|
Delta-viniferin
δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine (''Vitis vinifera'') leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in ''Rheum maximowiczii''. It is a grapevine phytoalexin following stresses like fungal infection (by ''Plasmopara viticola'', the agent of downy mildew), UV light irradiation or ozone treatment. ''Botryosphaeria obtusa'', a pathogen responsible for the black dead arm disease of grapevine, has also been shown to be able to oxidise wood δ-resveratrol into delta-viniferin. In cell cultures, the use of methyl jasmonate and jasmonic acid as elicitors stimulates δ-viniferin biosynthesis. Delta-viniferin can also be produced from resveratrol by human PTGS1 (COX-1, cyclooxygenase-1) or from ''trans''-resveratrol and (−)- epsilon-viniferin by horseradish peroxidase. See also * Phenolic content in wine The phenolic content in wine refers to the pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenolic Content In Wine
The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids. Origin of the phenolic compounds The natural phenols are not evenly distributed within the fruit. Phenolic acids are largely present in the pulp, anthocyanins and stilbenoids in the skin, and other phenols (catechins, proanthocyanidins and flavonols) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer (chemistry)
A dimer () ('' di-'', "two" + ''-mer'', "parts") is an oligomer consisting of two monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak, covalent or intermolecular. Dimers also have significant implications in polymer chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and biochemistry. The term ''homodimer'' is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A) and ''heterodimer'' when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerization is often called dissociation. When two oppositely charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as ''Bjerrum pairs'', after Niels Bjerrum. Noncovalent dimers Anhydrous carboxylic acids form dimers by hydrogen bonding of the acidic hydrogen and the carbonyl oxygen. For example, acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. Excimers and exciplexes are excited structures with a short lifetime. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resveratrol
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-''trans''-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts. Although commonly used as a dietary supplement and studied in laboratory models of human diseases, there is no high-quality evidence that resveratrol improves lifespan or has a substantial effect on any human disease. Research Resveratrol has been studied for its potential therapeutic use, with little evidence of anti-disease effects or health benefits in humans. Cardiovascular disease There is no evidence of benefit from resveratrol in people who already have heart disease. A 2018 meta-analysis found no effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure; a sub-analysis revealed a 2 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure only from res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoalexins
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized ''de novo'' by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection. Function Phytoalexins are produced in plants to act as toxins to the attacking organism. They may puncture the cell wall, delay maturation, disrupt metabolism or prevent reproduction of the pathogen in question. Their importance in plant defense is indicated by an increase in susceptibility of plant tissue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stilbenoid Dimers
Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene. They have a C6–C2–C6 structure. In biochemical terms, they belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with Chalconoid, chalcones. Most stilbenoids are produced by plants, and the only known exception is the antihelminthic and antimicrobial stilbenoid, 2-isopropyl-5-[(''E'')-2-phenylvinyl]benzene-1,3-diol, biosynthesized by the Gram-negative bacterium ''Photorhabdus luminescens.'' Chemistry Stilbenoids are hydroxylated derivatives of stilbene and have a C6–C2–C6 structure. They belong to the family of phenylpropanoids and share most of their biosynthesis pathway with Chalconoid, chalcones. Under UV irradiation, stilbene and its derivatives undergo intramolecular cyclization, called stilbene photocyclization to form dihydrophenanthrenes. Oligomeric forms are known as oligostilbenoids. Types ;Aglycones * Piceatannol in the roots of Norway spruces * Pinosylvin is a fungal toxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resveratrol Oligomers
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-''trans''-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts. Although commonly used as a dietary supplement and studied in laboratory models of human diseases, there is no high-quality evidence that resveratrol improves lifespan or has a substantial effect on any human disease. Research Resveratrol has been studied for its potential therapeutic use, with little evidence of anti-disease effects or health benefits in humans. Cardiovascular disease There is no evidence of benefit from resveratrol in people who already have heart disease. A 2018 meta-analysis found no effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure; a sub-analysis revealed a 2 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure only from r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R2-Viniferin
Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer (chemistry), tetramer found in plants of the genus ''Vitis''. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B. It shows an opposite effect to hopeaphenol on apoptosis of myocytes isolated from adult rat heart. References External links Website of the Schröder group Resveratrol oligomers Natural phenol tetramers Grape {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-Viniferin
Vitisin B is a resveratrol tetramer found in plants of the genus ''Vitis ''Vitis'' (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, b ...''.Opposite Effects of Two Resveratrol (trans-3,5,4′-Trihydroxystilbene) Tetramers, Vitisin A and Hopeaphenol, on Apoptosis of Myocytes Isolated from Adult Rat Heart. Kazuhiko Seya, Kouta Kanemaru, Chiharu Sugimoto, Megumi Suzuki, Teruko Takeo, Shigeru Motomura, Haruo Kitahara, Masatake Niwa, Yoshiteru Oshima and Ken-Ichi Furukawa, JPET January 2009 vol. 328 no. 1 90-98, References External links Vitisin B on www.chemindustry.com Resveratrol oligomers Natural phenol tetramers Grape varieties {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-Viniferin
α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from ''Caragana chamlagu'' and from '' Caragana sinica'' and from the stem bark of ''Dryobalanops aromatica''. It is also present in relation to resistance to ''Botrytis cinerea'' and ''Plasmopara viticola'' in ''Vitis vinifera'' and ''Vitis riparia''.Disease resistance of Vitis spp. and the production of the stress metabolites resveratrol, epsilon -viniferin, alpha -viniferin and pterostilbene. Langcake P, Physiological Plant Pathology, 1981, Vol. 18, No. 2, pages 213-226abstract) It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that a .... References Resveratrol oligomers Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viniferin , a synonym for the stilbenoid vitisin A
{{Chemistry index ...
Viniferin may refer to: * ''alpha''-Viniferin, a resveratrol trimer * ''beta''-Viniferin, a resveratrol cyclic tetramer * ''delta''-Viniferin, a resveratrol dehydrodimer * ''epsilon''-Viniferin, a resveratrol dimer * ''gamma''-Viniferin, a more highly polymerised oligomer of resveratrol * R-Viniferin, a synonym for the stilbenoid vitisin B * R2-Viniferin Vitisin A is a resveratrol tetramer (chemistry), tetramer found in plants of the genus ''Vitis''. It is a complex of two resveratrol dimers, (+)-epsilon-viniferin and ampelopsin B. It shows an opposite effect to hopeaphenol on apoptosis of myocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
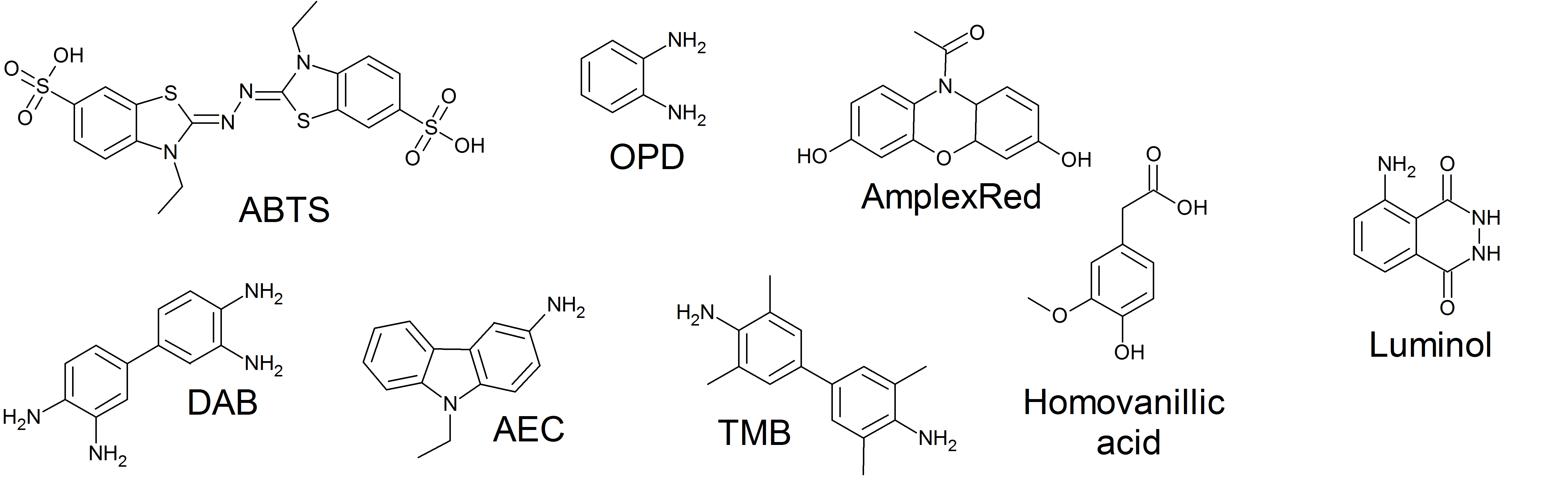
Horseradish Peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various organic substrates by hydrogen peroxide. Structure The structure of the enzyme was first solved by X-ray crystallography in 1997; and has since been solved several times with various substrates. It is a large alpha-helical glycoprotein which binds heme as a redox cofactor. Substrates Alone, the HRP enzyme, or conjugates thereof, is of little value; its presence must be made visible using a substrate that, when oxidized by HRP using hydrogen peroxide as the oxidizing agent, yields a characteristic color change that is detectable by spectrophotometric methods. Numerous substrates for horseradish peroxidase have been described and commercialized to exploit the desirable features of HRP. These substrates fall into several distinct cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |