|
Dental Insurance
Dental insurance is a form of health insurance designed to pay a portion of the costs associated with dental care. There are several different types of individual, family, or group dental insurance plans grouped into three primary categories: Indemnity, Preferred Provider Network (PPO), and Dental Health Managed Organizations (DHMO). Generally dental offices have a fee schedule, or a list of prices for the dental services or procedures they offer. Dental insurance companies have similar fee schedules which is generally based on Usual and Customary dental services, an average of fees in an area. The fee schedule is commonly used as the transactional instrument between the insurance company, dental office and/or dentist, and the consumer. Types of coverage Indemnity Dental Insurance Plan With indemnity dental plans, the insurance company generally pays the dentist a percentage of the cost of services. Restrictions may include the co-payment requirements, waiting period, stated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity. According to the Health Insurance Association of America, health insurance is defined as "coverage that provides for the payments of benefits as a result of sickness or injury. It includes insurance for losses from accident, medical expense, disability, or accidental death and dismemberment". Background A health i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endodontics
Endodontics (from the Greek roots ''endo-'' "inside" and ''odont-'' "tooth") is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp. Overview Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical sciences of normal dental pulp, the etiology, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and injuries of the dental pulp along with associated periradicular conditions. In clinical terms, endodontics involves either preserving part, or all of the dental pulp in health, or removing all of the pulp in irreversible disease. This includes teeth with irreversibly inflamed and infected pulpal tissue. Not only does endodontics involve treatment when a dental pulp is present, but also includes preserving teeth which have failed to respond to non-surgical endodontic treatment, or for teeth that have developed new lesions, e.g., when root canal re-treatment is required, or periradicular surgery. Endodontic treatment is one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NHS Dentistry
Dentistry provided by the National Health Service in the United Kingdom is supposed to ensure that dental treatment is available to the whole population. Most dentistry is provided by private practitioners, most of whom also provide, on a commercial basis, services which the NHS does not provide, largely cosmetic. Most adult patients have to pay some NHS charges, although these are often significantly cheaper than the cost of private dentistry. The majority of people choose NHS dental care rather than private care: as of 2005, the national average proportion of people opting for private care was 23%. NHS dentistry is not always available and is not managed in the way that other NHS services are managed. Scope of the service According to NHS Choices "All the treatment that your dentist believes is necessary to achieve and maintain good oral health is available on the NHS. This means that the NHS provides any treatment you need to keep your mouth, teeth and gums healthy and free of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
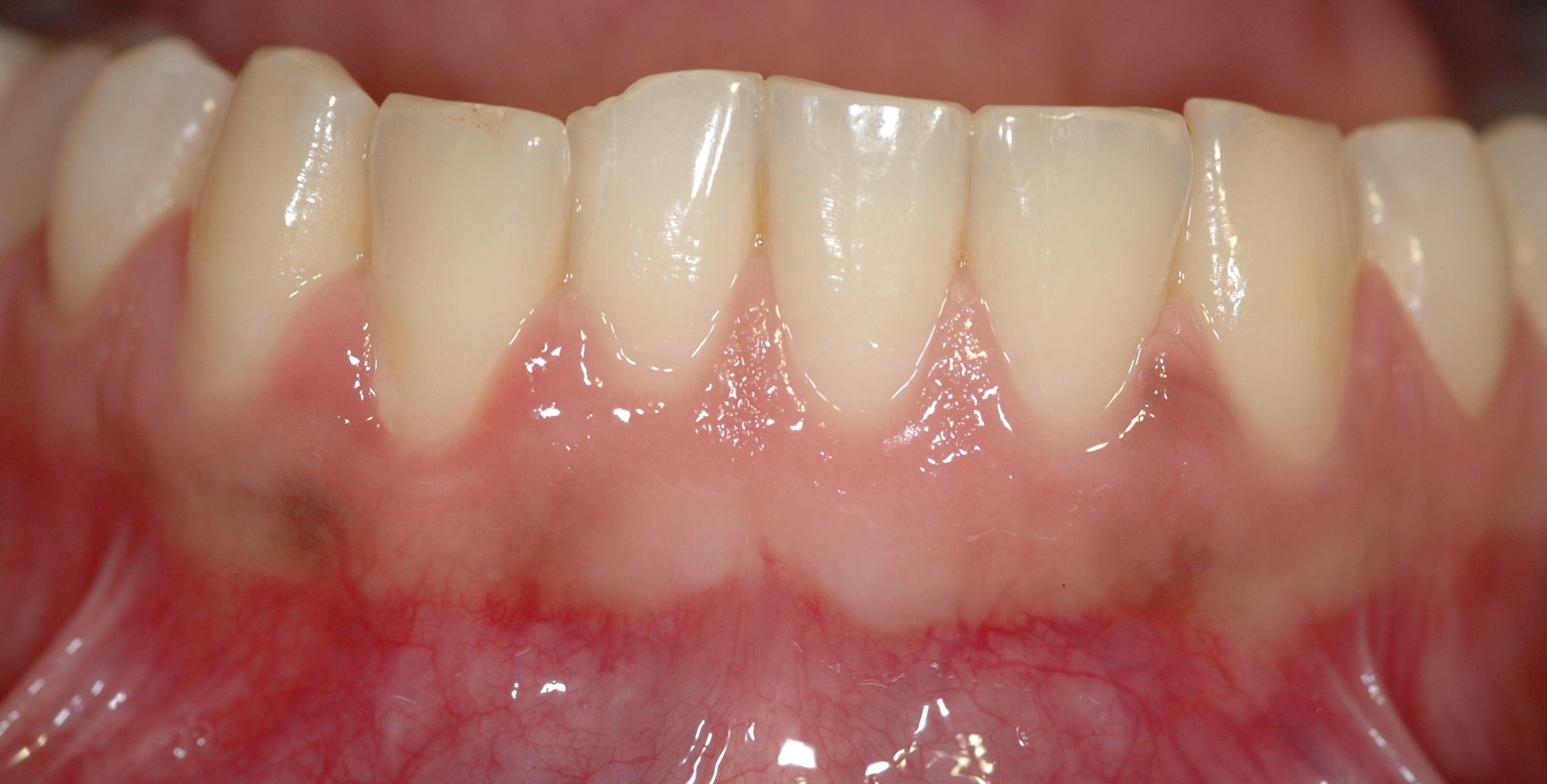
Periodontics
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone are known as the gingivae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Implant
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown. Success or failure of implants depends on the health of the person receiving the treatment, drugs which affect the chances of osseointegration, and the health of the tissues in the mouth. The amount of stress that will be put on the impla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, and are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants (fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they are used to replace missing teeth on the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch. Medical uses Dentures do not feel like real teeth, nor do they function like real teeth. Dentures can help people through: * Mastication or chewing ability is improved by replacing edentulous areas with denture teeth. * Aesthetics, because the presence of teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (dentistry)
In dentistry, a crown most commonly refers to a dental cap, a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large cavity threatens the health of a tooth. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using ''indirect methods''. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly. The most common method of crowning a tooth involves taking a dental impression of a tooth prepared by a dentist, then fabricating the crown outside of the mouth. The crown can then be inserted at a subsequent dental appointment. This ''indirect method'' of tooth restoration allows use of strong restorative material requiring time-consuming fabrication under intense heat, such as casting metal or firing porcelain, that would not be possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontology
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants. The periodontium The term ''periodontium'' is used to describe the group of structures that directly surround, support and protect the teeth. The periodontium is composed largely of the gingival tissue and the supporting bone. Gingivae Normal gingiva may range in color from light coral pink to heavily pigmented. The soft tissues and connective fibres that cover and protect the underlying cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone are known as the ging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which have gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and diseases) for which reas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Restoration
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—''direct'' and ''indirect''—and are further classified by location and size. A root canal filling, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides. Tooth preparation Restoring a tooth to good form and function requires two steps: # preparing the tooth for placement of restorative material or materials, and # placement of these materials. The process of preparation usually involves cutting the tooth with a rotary dental handpiece and dental burrs, a dental laser, or though air abrasion to make space for the planned restorative materials and to remove any dental decay or portions of the tooth that are structurally unsound. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |