|
Dialysis Tubing
Dialysis tubing, also known as ''Visking tubing'', is an artificial semi-permeable membrane tubing90% of a protein having a molecular mass of at least 10 kDa. Pore sizes typically range from ~10–100 Angstroms for 1K to 50K MWCO membranes. It is important to note that the MWCO of a membrane is not a sharply defined value. Molecules with mass near the MWCO of the membrane will diffuse across the membrane slower than molecules significantly smaller than the MWCO. In order for a molecule to rapidly diffuse across a membrane, it typically needs to be at least 20–50 times smaller than the membranes MWCO rating. Therefore, it is not practical to try separating a 30kDa protein from a 10kDa protein using dialysis across a 20K rated dialysis membrane. Dialysis tubing for laboratory use is typically made of a film of regenerated cellulose or cellulose ester. However; dialysis membranes made of polysulfone, polyethersulfone (PES), etched polycarbonate, or collagen are also extensively use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
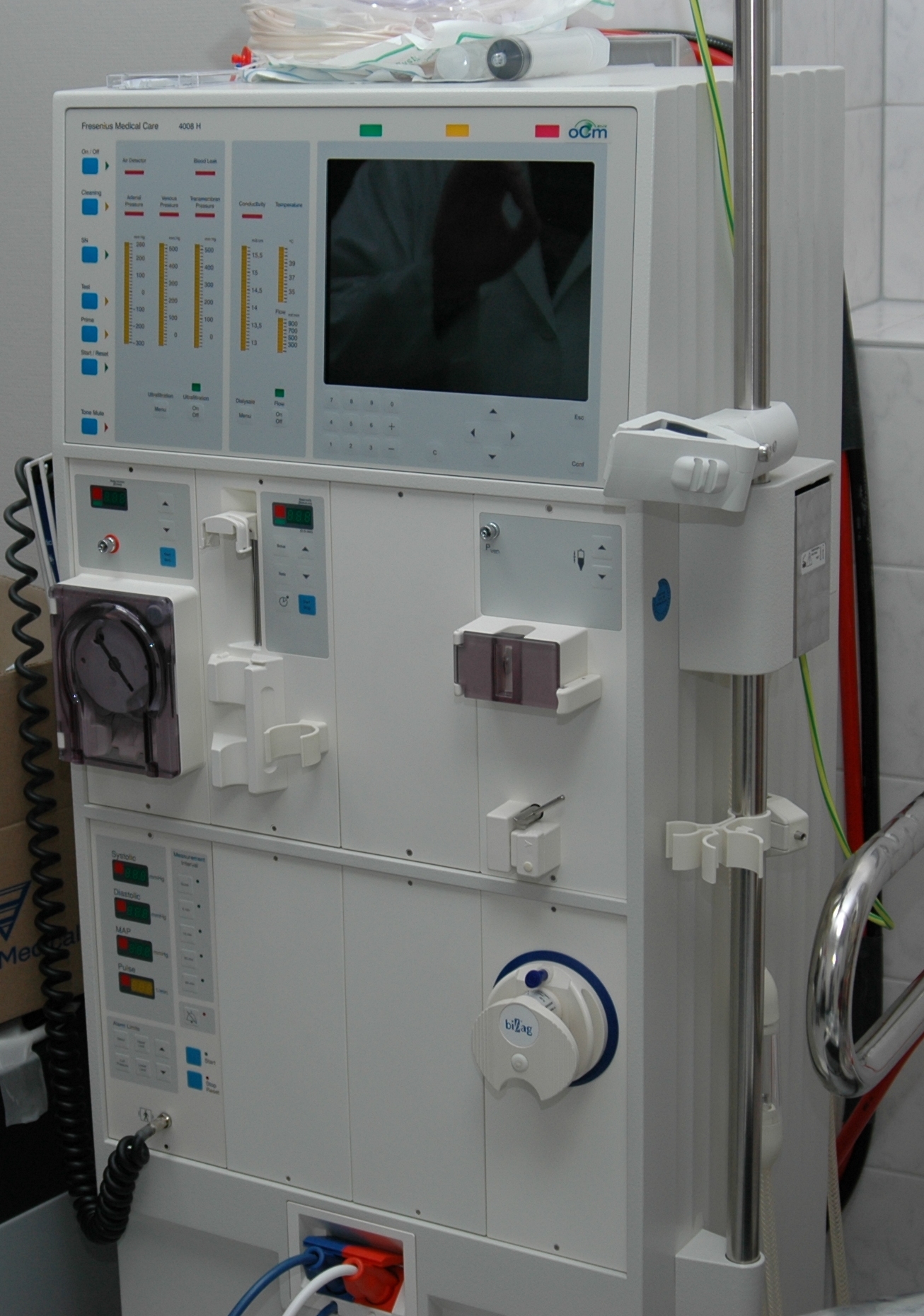
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated with nitrocellulose lacquer to prevent this. Cellophane is also used in transparent pressure-sensitive tape, tubing and many other similar applications. Cellophane is compostable and biodegradable, and can be obtained from biomaterials. Production, however, uses carbon disulfide (CS2), which has been found to be highly toxic to workers. The lyocell process, however, can be used to produce cellulose film without involving carbon disulfide. "Cellophane" is a generic term in some countries, while in other countries it is a registered trademark. Production Cellulose from wood, cotton, hemp, or other sources is dissolved in alkali and carbon disulfide to make a solution called viscose, which is then extruded through a slit into a bath of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filters
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming * Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream * Filter (video), a software component that performs some operation on a multimedia stream * Email filtering, the processing of email to organize it according to specified criteria * Content-control software also known as an Internet filter * Wordfilter, a script typically used on Internet forums or chat rooms * Berkeley Packet Filter, filter expression used in the qualification of network data * DSL filter, a low-pass filter installed between analog devices and a telephone line * Helicon Filter, a raster graphics editor * Filter (large eddy simulation), a mathematical operation intended to remove a range of small scales from the solution to the Navier-Stokes equations * Kalman filter, an approximating algorithm in optimal control applications and problems Device * Filter (ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, like in spinodal decomposition. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics ( particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, and price values). The central idea of diffusion, however, is common to all of these: a substance or collection undergoing diffusion spreads out from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection. A gradient is the change in the value of a quantity, for example, concentration, pressure, or temperature with the change in another variable, usually distance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pore Structure
Pore structure is a common term employed to characterize the porosity, pore size, pore size distribution, and pore morphology (such as pore shape, surface roughness, and tortuosity of pore channels) of a porous medium. Pores are the openings in the surfaces impermeable porous matrix which gases, liquids, or even foreign microscopic particles can inhabit them. The pore structure and fluid flow in porous media are intimately related. With micronanoscale pore radii, complex connectivity, and significant heterogeneity, the complexity of the pore structure affects the hydraulic conductivity and retention capacity of these fluids. The intrinsic permeability is the attribute primarily influenced by the pore structure, and the fundamental physical factors governing fluid flow and distribution are the grain surface-to-volume ratio and grain shape. The idea that the pore space is made up of a network of channels through which fluid can flow is particularly helpful. Pore openings are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humectant
A humectant is a hygroscopic (water-absorbing) substance used to keep things moist. They are used in many products, including food, cosmetics, medicines and pesticides. When used as a food additive, a humectant has the effect of keeping moisture in the food. Humectants are sometimes used as a component of antistatic coatings for plastics. A humectant attracts and retains the moisture in the air nearby via absorption, drawing the water vapor into or beneath the organism's or object's surface. This is the opposite use of a hygroscopic material where it is used as a desiccant used to draw moisture away. In pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, humectants can be used in topical dosage forms to increase the solubility of a chemical compound's active ingredients, increasing the active ingredients' ability to penetrate skin, or its activity time. This hydrating property can also be needed to counteract a dehydrating active ingredient (e.g., soaps, corticoids, and some alcohols), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulfone
Polysulfones are a family of high performance thermoplastics. These polymers are known for their toughness and stability at high temperatures. Technically used polysulfones contain an aryl- SO2-aryl subunit. Due to the high cost of raw materials and processing, polysulfones are used in specialty applications and often are a superior replacement for polycarbonates. Three polysulfones are used industrially: polysulfone (PSU), polyethersulfone (PES/PESU) and polyphenylene sulfone (PPSU). They can be used in the temperature range from -100 to +200 °C and are used for electrical equipment, in vehicle construction and medical technology. They are composed of para-linked aromatics, sulfonyl groups and ether groups and partly also alkyl groups. Polysulfones have outstanding resistance to heat and oxidation, hydrolysis resistance to aqueous and alkaline media and good electrical properties. Nomenclature The term "polysulfone" is normally used for polyarylethersulfones (PAES ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under development as a renewable fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Some animals, particularly ruminants and termites, can digest cellulose wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Weight Cut-off
Molecular weight cut-off or MWCO refers to the lowest molecular weight solute (in daltons) in which 90% of the solute is retained by the membrane, or the molecular weight of the molecule (e.g. globular protein) that is 90% retained by the membrane. This definition is not however standardized, and MWCOs can also be defined as the molecular weight at which 80% of the analytes (or solutes) are prohibited from membrane diffusion. Commercially available microdialysis probes typically have molecular weight cutoffs that range from 1,000 to 300,000 Da, and larger thresholds of filtration are measured in µm. Microdialysis may also be used to separate nanoparticle A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 10 ...s from the solutions in which they were formed. In such a separation, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, high blood potassium, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney disease. Diagnosis of acute f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Kolff
Willem Johan "Pim" Kolff (February 14, 1911 – February 11, 2009) was a pioneer of hemodialysis, artificial heart, as well as in the entire field of artificial organs. Willem was a member of the Kolff family, an old Dutch patrician family. He made his major discoveries in the field of dialysis for kidney failure during the Second World War. He emigrated in 1950 to the United States, where he obtained US citizenship in 1955, and received a number of awards and widespread recognition for his work. Netherlands Born in Leiden, Netherlands, Kolff was the eldest of a family of 5 boys. Kolff studied medicine in his hometown at Leiden University, and continued as a resident in internal medicine at Groningen University. One of his first patients was a 22-year-old man who was slowly dying of chronic kidney failure. This prompted Kolff to perform research on artificial renal function replacement. Also during his residency, Kolff organized the first blood bank in Europe (in 1940) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Graham (chemist)
Thomas Graham (21 December 1805 – 16 September 1869) was a British chemist known for his pioneering work in dialysis and the diffusion of gases. He is regarded as one of the founders of colloid chemistry. Life Graham was born in Glasgow, and educated at the High School of Glasgow. Graham's father was a successful textile manufacturer, and wanted his son to enter into the Church of Scotland. Instead, defying his father's wishes, Graham became a student at the University of Glasgow in 1819. There he developed a strong interest in chemistry, studying under Professor Thomas Thomson, who was impressed and influenced by the young man. He left the University after receiving his MA in 1824. He later studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and then briefly taught chemistry at the Glasgow University Portland Street Medical School. In 1828 he was elected an Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, his proposer was Edward Turner. He won the Society's Keith Medal for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |