|
Distal Radius Fracture
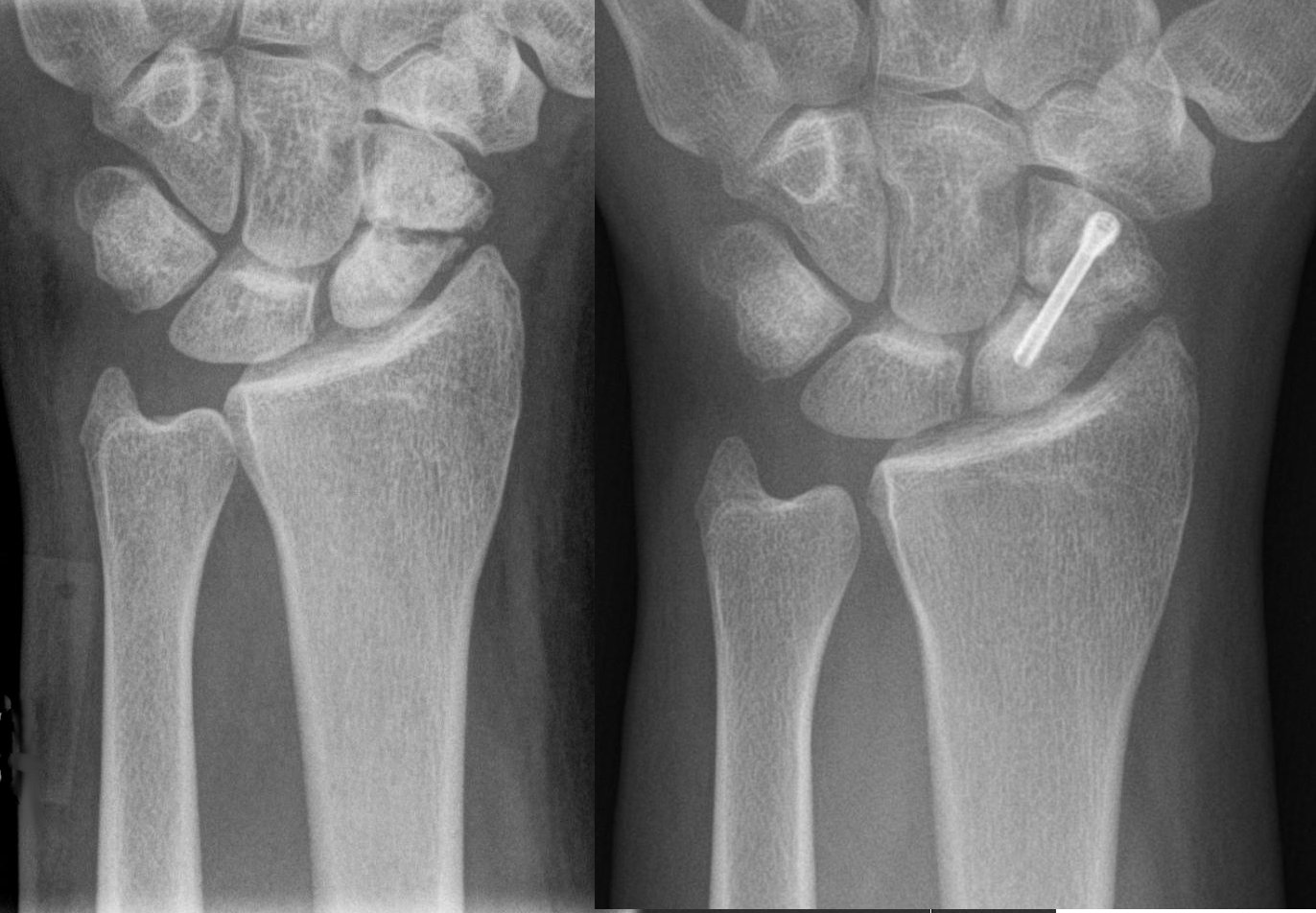
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken. In younger people, these fractures typically occur during sports or a motor vehicle collision. In older people, the most common cause is falling on an outstretched hand. Specific types include Colles, Smith, Barton, and Chauffeur's fractures. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on symptoms and confirmed with X-rays. Treatment is with casting for six weeks or surgery. Surgery is generally indicated if the joint surface is broken and does not line up, the radius is overly short, or the joint surface of the radius is tilted more than 10% backwards. Among those who are cast, repeated X-rays are recommended within three weeks to verify that a good position is maintained. Distal radius fractures are common, and are the most common type of fractures that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colles Fracture
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve. It typically occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand. Risk factors include osteoporosis. The diagnosis may be confirmed via X-rays. The tip of the ulna may also be broken. Treatment may include casting or surgery. Surgical reduction and casting is possible in the majority of cases in people over the age of 50. Pain management can be achieved during the reduction with procedural sedation and analgesia or a hematoma block. A year or two may be required for healing to occur. About 15% of people have a Colles' fracture at some point in their life. They occur more commonly in young adults and older people than in children and middle-aged adults. Women are more frequently affected than men. The fracture is named after Abraham Colles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
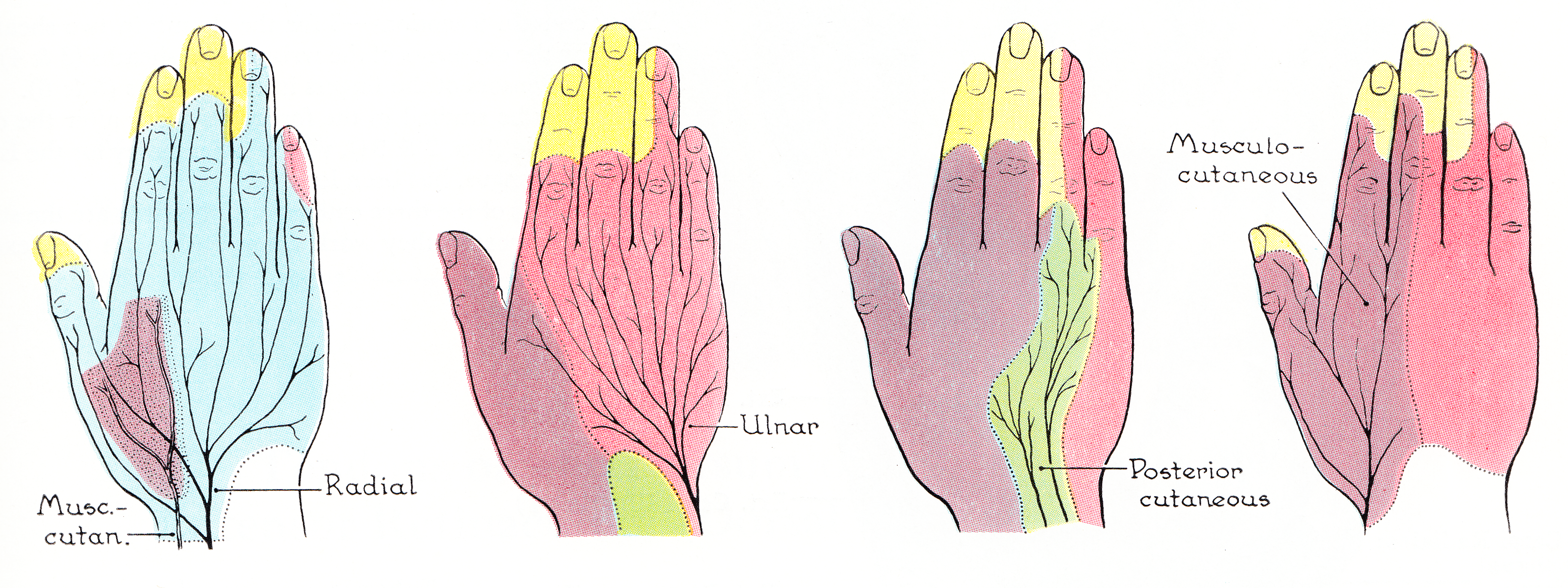
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C5-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brachial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle. Structure The extensor pollicis longus arises from the dorsal surface of the ulna and from the interosseous membrane, next to the origins of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis. Passing through the third tendon compartment, lying in a narrow, oblique groove on the back of the lower end of the radius,''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox it crosses the wrist close to the dorsal midline before turning towards the thumb using Lister's tubercle on the distal end of the radius as a pulley. It obliquely crosses the tendons of the extensores carpi radialis longus and brevis, and is separated from the extensor pollicis brevis by a triangular interval, the anatomical snuff box in which the radial artery is found. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Styloid Process
The styloid process of the ulna is a bony prominence found at distal end of the ulna in the forearm. Structure The styloid process of the ulna projects from the medial and back part of the ulna. It descends a little lower than the head. The head is separated from the styloid process by a depression for the attachment of the apex of the triangular articular disk, and behind, by a shallow groove for the tendon of the extensor carpi ulnaris muscle. The styloid process of the ulnar varies in length between 2 mm and 6 mm. Function The rounded end of the styloid process of the ulna connects to the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist. The radioulnar ligaments also attaches to the base of the styloid process of the ulna. Clinical significance Fractures of the styloid process of the ulna seldom require treatment when they occur in association with a distal radius fracture. The major exception is when the joint between these bones, the distal radioulnar joint (or DRUJ), is unst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time. Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs; the knee and hip joints; and the joints of the neck and lower back. Joints on one side of the body are often more affected than those on the other. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malunion
A malunion is when a fractured bone does not heal properly. Some ways that it shows is by having the bone being twisted, shorter, or bent. Malunions can occur by having the bones improperly aligned when immobilized, having the cast taken off too early, or never seeking medical treatment after the break. Malunions are painful and commonly produce swelling around the area, possible immobilization, and deterioration of the bone and tissue. Signs and symptoms Malunions are presented by excessive swelling, twisting, bending, and possibly shortening of the bone. Patients may have trouble placing weight on or near the malunion. Diagnosis An X-ray is essential for the proper diagnosis of a malunion. The doctor will look into the patient’s history and the treatment process for the bone fracture. Oftentimes a CT scan and probably an MRI are also used in diagnosis. MRI are used to check of cartilage and ligament issues that developed due to the malunion and misalignment. CT scans ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonunion
Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention (such as surgery) is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false joint" or pseudoarthrosis (from Greek ''pseudo-'', meaning false, and , meaning joint). The diagnosis is generally made when there is no healing between two sets of medical imaging, such as X-ray or CT scan. This is generally after 6–8 months.Page 542 in: Nonunion is a serious complication of a fracture and may occur when the fracture moves too much, has a poor supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the leg or arm are most commonly involved. Symptoms of acute compartment syndrome (ACS) can include severe pain, poor pulses, decreased ability to move, numbness, or a pale color of the affected limb. It is most commonly due to physical trauma such as a bone fracture (up to 75% of cases) or crush injury, but it can also be caused by acute exertion during sport. It can also occur after blood flow returns following a period of poor blood flow. Diagnosis is generally based upon a person's symptoms and may be supported by measurement of intracompartmental pressure before, during, and after activity. Normal compartment pressure should be within 12-18 mmHg; anything greater than that is considered abnormal and would need treatment. Treatment i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
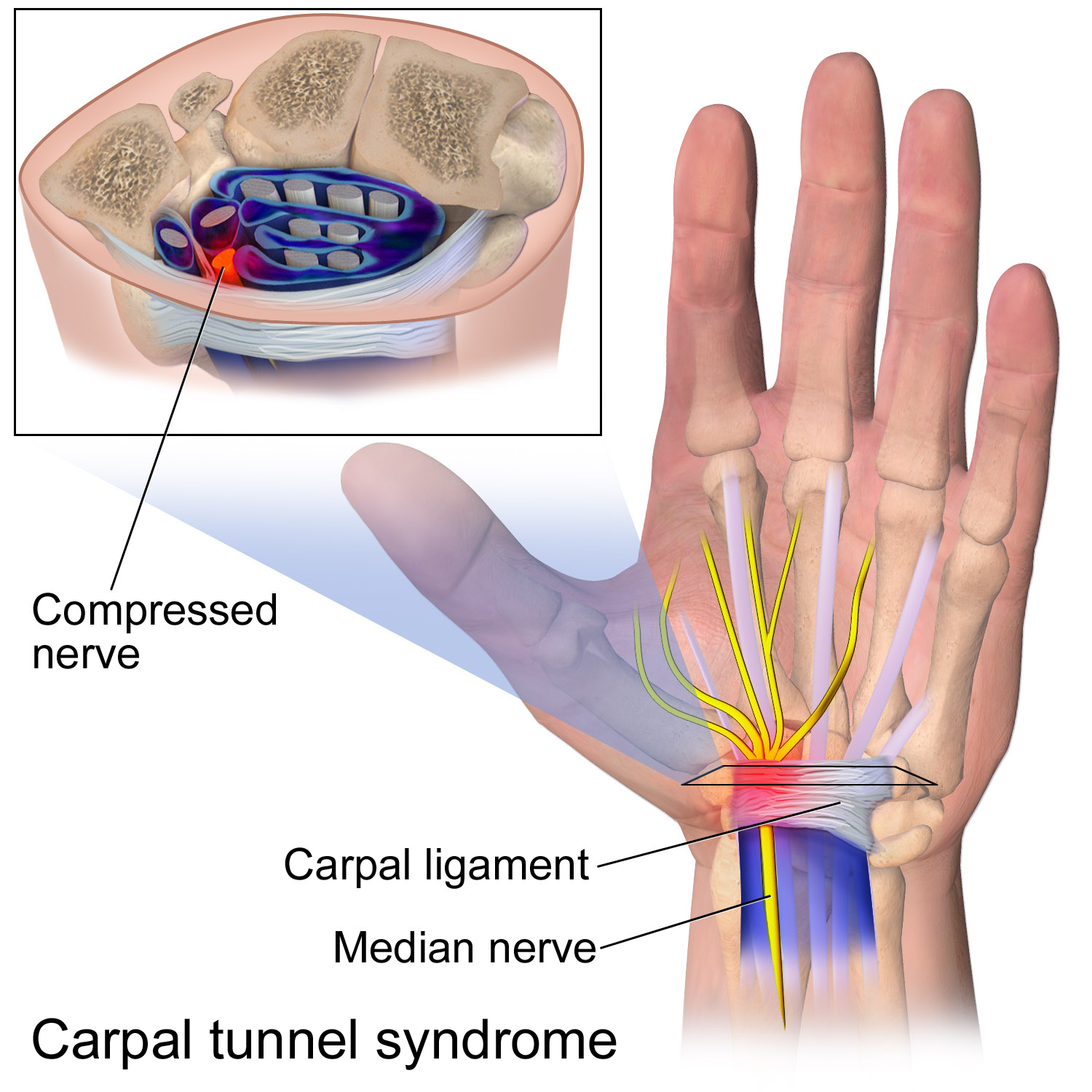
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT). Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics. Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial lining of the tendons causes compression. The main symptoms are numbness and tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger and the thumb side of the ring finger. People often report pain, but pain without tingling is not characteristic of IMNCT. Rather, the numbness can be so intense that it is described as painful. Symptoms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Fracture
An open fracture, also called a compound fracture, is a type of bone fracture in orthopedics that is frequently caused by high energy trauma. It is a bone fracture, also known as a broken bone, associated with a break in the skin continuity which can cause complications such as infection, malunion, and nonunion. Gustilo open fracture classification is the most commonly used method to classify open fractures, to guide treatment and to predict clinical outcomes. Advanced trauma life support is the first line of action in dealing with open fractures and to rule out other life-threatening condition in cases of trauma. Cephalosporins are generally the first line of antibiotics. The antibiotics are continued for 24 hours to minimize the risk of infections. Therapeutic irrigation, wound debridement, early wound closure and bone fixation are the main management of open fractures. All these actions aimed to reduce the risk of infections. Classification There are a number of classificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
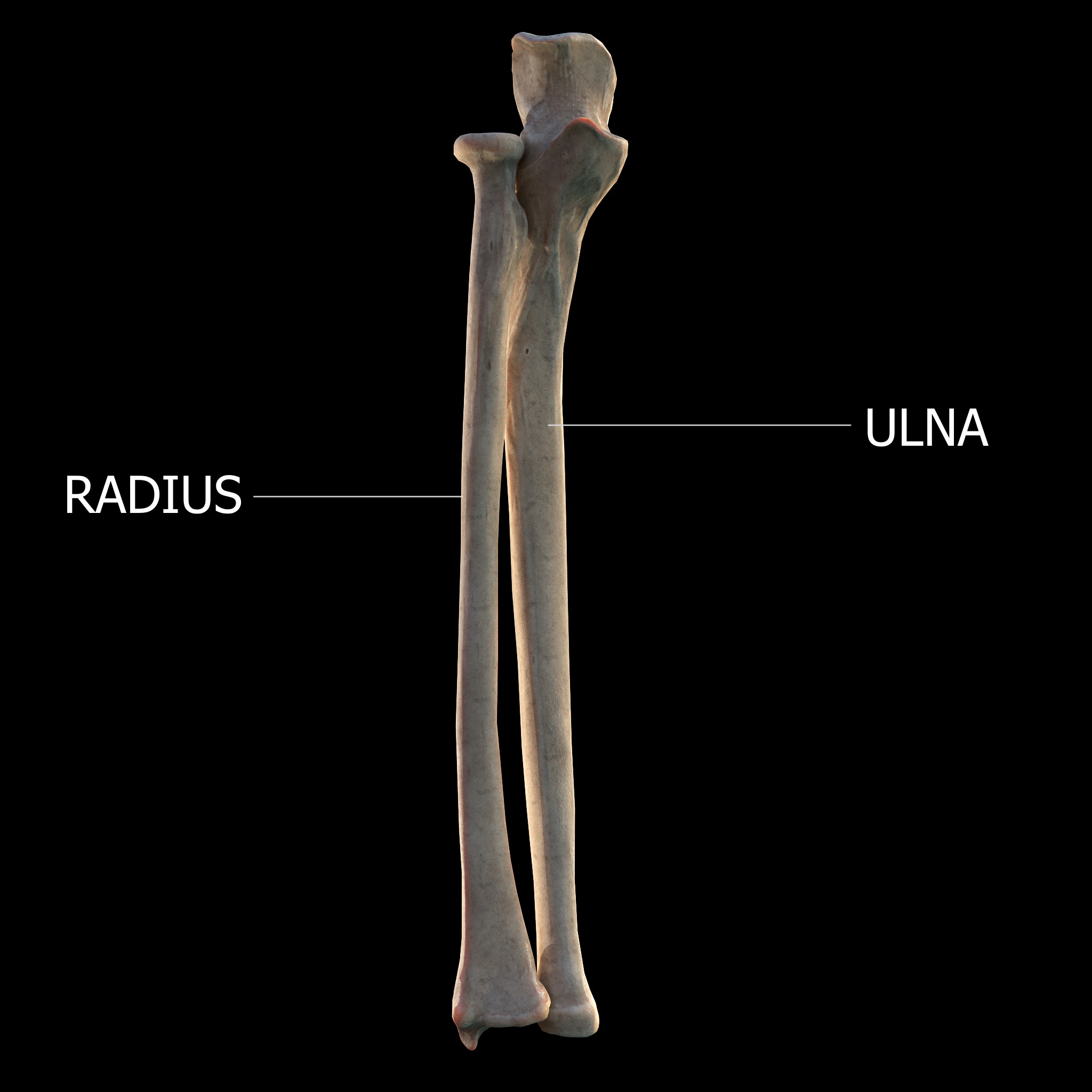
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |