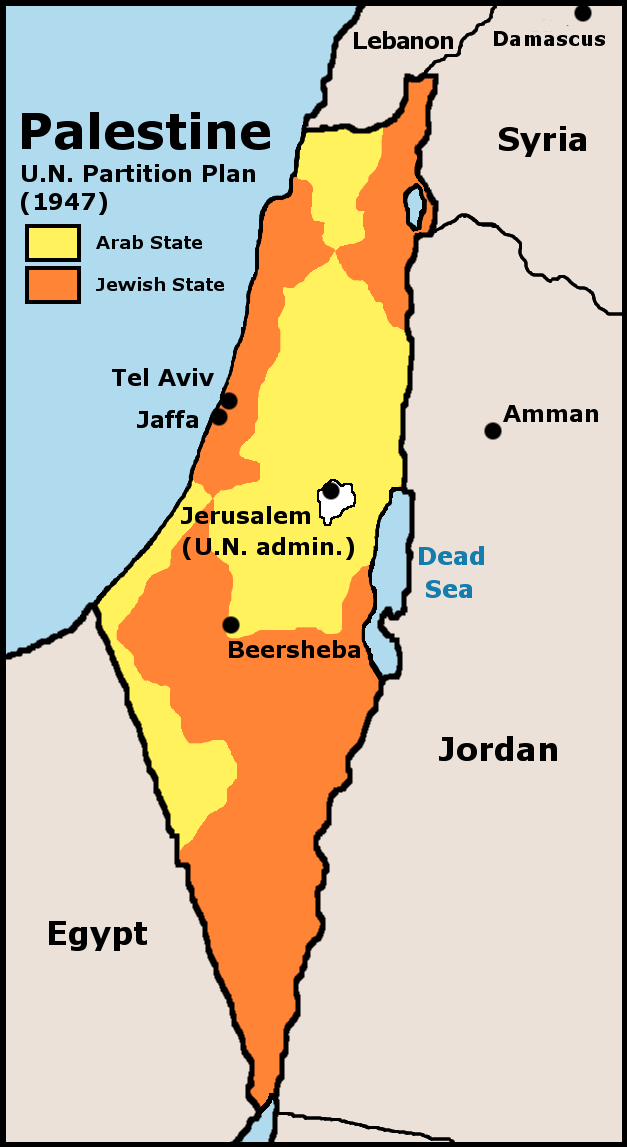
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had been issued earlier that day, and a military coalition of Arab states entered the territory of British Palestine in the morning of 15 May. The day after the 29 November 1947 adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine – which planned to divide Palestine into an Arab state, a Jewish state, and the Special International Regime encompassing the cities of Jerusalem and Bethlehem – an ambush of two buses carrying Jews took place in an incident regarded as the first in the civil war which broke out after the UN decision. The violence had certain continuities with the past, the Fajja bus attack being a direct response to a Lehi massacre on 19 November of five members of an Arab family, suspected of being British infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Declaration Of Independence
The Israeli Declaration of Independence, formally the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel ( he, הכרזה על הקמת מדינת ישראל), was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 ( 5 Iyar 5708) by David Ben-Gurion, the Executive Head of the World Zionist Organization, Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and soon to be first Prime Minister of Israel. It declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel, which would come into effect on termination of the British Mandate at midnight that day. The event is celebrated annually in Israel with a national holiday Independence Day on 5 Iyar of every year according to the Hebrew calendar. Background The possibility of a Jewish homeland in Palestine had been a goal of Zionist organizations since the late 19th century. In 1917 British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour stated in a letter to British Jewish community leader Walter, Lord Rothschild that: His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1947–1948 Civil War In Mandatory Palestine
The 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine was the first phase of the 1947–1949 Palestine war. It broke out after the General Assembly of the United Nations adopted a resolution on 29 November 1947 recommending the adoption of the Partition Plan for Palestine. During the civil war, the Jewish and Arab communities of Palestine clashed (the latter supported by the Arab Liberation Army) while the British, who had the obligation to maintain order, organized their withdrawal and intervened only on an occasional basis. When the British Mandate of Palestine expired on 14 May 1948, and with the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel, the surrounding Arab states—Egypt, Transjordan, Iraq and Syria—invaded what had just ceased to be Mandatory Palestine, Benny Morris (2008), p. 180 and further and immediately attacked Israeli forces and several Jewish settlements. The conflict thus escalated and became the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Background Under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Hoc Committee On The Palestinian Question
The Ad Hoc Committee on the Palestinian Question, also known as the Ad Hoc Committee on Palestine or just the Ad Hoc Committee was a committee formed by a vote of the United Nations General Assembly on 23 September 1947, following the publication of the report of the United Nations Special Committee on Palestine (UNSCOP) on 3 September 1947, which contained majority and minority proposals. The Committee was chaired by H. V. Evatt, who was later to write in his memoirs: "I regard the establishment of Israel as a great victory of the United Nations." The General Assembly vote for the formation of the committee was 29 to 11, with 16 abstaining. The creation of the committee was strongly opposed by Arab states, who wanted the question referred to the UN Political Committee, since according to Lebanon's Charles Malik, an Ad Hoc Committee would be more susceptible to the influence of “certain pressure groups”. Two subcommittees were created on 22 October to assess the UNSCOP major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Creech Jones
Arthur Creech Jones (15 May 1891 – 23 October 1964) was a British trade union official and politician. Originally a civil servant, his imprisonment as a conscientious objector during the First World War forced him to change careers. He was elected to Parliament in 1935 and developed a reputation for interest in colonial matters, gaining the nickname "unofficial member of the Kikuyu at Westminster". He served in the Colonial Office in the Labour government of 1945–1950. After losing his seat in the 1950 general election he was involved in writing and lecturing about British colonies, before returning to Parliament in 1954. Initially, he was known as Arthur Jones, but throughout his time in politics he invariably used his middle name. Early life Creech Jones was the son of a lithographic printer from Bristol. He went to Whitehall Boys' School, and won a scholarship to study French, Mathematics and Commerce for an extra year when he was 13. On leaving school in 1905, he wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |