|
Driftwood
Driftwood is a wood that has been washed onto a shore or beach of a sea, lake, or river by the action of winds, tides or waves. It is part of beach wrack. In some waterfront areas, driftwood is a major nuisance. However, the driftwood provides shelter and food for birds, fish and other aquatic species as it floats in the ocean. Gribbles, shipworms and bacteria decompose the wood and gradually turn it into nutrients that are reintroduced to the food web. Sometimes, the partially decomposed wood washes ashore, where it also shelters birds, plants, and other species. Driftwood can become the foundation for sand dunes. Most driftwood is the remains of trees, in whole or part, that have been washed into the ocean, due to flooding, high winds, or other natural occurrences, or as the result of logging. There is also a subset of driftwood known as drift lumber. Drift lumber includes the remains of man-made wooden objects, such as buildings and their contents washed into the sea duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquascaping
Aquascaping is the craft of arranging aquatic plants, as well as rocks, stones, cavework, or driftwood, in an aesthetically pleasing manner within an aquarium—in effect, gardening under water. Aquascape designs include a number of distinct styles, including the garden-like Dutch style and the Japanese-inspired nature style. Typically, an aquascape fishkeeping, houses fish as well as plants, although it is possible to create an aquascape with plants only, or with rockwork or other hardscape and no plants. Aquascaping appears to have begun to be a popular hobby in the 1930s in the Netherlands, following the introduction of the Dutch-style aquascaping techniques. With the increasing availability of mass-produced freshwater fishkeeping products and popularity of fishkeeping following the First World War, hobbyists began exploring the new possibilities of creating an aquarium that did not have fish as the main attraction. Although the primary aim of aquascaping is to create an artfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and the Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Inuit languages are part of the Eskaleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskimo–Aleut. Canadian Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, the Nunatsiavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories and Yukon (traditionally), particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. These areas are known, by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami and the Government of Canada, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beach Wrack
Beach wrack or marine wrack is organic material (e.g. kelp, seagrass, driftwood) and other debris deposited at high tide on beaches and other coastal areas. This material acts as a natural input of marine resources into a terrestrial system, providing food and habitat for a variety of coastal organisms. Physical characteristics The wrack zone is most commonly associated with a sandy beach habitat but can also be present in rocky shores, mangroves, salt marshes, and other coastal systems. Debris is carried up the intertidal zone as the tide comes in, and is deposited on the sand when the tide goes out. The zone can be recognized as a linear patch of debris toward the upper part of a beach running parallel to the water's edge. The location of the wrack zone varies geographically and temporally. It is found at a higher elevation during spring tides compared to neap tides. The size of a beach and its intertidal zone will influence the location of wrack deposition. Additionally, sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia as the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The North Germanic languages, northernmost extension of Germanic mythology and stemming from Proto-Germanic folklore, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition. The source texts mention numerous gods such as the thunder-god Thor, the Huginn and Muninn, raven-flanked god Odin, the goddess Freyja, and List of Germanic deities, numerous other deities. Most of the surviving mythology centers on the plights of the gods and their interaction with several other beings, such as humanity and the jötnar, beings who may be friends, lovers, foes, or family members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
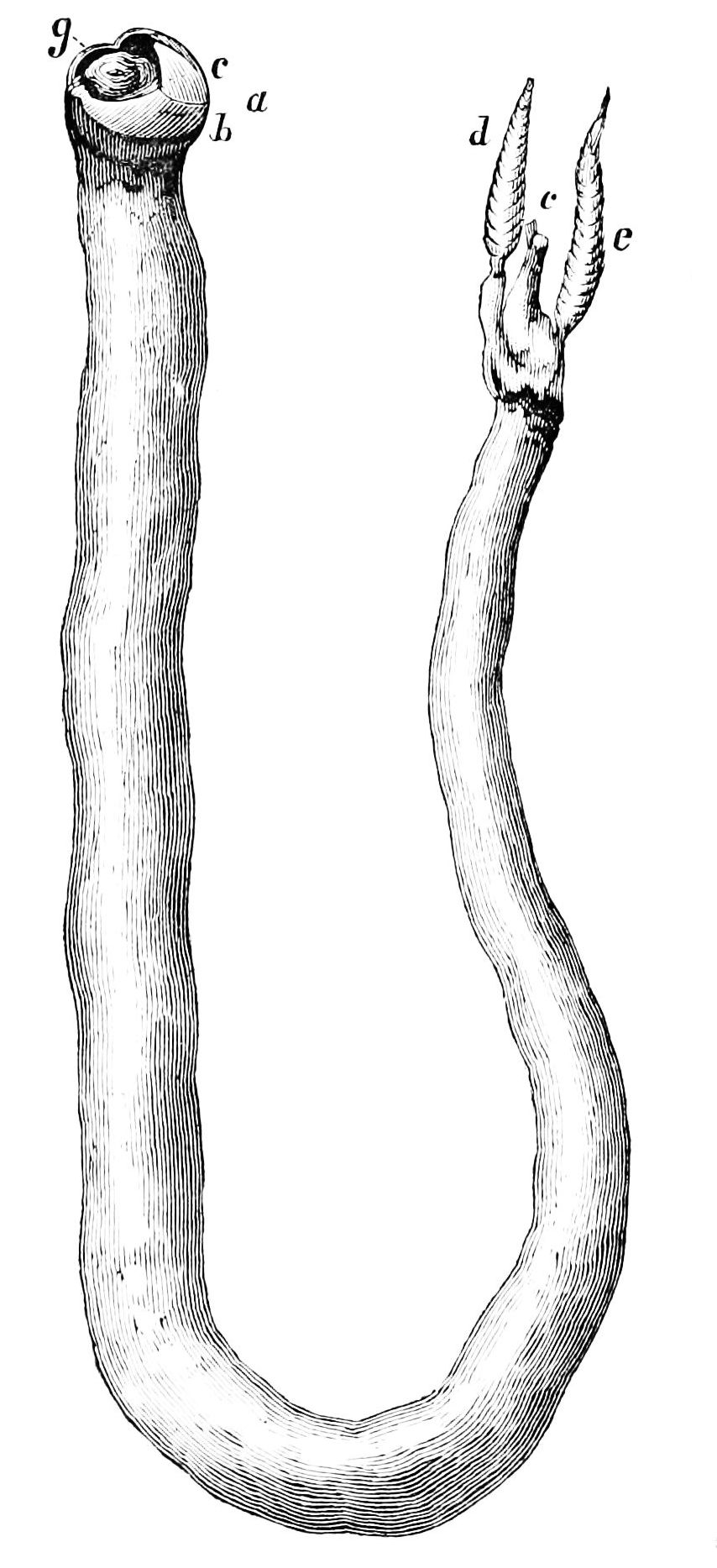
Gribble
A gribble () or gribble worm is any of about 56 species of marine isopod from the family Limnoriidae. They are mostly pale white and small ( long) crustaceans, although '' Limnoria stephenseni'' from subantarctic waters can reach . Classification The term "gribble" was originally assigned to the wood-boring species, especially the first species described from Norway by Jens Rathke in 1799, '' Limnoria lignorum''. The Limnoriidae are now known to include seaweed and seagrass borers, as well as wood borers. Those gribbles able to bore into living marine plants are thought to have evolved from a wood (dead plant) boring species. Ecology Gribbles bore into wood and plant material, and the material is ingested for food; the cellulose of wood is digested, most likely with the aid of cellulases produced by the gribbles themselves. The most destructive species are '' Limnoria lignorum'', '' L. tripunctata'' and '' L. quadripunctata''. Due to dispersal while inhabiting wooden ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipworm
The shipworms, also called teredo worms or simply teredo (, via Latin ), are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae, a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in seawater, including such structures as wooden piers, docks, and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (" valves") borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. They are sometimes called "termites of the sea". Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name '' Teredo'' to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic ''magnum opus'', '' Systema Naturæ'' (1758). Characteristics Removed from its burrow, the fully grown teredo ranges from several centimeters to about a meter in length, depending on the species. An average adult shipworm measures in length and less than in diameter, but some species grow to considerable size. The body is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fir Island (Washington)
Fir Island is bounded by North and South Forks of the Skagit River and Skagit Bay of Puget Sound in the southwestern corner of Skagit County, Washington. Triangular in outline, east–west by north–south with an area of nearly , Fir Island is occupied by 195 families. The island is connected by bridge to the village of Conway, located on the east shore of the South Fork of the Skagit River. A second bridge, across the North Fork of the Skagit River, leads to La Conner, northwest. Near the northeast tip of Fir Island is the site of the 19th-century town of Skagit City which declined after upstream log jams were removed in 1877. Natural history A major component of the Skagit River Delta, the island is an important habitat for wildlife. Migrating from the northern portion of Wrangel Island in Russia, 30,000 to 70,000 snow geese spend the winter on the Skagit River Delta and the Fraser River Delta of British Columbia. Important internationally, this population and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunnage
Dunnage is inexpensive or waste material used to load and secure cargo during transportation; more loosely, it refers to miscellaneous baggage, brought along during travel. The term can also refer to low-priority cargo used to fill out transport capacity which would otherwise ship underweight. In the context of shipping manufactured goods, dunnage refers to the packing material used as protective fill inside the carton, box or other type container used to prevent the merchandise from being damaged during shipment. These materials include bubble wrap; wadded, crumpled or shredded paper; styrofoam; inflated air packs; and other materials. International laws When a ship is unloaded, sometimes the dunnage may not be landed because of customs duties on imported timber or quarantine rules to prevent foreign insect Pest (organism), pests from moving ashore, and as a result often the unwanted dunnage is later furtively jettisoned overside and adds to the area's driftwood problem. Accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bald Eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche as the bald eagle in the Palearctic. Its range includes most of Canada and Alaska, all of the contiguous United States, and northern Mexico. It is found near large bodies of open water with an abundant food supply and old-growth trees for nesting. The bald eagle is an opportunistic feeder that subsists mainly on fish, upon which it swoops down and snatches from the water with its talons. It builds the largest nest of any North American bird and the largest tree nests ever recorded for any animal species, up to deep, wide, and in weight. Sexual maturity is attained at the age of four to five years. Bald eagles are not bald; the name derives from an older meaning of the word, "white-headed". The adult is mainly brown with a white head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ash (tree)
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae, and comprises 45–65 species of usually medium-to-large trees, most of which are deciduous trees, although some subtropical species are evergreen trees. The genus is widespread throughout much of Europe, Asia, and North America. The leaves are opposite (rarely in whorls of three), and mostly pinnately compound, though simple in a few species. The seeds, popularly known as "keys" or "helicopter seeds", are a type of fruit known as a samara. Some ''Fraxinus'' species are dioecious, having male and female flowers on separate plants but sex in ash is expressed as a continuum between male and female individuals, dominated by unisexual trees. With age, ash may change their sexual function from predominantly male and hermaphrodite towards femaleness; if grown as an ornamental and both sexes are present, ashes can cause a considerable litter problem with their seeds. Rowans, or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
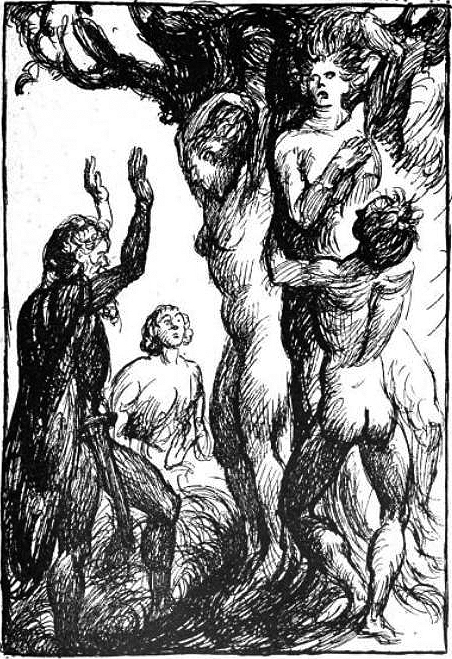
Ask And Embla
In Norse mythology, Ask and Embla ()—man and woman respectively—were the first two humans, created by the gods. The pair are attested in both the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', composed in the 13th century. In both sources, three gods, one of whom is Odin, find Ask and Embla and bestow upon them various corporeal and spiritual gifts. A number of theories have been proposed to explain the two figures, and there are occasional references to them in popular culture. Etymology Old Norse literally means " ash tree" but the etymology of ''embla'' is uncertain, and two possibilities of the meaning of ''embla'' are generally proposed. The first meaning, " elm tree", is problematic, and is reached by deriving ''*Elm-la'' from ''*Almilōn'' and subsequently to ('elm'). The second suggestion is "vine", which is reached through ''*Ambilō'', which may be related to the Greek term (), itself meaning "vine, lian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |