|
Danger Space
The danger space or alar space, is a region of the neck. The common name originates from the risk that an infection in this space can spread directly to the thorax, and, due to being a space continuous on the left and right, can furthermore allow infection to spread easily to either side. Structure It is bounded at the top by the skull base, at the front by the alar fascia and behind by the prevertebral fascia. It comes to an end at the level of the diaphragm. The retropharyngeal space is found anterior to the danger space, between the alar fascia and buccopharyngeal fascia. There exists a midline raphe in this space so some infections of this space appear unilateral. Clinical significance On CT or MRI it is only visible when distended by fluid or pus, below the level of T1-T6, as the retropharyngeal space ends at this level, allowing distinction between the two entities. Superior spread of infection can affect the contents of the carotid sheath, including the internal jugular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
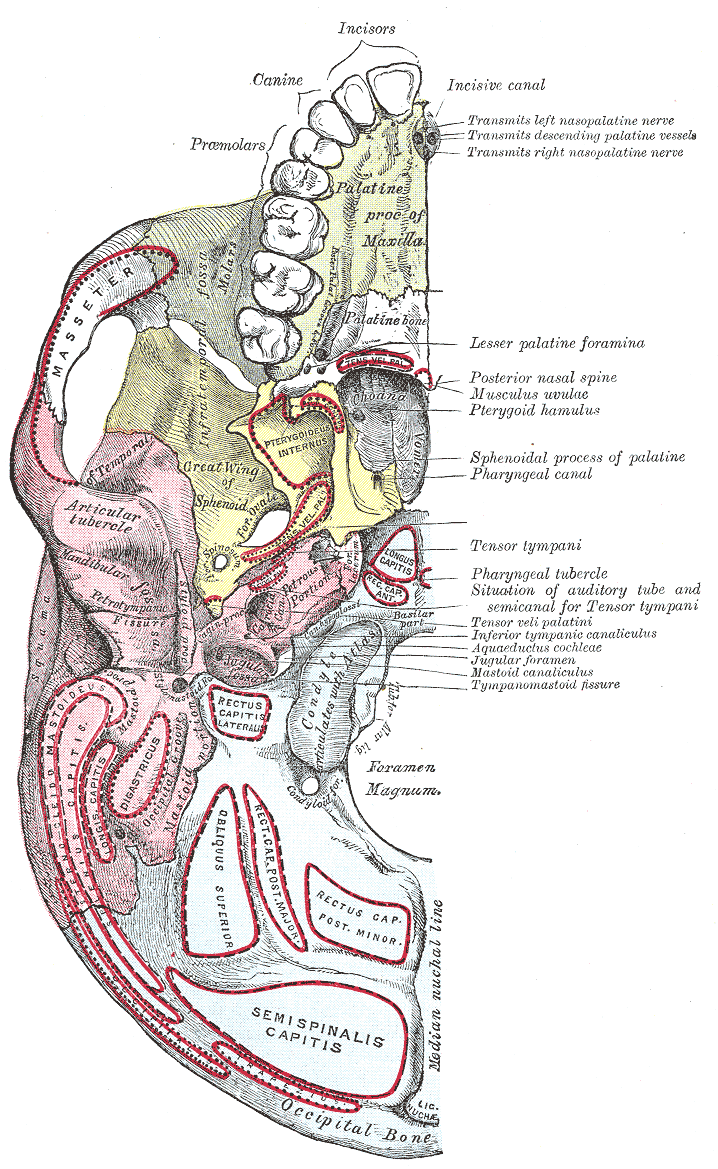
Skull Base
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus *Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal *Jugular tubercle *Tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alar Fascia
The alar fascia is a layer of fascia, sometimes described as part of the prevertebral fascia, and sometimes as in front of it. Anatomy Cranially, it reaches the skull, and caudally, it reaches the second thoracic vertebra. In 2015, the anatomy of the alar fascia was revisited using dissection in conjunction with E12 plastination. The authors revealed that the alar fascia originated as a well defined midline structure at the level of C1 and does not reach the base of the skull. It is suggested that the area between C1 and the base of the skull is a potential entry into the danger space. Anatomical relations The alar fascia represents the posterior boundary of the retropharyngeal space The retropharyngeal space (abbreviated as "RPS") is a potential space and deep compartment of the head and neck situated posterior to the pharynx. The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the alar fascia, and la .... See also * Retrovisceral space Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevertebral Fascia
The prevertebral fascia (or prevertebral layer of cervical fascia) is a fascia in the neck. Variations In some literature, the prevertebral fascia also includes the other fascial layers extending around the vertebral column and enclosing all muscles laterally and posteriorly to it. However, in this article, it is assumed to be as marked in the corresponding picture. Location The prevertebral fascia extends medially behind the carotid vessels, where it assists in forming their sheath, and passes in front of the prevertebral muscles. The prevertebral fascia is fixed above to the base of the skull, and below it extends behind the esophagus into the posterior mediastinal cavity of the thorax. It descends in front of the longus colli muscles. The prevertebral fascia is prolonged downward and laterally behind the carotid vessels and in front of the scalene muscles. It forms a sheath for the brachial nerves, subclavian artery, and subclavian vein in the posterior triangle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retropharyngeal Space
The retropharyngeal space (abbreviated as "RPS") is a potential space and deep compartment of the head and neck situated posterior to the pharynx. The RPS is bounded anteriorly by the buccopharyngeal fascia, posteriorly by the alar fascia, and laterally by the carotid sheath. It spans from the base of the skull superiorly to the mediastinum inferiorly. It contains the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Sources consider the retropharyngeal space to be in principle subdivided into the so-called "true retropharyngeal space" or "retropharyngeal space proper" (part of the RSP situated anterior to the alar fascia), and the danger space (part of the RSP situated posterior to the alar fascia). The danger space is sometimes also lumped together with the true RPS and the whole referred to as the RPS because the alar fascia is an ineffective barrier. Infections from the head and neck can spread down through the danger space into the posterior mediastinum. Anatomy Superiorly, the retropharingeal sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccopharyngeal Fascia
The buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia in the head and neck. Structure The buccopharyngeal runs parallel to the medial aspect of the carotid sheath. It is a thin lamina given off from the pretracheal fascia. It is attached to the prevertebral fascia by loose connective tissue, with the retropharyngeal space found between them. It may also be attached to the alar fascia posteriorly at C3 and C6 levels. The thyroid gland wraps around the trachea and oesophagus anterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia, so that the lateral parts of the thyroid gland border it. Function The buccopharyngeal fascia envelops the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It closely invests the constrictor muscles of the pharynx. It is continued forward from the constrictor pharyngis superior onto the buccinator The buccinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Sheath
The carotid sheath is an anatomical term for the fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the vascular compartment of the neck. It is part of the deep cervical fascia of the neck, below the superficial cervical fascia meaning the subcutaneous adipose tissue immediately beneath the skin. The deep cervical fascia of the neck includes four parts: * The investing layer (encloses the SCM and Trapezius) * The carotid sheath (encloses the vascular region of the neck) * The pretracheal fascia (encloses the visceral region of the neck) * The prevertebral fascia (encloses the vertebral region of the neck) Structure The carotid sheath is located at the lateral boundary of the retropharyngeal space at the level of the oropharynx on each side of the neck and deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It extends from the base of the skull to the first rib and sternum, varying between C7 and T4. It merges with the axillary sheath when it reaches the subclavian vein. Contents The four major stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Jugular Vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve. It begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull. It is somewhat dilated at its origin, which is called the ''superior bulb''. This vein also has a common trunk into which drains the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein, the facial vein, and the lingual vein. It runs down the side of the neck in a vertical direction, being at one end lateral to the internal carotid artery, and then lateral to the common carotid artery, and at the root of the neck, it unites with the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein (innominate vein); a little above its termination is a second dilation, the ''inferior bulb''. Above, it lies upon the rectus capitis lateralis, behind the internal carotid artery and the nerves passing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |