|
Degree-day
A degree day is a measure of heating or cooling. Total degree days from an appropriate starting date are used to plan the planting of crops and management of pests and pest control timing. Weekly or monthly degree-day figures may also be used within an energy monitoring and targeting scheme to monitor the heating and cooling costs of climate controlled buildings, while annual figures can be used for estimating future costs. A degree day is computed as the integral of a function of time that generally varies with temperature. The function is truncated to upper and lower limits that vary by organism, or to limits that are appropriate for climate control. The function can be estimated or measured by one of the following methods, in each case by reference to a chosen base temperature: * Frequent measurements and continuously integrating the temperature deficit or excess; * Treating each day's temperature profile as a sine wave with amplitude equal to the day's temperature variation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growing Degree Day
Growing degree days (GDD), also called growing degree units (GDUs), are a heuristic tool in phenology. GDD are a measure of heat accumulation used by horticulturists, gardeners, and farmers to predict plant and animal development rates such as the date that a flower will bloom, an insect will emerge from dormancy, or a crop will reach maturity. Introduction In the absence of extreme conditions such as unseasonal drought or disease, plants grow in a cumulative stepwise manner which is strongly influenced by the ambient temperature. Growing degree days take aspects of local weather into account and allow gardeners to predict (or, in greenhouses, even to control) the plants' pace toward maturity. Unless stressed by other environmental factors like moisture, the development rate from emergence to maturity for many plants depends upon the daily air temperature. Because many developmental events of plants and insects depend on the accumulation of specific quantities of heat, it is possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
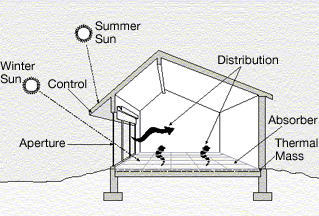
Heating Degree Day
Heating degree day (HDD) is a measurement designed to quantify the demand for energy needed to heat a building. HDD is derived from measurements of outside air temperature. The heating requirements for a given Architectural structure, building at a specific location are considered to be directly proportional to the number of HDD at that location. Related measurements include the cooling degree day (CDD), which quantifies demand for air conditioning. Definition Heating degree days are defined relative to a base temperature—the outside temperature above which a building needs no heating. Base temperatures may be defined for a particular building as a function of the temperature that the building is heated to, or it may be defined for a country or region for example. In the latter case, building standards or conventions may exist for the temperature threshold. These include: The base temperature does not necessarily correspond to the building mean internal temperature, as standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating Degree Day
Heating degree day (HDD) is a measurement designed to quantify the demand for energy needed to heat a building. HDD is derived from measurements of outside air temperature. The heating requirements for a given Architectural structure, building at a specific location are considered to be directly proportional to the number of HDD at that location. Related measurements include the cooling degree day (CDD), which quantifies demand for air conditioning. Definition Heating degree days are defined relative to a base temperature—the outside temperature above which a building needs no heating. Base temperatures may be defined for a particular building as a function of the temperature that the building is heated to, or it may be defined for a country or region for example. In the latter case, building standards or conventions may exist for the temperature threshold. These include: The base temperature does not necessarily correspond to the building mean internal temperature, as standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Monitoring And Targeting
Energy monitoring and targeting (M&T) is an energy efficiency technique based on the standard management axiom stating that “you cannot manage what you cannot measure”. M&T techniques provide energy managers with feedback on operating practices, results of energy management projects, and guidance on the level of energy use that is expected in a certain period. Importantly, they also give early warning of unexpected excess consumption caused by equipment malfunctions, operator error, unwanted user behaviours, lack of effective maintenance and the like. The foundation of M&T lies in determining the normal relationships of energy consumptions to relevant driving factors (HVAC equipment, production though puts, weather, occupancy available daylight, etc.) and the goal is to help business managers: * Identify and explain excessive energy use * Detect instances when consumption is unexpectedly higher or lower than would usually have been the case * Visualize energy consumption tren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC 2005 Rigueur Climatique
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
#REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-SI Units Mentioned In The SI
This is a list of units that are not defined as part of the International System of Units (SI) but are otherwise mentioned in the SI Brochure, Bureau international des poids et mesures, "Non-SI units that are accepted for use with the SI", inLe Système international d'unités (SI) / The International System of Units (SI), 9th ed.(Sèvres: 2019), , c. 4, pp. 145–146. listed as being accepted for use alongside SI-units, or for explanatory purposes. Units officially accepted for use with the SI The SI prefixes can be used with several of these units, but not, for example, with the non-SI units of time. Other units defined but not officially sanctioned The following table lists units that are effectively defined in side- and footnotes in the 9th SI brochure. Units that are mentioned without a definition or that occur in historical material recorded in the appendices are not included. Changes to units mentioned in the SI With the publication of each edition of the SI broch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorological Indices
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological phenom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-work transformations (and their reverse) that take place in the earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodynamics, to describe and explain such phenomena as the properties of moist air, the formation of clouds, atmospheric convection, boundary layer meteorology, and vertical instabilities in the atmosphere. Atmospheric thermodynamic diagrams are used as tools in the forecasting of storm development. Atmospheric thermodynamics forms a basis for cloud microphysics and convection parameterizations used in numerical weather models and is used in many climate considerations, including convective-equilibrium climate models. Overview The atmosphere is an example of a non-equilibrium system. Atmospheric thermodynamics describes the effect of buoyant forces that cause the rise of less dense (warmer) air, the descent of more dense air, and the transformation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Terminology
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and non-food crops such as grass and ornamental trees and plants. It also includes plant conservation, landscape restoration, landscape and garden design, construction, and maintenance, and arboriculture, ornamental trees and lawns. The study and practice of horticulture have been traced back thousands of years. Horticulture contributed to the transition from nomadic human communities to sedentary, or semi-sedentary, horticultural communities.von Hagen, V.W. (1957) The Ancient Sun Kingdoms Of The Americas. Ohio: The World Publishing Company Horticulture is divided into several categories which focus on the cultivation and processing of different types of plants and food items for specific purposes. In order to conserve the science of horticultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orders Of Magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic distributions are common in nature and considering the order of magnitude of values sampled from such a distribution can be more intuitive. When the reference value is 10, the order of magnitude can be understood as the number of digits in the base-10 representation of the value. Similarly, if the reference value is one of some powers of 2, since computers store data in a binary format, the magnitude can be understood in terms of the amount of computer memory needed to store that value. Differences in order of magnitude can be measured on a base-10 logarithmic scale in “decades” (i.e., factors of ten). Examples of numbers of different magnitudes can be found at Orders of magnitude (numbers). Definition Generally, the order of magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |