|
Dummy Pronoun
A dummy pronoun is a deictic pronoun that fulfills a syntactical requirement without providing a contextually explicit meaning of its referent. As such, it is an example of exophora. Dummy pronouns are used in many Germanic languages, including German and English. Pronoun-dropping languages such as Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, and Turkish do not require dummy pronouns. A dummy pronoun is used when a particular verb argument (or preposition) is nonexistent (it could also be unknown, irrelevant, already understood, or otherwise "not to be spoken of directly") but when a reference to the argument (a pronoun) is nevertheless syntactically required. For example, in the phrase "It is obvious that the violence will continue", ''it'' is a dummy pronoun, not referring to any agent. Unlike a regular pronoun of English, it cannot be replaced by any noun phrase. The term ''dummy pronoun'' refers to the function of a word in a particular sentence, not a property of individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
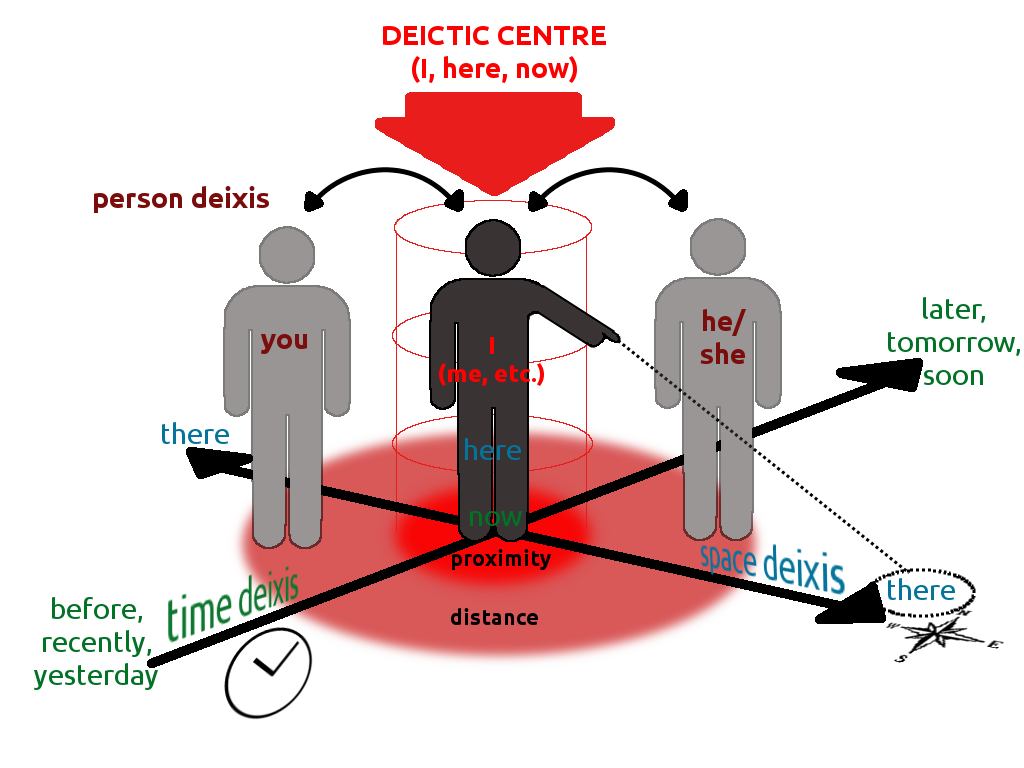
Deixis
In linguistics, deixis (, ) is the use of general words and phrases to refer to a specific time, place, or person in context, e.g., the words ''tomorrow'', ''there'', and ''they''. Words are deictic if their semantic meaning is fixed but their denoted meaning varies depending on time and/or place. Words or phrases that require contextual information to be fully understood—for example, English pronouns—are deictic. Deixis is closely related to anaphora. Although this article deals primarily with deixis in spoken language, the concept is sometimes applied to written language, gestures, and communication media as well. In linguistic anthropology, deixis is treated as a particular subclass of the more general semiotic phenomenon of indexicality, a sign "pointing to" some aspect of its context of occurrence. Although this article draws examples primarily from English, deixis is believed to be a feature (to some degree) of all natural languages.Lyons, John (1977) "Deixis, space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Pronoun
The English personal pronouns are a subset of English pronouns taking various forms according to number, person, case and natural gender. Modern English has very little inflection of nouns or adjectives, to the point where some authors describe it as an analytic language, but the Modern English system of personal pronouns has preserved some of the inflectional complexity of Old English and Middle English. Forms Unlike nouns, which are not inflected for case except for possession (''woman/woman's''), English personal pronouns have a number of forms, which are named according to their typical grammatical role in a sentence: * objective (accusative) case (''me'', ''us'', etc.), used as the object of a verb, complement of a preposition, and the subject of a verb in some constructions (see below). The same forms are also used as disjunctive pronouns. * subjective (nominative) case (''I'', ''we'', etc.), used as the subject of a verb (see also below). * reflexive form (''mys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raising (linguistics)
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the movement of an argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause; in other words, a raising predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument, but is rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. For example, in ''they seem to be trying'', the predicand of ''trying'' is the subject of ''seem''. Although English has raising constructions, not all languages do. The term ''raising'' has its origins in the transformational analysis of such constructions; the constituent in question is seen as being "raised" from its initial deep structure position, as the subject of the embedded predicate, to its surface structure position in the matrix predicate/verb. Raising predicates/verbs are related to control predicates, although there are important differences between the two predicate/verb types. Examples There are at least two types of raising predicates/verbs: rais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwight Bolinger
Dwight Le Merton Bolinger (August 18, 1907 – February 23, 1992) was an American linguist and Professor of Romance Languages and Literatures at Harvard University. He began his career as the first editor of the "Among the New Words" feature for '' American Speech''. As an expert in Spanish, he was elected president of the American Association of Teachers of Spanish and Portuguese in 1960. He was known for the support and encouragement he gave younger scholars and for his hands-on approach to the analysis of human language. His work touched on a wide range of subjects, including semantics, intonation, phonesthesia, and the politics of language. His 1971 book ''The Phrasal Verb in English'', heretofore a subject of concern primarily to teachers of English as a foreign language, brought the need for a scientific treatment of phrasal verbs to the attention of many linguists. His 1977 work ''Meaning and Form'' was instrumental in establishing the principle that a difference i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
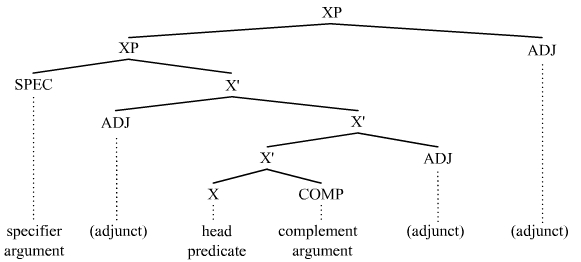
Argument (linguistics)
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the '' complement'' is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a ''predicate-argument structure''. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjunct (grammar)
In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or ''structurally dispensable'', part of a sentence, clause, or phrase that, if removed or discarded, will not structurally affect the remainder of the sentence. Example: In the sentence ''John helped Bill in Central Park'', the phrase ''in Central Park'' is an adjunct.See Lyons (1968). A more detailed definition of the adjunct emphasizes its attribute as a modifying form, word, or phrase that depends on another form, word, or phrase, being an element of clause structure with adverbial function. An adjunct is not an argument (nor is it a predicative expression), and an argument is not an adjunct. The argument–adjunct distinction is central in most theories of syntax and semantics. The terminology used to denote arguments and adjuncts can vary depending on the theory at hand. Some dependency grammars, for instance, employ the term ''circonstant'' (instead of ''adjunct''), following Tesnière (1959). The area of grammar that explores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Verb
In linguistics, an impersonal verb is one that has no determinate subject. For example, in the sentence "''It rains''", ''rain'' is an impersonal verb and the pronoun ''it'' does not refer to anything. In many languages the verb takes a third person singular inflection and often appears with an expletive subject. In the active voice, impersonal verbs can be used to express operation of nature, mental distress, and acts with no reference to the doer. Impersonal verbs are also called weather verbs because they frequently appear in the context of weather description. Also, indefinite pronouns may be called "impersonal", as they refer to an unknown person, like ''one'' or ''someone'', and there is overlap between the use of the two. Valency Impersonal verbs appear only in non-finite forms or with third-person inflection. In the third person, the subject is either implied or a dummy referring to people in general. The term "impersonal" simply means that the verb does not change ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject (grammar)
The subject in a simple English sentence such as ''John runs'', ''John is a teacher'', or ''John drives a car'', is the person or thing about whom the statement is made, in this case ''John''. Traditionally the subject is the word or phrase which controls the verb in the clause, that is to say with which the verb agrees (''John is'' but ''John and Mary are''). If there is no verb, as in ''John what an idiot!'', or if the verb has a different subject, as in ''John I can't stand him!'', then 'John' is not considered to be the grammatical subject, but can be described as the ''topic'' of the sentence. While these definitions apply to simple English sentences, defining the subject is more difficult in more complex sentences and in languages other than English. For example, in the sentence ''It is difficult to learn French'', the subject seems to be the word ''it'', and yet arguably the real subject (the thing that is difficult) is ''to learn French''. A sentence such as ''It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is a Laureate Professor of Linguistics at the University of Arizona and an Institute Professor Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and is the author of more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, politics, and mass media. Ideologically, he aligns with anarcho-syndicalism and libertarian socialism. Born to Ashkenazi Jews, Jewish immigrants in Philadelphia, Chomsky developed an early interest in anarchism from alternative bookstores in New York City. He studied at the University of Pennsylvania. During his postgraduate work in the Harvard Society of Fellows, Chomsky developed the theory of transformat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intransitive Verb
In grammar, an intransitive verb is a verb whose context does not entail a direct object. That lack of transitivity distinguishes intransitive verbs from transitive verbs, which entail one or more objects. Additionally, intransitive verbs are typically considered within a class apart from modal verbs and defective verbs. Examples In the following sentences, verbs are used without a direct object: *"Rivers flow." *"I sneezed." *"My dog ran." *"Water evaporates when it's hot." *"You've grown since I last saw you!" *"I wonder how old I will be when I die." The following sentences contain transitive verbs (they entail one or more objects): *"We watched ''a movie'' last night." *"She's making ''promises''." *"When I said that, my sister smacked ''me''." *"Santa gave ''me'' ''a present''." *"He continuously clicked ''his pen'' and it was incredibly annoying to me." Some verbs, called ambitransitive verbs, may entail objects but do not always require one. Such a verb may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impersonal Verb
In linguistics, an impersonal verb is one that has no determinate subject. For example, in the sentence "''It rains''", ''rain'' is an impersonal verb and the pronoun ''it'' does not refer to anything. In many languages the verb takes a third person singular inflection and often appears with an expletive subject. In the active voice, impersonal verbs can be used to express operation of nature, mental distress, and acts with no reference to the doer. Impersonal verbs are also called weather verbs because they frequently appear in the context of weather description. Also, indefinite pronouns may be called "impersonal", as they refer to an unknown person, like ''one'' or ''someone'', and there is overlap between the use of the two. Valency Impersonal verbs appear only in non-finite forms or with third-person inflection. In the third person, the subject is either implied or a dummy referring to people in general. The term "impersonal" simply means that the verb does not change acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |