|
Early Holocene Sea Level Rise
The early Holocene sea level rise (EHSLR) was a significant jump in Past sea level, sea level by about during the early Holocene, between about 12,000 and 7,000 years ago, spanning the Eurasian Mesolithic. The rapid rise in sea level and associated Climate change (general concept), climate change, notably the 8.2-kiloyear event, 8.2 ka cooling event (8,200 years ago), and the loss of coastal land favoured by early farmers, may have contributed to the spread of the Neolithic Revolution to Europe in Neolithic Europe, its Neolithic period. During deglaciation since the Last Glacial Maximum, between about 20,000 to 7,000 years ago (20–7 ka), the sea level rose by a total of about , at times at extremely high rates, due to the rapid melting of the Irish Sea Glacier, British-Irish Sea, Weichselian glaciation, Fennoscandian, Laurentide Ice Sheet, Laurentide, Barents–Kara Ice Sheet, Barents-Kara, Patagonian Ice Sheet, Patagonian, Wisconsin glaciation, Innuitian and parts of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Glacial Sea Level
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
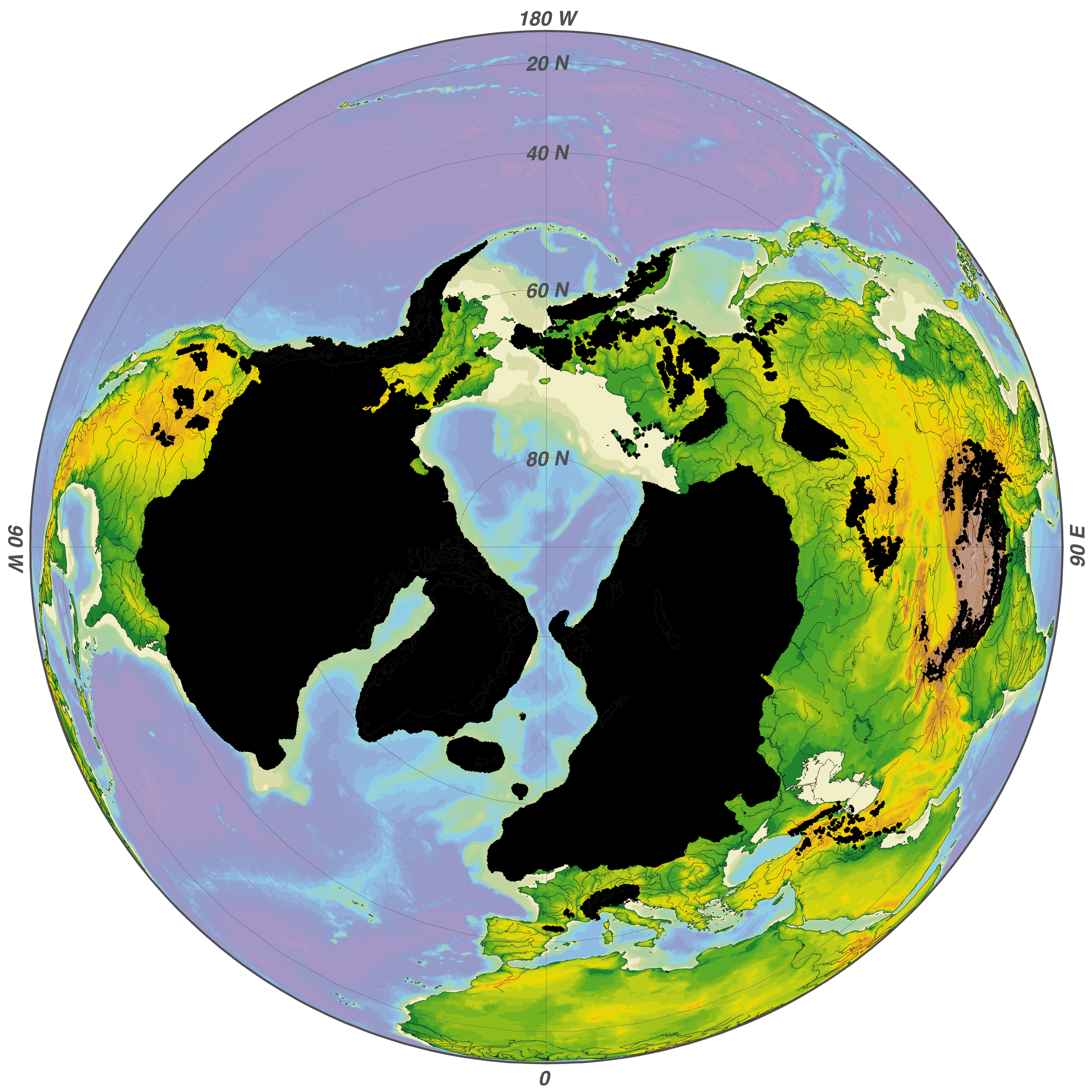
Barents–Kara Ice Sheet
The Barents–Kara Ice Sheet was an ice sheet which existed during the Weichselian Glaciation. It is named after the seas it was centred upon: Barents Sea and Kara Sea. The ice sheet covered the Pechora Sea, the southeastern part of the Barents Sea, Novaya Zemlya and the Kara Sea, likely reaching up to Svalbard and Franz Joseph Land in the north. In the continent, it covered from the North Russian Plain to the North Siberian Lowland. During the periods 90–80 ka and 60–50 ka, the produced ice-damming resulted in the creation of lakes and a significant rerouting of drainage in northern Eurasia, including the major rivers Yenisei, Ob, Pechora and Mezen that now flow northwards.Mangerud, J., V. Astakhov and J.-I. Svendsen ''The extent of the Barents-Kara ice sheet during the Last Glacial Maximum'' Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, v.21 111–119.Polyak, L., V. Gataullin, O. Okuneva and V. Stelle ''New constraints on the limits of the Barents-Kara ice sheet during the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datum A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for precisely representing the position of locations on Earth or other p ...that is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and Navigation, marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to Calibration, calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a Tide, mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meltwater
Meltwater is water released by the melting of snow or ice, including glacial ice, tabular icebergs and ice shelves over oceans. Meltwater is often found in the ablation zone of glaciers, where the rate of snow cover is reducing. Meltwater can be produced during volcanic eruptions, in a similar way in which the more dangerous lahars form. When meltwater pools on the surface rather than flowing, it forms melt ponds. As the weather gets colder meltwater will often re-freeze. Meltwater can collect or melt under the ice's surface. These pools of water, known as subglacial lakes can form due to geothermal heat and friction. Water source Meltwater provides drinking water for a large proportion of the world's population, as well as providing water for irrigation and hydroelectric plants. This meltwater can originate from seasonal snowfall, or from the melting of more permanent glaciers. Climate change threatens the precipitation of snow and the shrinking volume of glaciers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60th Century BC
The 6th millennium BC spanned the years 6000 BC to 5001 BC (c. 8 ka to c. 7 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis. The only exceptions are the felling dates for some construction timbers from neolithic wells in Central Europe. This millennium is reckoned to mark the end of the global deglaciation which had followed the Last Glacial Maximum and caused sea levels to rise by some over a period of about 5,000 years. Communities Neolithic culture and technology had spread from the Near East and into eastern Europe by 6000 BC. Its development in the Far East grew apace and there is increasing evidence through the millennium of its presence in Prehistoric Egypt and the Far East. In much of the world, however, including north and western Europe, people still lived in scattered Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer communities. The worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch (c. 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP) and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and long lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial (c. 14,670 to 12,900 BP). The change was relatively sudden, taking place in decades, and it resulted in a decline of temperatures in Greenland by 4~10 °C (7.2~18 °F), and advances of glaciers and drier conditions over much of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. A number of theories have been put forward about the cause, and the most widely supported by scientists is that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, which transports warm water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meltwater Pulse 1B
Meltwater pulse 1B (MWP1b) is the name used by Quaternary geologists, paleoclimatologists, and oceanographers for a period of either rapid or just accelerated post-glacial sea level rise that some hypothesize to have occurred between 11,500 and 11,200 calendar years ago at the beginning of the Holocene and after the end of the Younger Dryas. Meltwater pulse 1B is also known as catastrophic rise event 2 (CRE2) in the Caribbean Sea. Other named, postglacial meltwater pulses are known most commonly as meltwater pulse 1A0 (meltwater pulse19ka), meltwater pulse 1A, meltwater pulse 1C, meltwater pulse 1D, and meltwater pulse 2. It and these other periods of proposed rapid sea level rise are known as ''meltwater pulses'' because the inferred cause of them was the rapid release of meltwater into the oceans from the collapse of continental ice sheets.Cronin, T.M. (2012) ''Rapid sea-level rise.'' Quaternary Science Reviews. 56:11-30. Sea level There is considerable unresolved disagreem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meltwater Pulse 1A
Meltwater pulse 1A (MWP1a) is the name used by Quaternary geologists, paleoclimatologists, and oceanographers for a period of rapid post-glacial sea level rise, between 13,500 and 14,700 calendar years ago, during which global sea level rose between and in about 400–500 years, giving mean rates of roughly /yr. Meltwater pulse 1A is also known as catastrophic rise event 1 (CRE1) in the Caribbean Sea.Blanchon, P., and J. Shaw (1995) ''Reef drowning during the last deglaciation: Evidence for catastrophic sea-level rise and ice-sheet collapse.'' Geology. 23(1):4-8. The rates of sea level rise associated with meltwater pulse 1A are the highest known rates of post-glacial, eustatic sea level rise. Meltwater pulse 1A is also the most widely recognized and least disputed of the named, postglacial meltwater pulses. Other named, postglacial meltwater pulses are known most commonly as ''meltwater pulse 1A0'' (''meltwater pulse 19ka''), '' meltwater pulse 1B'', '' meltwater pulse 1C'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups. Coral belongs to the class Anthozoa in the animal phylum Cnidaria, which includes sea anemones and jellyfish. Unlike sea anemones, corals secrete hard carbonate exoskeletons that support and protect the coral. Most reefs grow best in warm, shallow, clear, sunny and agitated water. Coral reefs first appeared 485 million years ago, at the dawn of the Early Ordovician, displacing the microbial and sponge reefs of the Cambrian. Sometimes called ''rainforests of the sea'', shallow coral reefs form some of Earth's most diverse ecosystems. They occupy less than 0.1% of the world's ocean area, about half the area of France, yet they provide a home for at least 25% of all marine species, including fish, mollusks, worms, crustaceans, echinode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Ice Sheet
The Antarctic ice sheet is one of the two polar ice caps of Earth. It covers about 98% of the Antarctic continent and is the largest single mass of ice on Earth, with an average thickness of over 2 kilometers. It covers an area of almost and contains of ice. A cubic kilometer of ice weighs approximately 0.92 metric gigatonnes, meaning that the ice sheet weighs ~24,380,000 gigatonnes. It holds approximately 61% of all fresh water on Earth, equivalent to about 58 meters of sea level rise if all the ice were above sea level. In East Antarctica, the ice sheet rests on a major land mass, while in West Antarctica the bed can extend to more than 2,500 m below sea level. Satellite measurements by NASA indicate a still increasing sheet thickness above the continent, outweighing the losses at the edge. The reasons for this are not fully understood, but suggestions include the climatic effects on ocean and atmospheric circulation of the ozone hole, and/or cooler ocean surface t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the ''Late Wisconsin'' in North America. This glaciation radically altered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonian Ice Sheet
upright=1.4, Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the Strait of Magellan area during the last glacial period. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots. Sea level was much lower than shown here. The Patagonian Ice Sheet was a large elongated and narrow ice sheet centered in the southern Andes that existed during the Llanquihue glaciation. The ice sheet covered all of Chile south of Puerto Montt plus the western fringes of Argentine Patagonia. The ice sheet extended beyond the crest of the Andes into Argentina, but because of the dryness of the climate it did not reach beyond present-day lakes such as the Yagagtoo, Musters, and Colhue Huapi. At its peak (about 18,000-17,500 years ago), the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered about 480,000 km² of land with an estimated ice-volume of more than 500,000 km³,Hulton, N.R.J., R.S. Purvesa, R.D. McCullocha, D.E. Sugdena, M.J. Bentleyb. 2002. The Last Glacial Maximum and eglaciation in southern South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)