|
Electronic Band Structure
In solid-state physics, the electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a solid describes the range of energy levels that electrons may have within it, as well as the ranges of energy that they may not have (called ''band gaps'' or ''forbidden bands''). Band theory derives these bands and band gaps by examining the allowed quantum mechanical wave functions for an electron in a large, periodic lattice of atoms or molecules. Band theory has been successfully used to explain many physical properties of solids, such as electrical resistivity and optical absorption, and forms the foundation of the understanding of all solid-state devices (transistors, solar cells, etc.). Why bands and band gaps occur The electrons of a single, isolated atom occupy atomic orbitals each of which has a discrete energy level. When two or more atoms join together to form a molecule, their atomic orbitals overlap and hybridize. Similarly, if a large number ''N'' of identical atoms come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. It also has direct applications, for example in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and Elasticity (physics), elasticity), Heat conduction, thermal, Electrical conduction, electrical, Magnetism, magnetic and Crystal optics, optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric pattern (crystal, crystalline solids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (in electron volts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote a valence electron bound to an atom to become a conduction electron, which is free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as a charge carrier to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric-field Screening
In physics, screening is the damping of electric fields caused by the presence of mobile charge carriers. It is an important part of the behavior of charge-carrying fluids, such as ionized gases (classical plasmas), electrolytes, and charge carriers in electronic conductors (semiconductors, metals). In a fluid, with a given permittivity , composed of electrically charged constituent particles, each pair of particles (with charges and ) interact through the Coulomb force as \mathbf = \frac\hat, where the vector is the relative position between the charges. This interaction complicates the theoretical treatment of the fluid. For example, a naive quantum mechanical calculation of the ground-state energy density yields infinity, which is unreasonable. The difficulty lies in the fact that even though the Coulomb force diminishes with distance as , the average number of particles at each distance is proportional to , assuming the fluid is fairly isotropic. As a result, a charge fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather than inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitance
Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: ''self capacitance'' and ''mutual capacitance''. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operations of the capacitor, a device designed for this purpose as an elementary Linear circuit, linear electronic component. Capacitance is a function only of the geometry of the design of the capacitor, e.g., the opposing surface area of the plates and the distance between them, and the permittivity of the dielectric material between the plates. For many dielectric materials, the permittivity and thus the capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
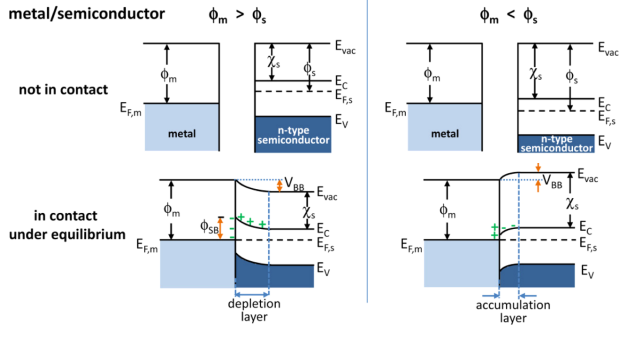
Band Bending
In solid-state physics, band bending refers to the process in which the electronic band structure in a material curves up or down near a junction or interface. It does not involve any physical (spatial) bending. When the electrochemical potential of the free charge carriers around an interface of a semiconductor is dissimilar, charge carriers are transferred between the two materials until an equilibrium state is reached whereby the potential difference vanishes. The band bending concept was first developed in 1938 when Mott, Davidov and Schottky all published theories of the rectifying effect of metal-semiconductor contacts. The use of semiconductor junctions sparked the computer revolution in 1990. Devices such as the diode, the transistor, the photocell and many more still play an important role in technology. Qualitative description Band bending can be induced by several types of contact. In this section metal-semiconductor contact, surface state, applied bias and adsorption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor. Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be ''low'' or ''light''. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as ''high'' or ''heavy''. This is often shown as ''n+'' for n-type doping or ''p+'' for p-type doping. (''See the article on semiconductors for a more detailed description of the doping mechanism.'') A semiconductor doped to such high levels that it acts more like a conductor than a semiconductor is referred to as a degenerate semiconductor. A semiconductor can be considered i-type semiconductor if it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When doped into crystalline substances, the dopant's atoms get incorporated into its crystal lattice. The crystalline materials are frequently either crystals of a semiconductor such as silicon and germanium for use in solid-state electronics, or transparent crystals for use in the production of various laser types; however, in some cases of the latter, noncrystalline substances such as glass can also be doped with impurities. In solid-state electronics using the proper types and amounts of dopants in semiconductors is what produces the p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors that are essential for making transistors and diodes. Transparent crystals Lasing media The procedure of doping tiny amounts of the metals chromium (Cr), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface States
Surface states are electronic states found at the surface of materials. They are formed due to the sharp transition from solid material that ends with a surface and are found only at the atom layers closest to the surface. The termination of a material with a surface leads to a change of the electronic band structure from the bulk material to the vacuum. In the weakened potential at the surface, new electronic states can be formed, so called surface states. Origin at condensed matter interfaces As stated by Bloch's theorem, eigenstates of the single-electron Schrödinger equation with a perfectly periodic potential, a crystal, are Bloch waves : \begin \Psi_ &=\mathrm^u_(\boldsymbol). \end Here u_(\boldsymbol) is a function with the same periodicity as the crystal, ''n'' is the band index and k is the wave number. The allowed wave numbers for a given potential are found by applying the usual Born–von Karman cyclic boundary conditions. The termination of a crystal, i.e. the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectric effect, Eins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Vibration
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical quantization of the modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name ''phonon'' comes from the Greek word (), which translates to ''sound'' or ''voice'', because long-wavelength phonons give rise to sound. The name is analogous to the word ''photon''. Definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2DEG
A two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) is a scientific model in solid-state physics. It is an electron gas that is free to move in two dimensions, but tightly confined in the third. This tight confinement leads to quantized energy levels for motion in the third direction, which can then be ignored for most problems. Thus the electrons appear to be a 2D sheet embedded in a 3D world. The analogous construct of holes is called a two-dimensional hole gas (2DHG), and such systems have many useful and interesting properties. Realizations Most 2DEGs are found in transistor-like structures made from semiconductors. The most commonly encountered 2DEG is the layer of electrons found in MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors). When the transistor is in inversion mode, the electrons underneath the gate oxide are confined to the semiconductor-oxide interface, and thus occupy well defined energy levels. For thin-enough potential wells and temperatures not too high, only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |