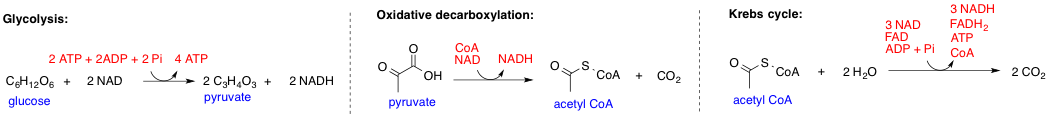|
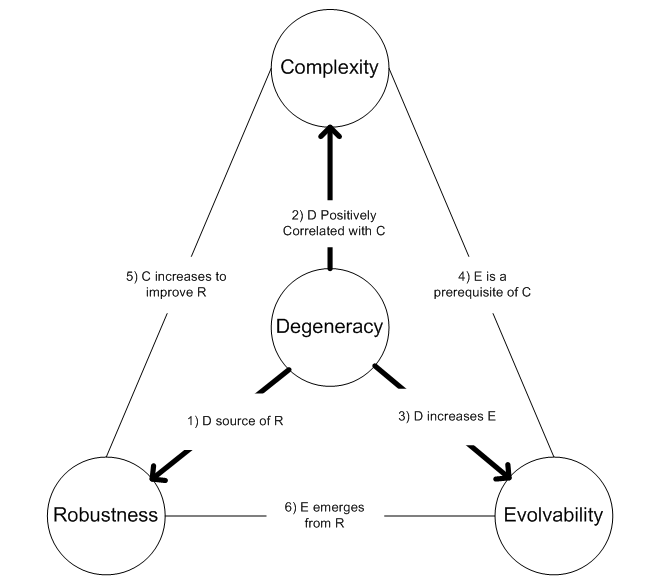
Degeneracy (biology)
Within biological systems, degeneracy occurs when structurally dissimilar components/modules/pathways can perform similar functions (i.e. are effectively interchangeable) under certain conditions, but perform distinct functions in other conditions. Degeneracy is thus a relational property that requires comparing the behavior of two or more components. In particular, if degeneracy is present in a pair of components, then there will exist conditions where the pair will appear functionally redundant but other conditions where they will appear functionally distinct. Note that this use of the term has practically no relevance to the questionably meaningful concept of evolutionarily degenerate populations that have lost ancestral functions. Biological examples Examples of degeneracy are found in the genetic code, when many different nucleotide sequences encode the same polypeptide; in protein folding, when different polypeptides fold to be structurally and functionally equivalent; in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Trait
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotype, phenotypic characteristic of an organism; it may be either heredity, inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two.Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. For example, having eye color is a ''character'' of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel versions of eye colour are ''traits''. The term ''trait'' is generally used in genetics, often to describe phenotypic expression of different combinations of alleles in different individual organisms within a single Population genetics, population, such as the famous purple vs. white flower coloration in Gregor Mendel, Gregor Mendel's pea plants. By contrast, in systematics, the term is ''character state'' is employed to describe features that represent fixed diagnostic differences among taxa, such as the absence of tails in great apes, relative to othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolvability
Evolvability is defined as the capacity of a system for adaptive evolution. Evolvability is the ability of a population of organisms to not merely generate genetic diversity, but to generate ''adaptive'' genetic diversity, and thereby evolve through natural selection. In order for a biological organism to evolve by natural selection, there must be a certain minimum probability that new, heritable variants are beneficial. Random mutations, unless they occur in DNA sequences with no function, are expected to be mostly detrimental. Beneficial mutations are always rare, but if they are too rare, then adaptation cannot occur. Early failed efforts to evolve computer programs by random mutation and selection showed that evolvability is not a given, but depends on the representation of the program as a data structure, because this determines how changes in the program map to changes in its behavior. Analogously, the evolvability of organisms depends on their genotype–phenotype map. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relationships Between Degeneracy, Complexity, Robustness, And Evolvability
Relationship most often refers to: * Family relations and relatives: consanguinity * Interpersonal relationship, a strong, deep, or close association or acquaintance between two or more people * Correlation and dependence, relationships in mathematics and statistics between two variables or sets of data * Semantic relationship, an ontology component * Romance (love), a connection between two people driven by love and/or sexual attraction Relationship or Relationships may also refer to: Arts and media * "Relationship" (song), by Young Thug featuring Future * "Relationships", an episode of the British TV series ''As Time Goes By'' * The Relationship, an American rock band ** ''The Relationship'' (album), their 2010 album * The Relationships, an English band who played at the 2009 Truck Festival * ''Relationships'', a 1994 album by BeBe & CeCe Winans * ''Relationships'', a 2001 album by Georgie Fame * "Relationship", a song by Lakeside on the 1987 album ''Power'' * "Relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high- affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains. History The first RTKs to be discovered were EGF and NGF in the 1960s, but the classification of receptor tyrosine kinases was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivation (Transcription)
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EGF Receptor , China Railway telegraph code EGF
{{disambiguation ...
EGF may refer to: * E.G.F., a Gabonese company * East Grand Forks, Minnesota, a city * East Garforth railway station in England * Epidermal growth factor * Equity Group Foundation, a Kenyan charity * European Gendarmerie Force, a military unit of the European Union * European Genetics Foundation, a training organization * European Globalisation Adjustment Fund * European Go Federation * Exponential generating function * Xinxiang East railway station Xinxiang East railway station () is a railway station on the Beijing–Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong high-speed railway located in Xinxiang, Henan, People's Republic of China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as '' catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. It is known as the brewer's yeast or baker's yeast. They are unicellular and saprotrophic fungi. One example is ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', which is used in making bread, wine, and beer, and for human and animal health. Other members of this genus include the wild yeast '' Saccharomyces paradoxus'' that is the closest relative to ''S. cerevisiae'', '' Saccharomyces bayanus'', used in making wine, and ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' var. ''boulardii'', used in medicine. Morphology Colonies of ''Saccharomyces'' grow rapidly and mature in three days. They are flat, smooth, moist, glistening or dull, and cream in color. The inability to use nitrate and ability to ferment various carbohydrates are typical characteristics of ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesin Molecule (immunoglobulin -like)
In molecular biology, the adhesin molecule (immunoglobulin-like) is a protein domain. This domain is found in mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 proteins (MAdCAM-1). These are cell adhesion molecules gene expression, expressed on the endothelium in mucosa that guide the specific homing of lymphocytes into mucosal tissue (biology), tissues. MAdCAM-1 belongs to a subclass of the antibody, immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), the members of which are ligands for integrins. The crystal structure of this domain has been reported; it adopts an immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich structure, with seven strands arranged in two beta-sheets in a Greek-key topology. See also *Bacterial adhesin *Cell adhesion *Fungal adhesin References {{InterPro content, IPR015169 Protein domains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |