|
Dose–response Relationship
The dose–response relationship, or exposure–response relationship, describes the magnitude of the response of an organism, as a function of exposure (or doses) to a stimulus or stressor (usually a chemical) after a certain exposure time. Dose–response relationships can be described by dose–response curves. This is explained further in the following sections. A stimulus response function or stimulus response curve is defined more broadly as the response from any type of stimulus, not limited to chemicals. Motivation for studying dose–response relationships Studying dose response, and developing dose–response models, is central to determining "safe", "hazardous" and (where relevant) beneficial levels and dosages for drugs, pollutants, foods, and other substances to which humans or other organisms are exposed. These conclusions are often the basis for public policy. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has developed extensive guidance and reports on dose–resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dose Response Curve Stimulation
Dose or Dosage may refer to: Music * ''Dose'' (Gov't Mule album), 1998 * ''Dose'' (Latin Playboys album) * ''Dosage'' (album), by the band Collective Soul * "Dose" (song), a 2018 song by Ciara * "Dose", song by Filter from the album '' Short Bus'' Science * Dose (biochemistry), a measured quantity of a medicine, nutrient, or pathogen which is delivered as a unit. * Dosage form, a mixture of active and inactive components used to administer a medication * Dosing, feeding chemicals or medicines when used in small quantities * Effective dose (pharmacology), a dose or concentration of a drug that produces a biological response *Absorbed dose, a measure of energy deposited in matter from ionizing radiation *Equivalent dose, a measure of cancer/heritable health risk in tissue from ionizing radiation *Effective dose (radiation), a measure of cancer/heritable health risk to the whole body from ionizing radiation *Median lethal dose, a measure of the lethal dose of a toxin, radiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprenaline
Isoprenaline, or isoproterenol (brand name: Isoprenaline Macure), is a medication used for the treatment of bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, and rarely for asthma. It is a non-selective β adrenoceptor agonist that is the isopropylamine analog of epinephrine (adrenaline). Medical uses It is used to treat heart block and episodes of Adams–Stokes syndrome that are not caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, in emergencies for cardiac arrest until electric shock can be administered, for bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia, and as an adjunct in the treatment of hypovolemic shock, septic shock, low cardiac output (hypoperfusion) states, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock. It is also used to prevent Torsades de Pointes in patients with long QT refractory to magnesium and to treat patients with intermittent Torsades de Pointes refractory to treatment with magnesium. Historically, it was used to treat asthma via metered aerosol or nebulizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ... which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma radiation (γ) * '' particle radiation'', such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation (particles of non-zero rest energy) * '' acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves (dependent on a physical transmission medium) * '' gravitational radiation'', that takes the form of gravitational waves, or ripples in the curvature of spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either '' ionizing'' or '' non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 eV, which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules and break chemical bonds. This is an important distinction due to the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Today, the term ''endotoxin'' is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins (in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by '' Bacillus thuringiensis''. Lipopolysaccharides can have substantial impacts on human health, primarily through interactions with the immune system. LPS is a potent activator of the immune system and pyrogen (agent that causes fever). In severe cases, LPS can play a role in causing septic shock. In lower levels and over a longer time period, there is evidence LPS may play an important and harmful ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Receptor
A thermoreceptor is a non-specialised sense receptor, or more accurately the receptive portion of a sensory neuron, that codes absolute and relative changes in temperature, primarily within the innocuous range. In the mammalian peripheral nervous system, warmth receptors are thought to be unmyelinated C-fibres (low conduction velocity), while those responding to cold have both C-fibers and thinly myelinated A delta fibers (faster conduction velocity). The adequate stimulus for a warm receptor is warming, which results in an increase in their action potential discharge rate. Cooling results in a decrease in warm receptor discharge rate. For cold receptors their firing rate increases during cooling and decreases during warming. Some cold receptors also respond with a brief action potential discharge to high temperatures, i.e. typically above 45 °C, and this is known as a paradoxical response to heat. The mechanism responsible for this behavior has not been determined. Locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955 and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, who soon followed with diazepam (Valium) in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide. Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic ( sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimulus. Some of them, like benzodiazepines, are drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to (i.e., an ''allosteric site'') is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind (i.e., an ''orthosteric site''). Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands. Allosteric modulators can be 1 of 3 types either: positive, negative or neutral. Positive types increase the response of the receptor by increasing the probability that an agonist will bind to a receptor (i.e. affinity), increasing its ability to activate the receptor (i.e. efficacy), or both. Negative types decrease the agonist affinity and/or efficacy. Neutral types don't affect agonist activity but can stop other modulators from binding to an allosteric site. Some modulators also work as allosteric agonists. The term "allosteric" de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
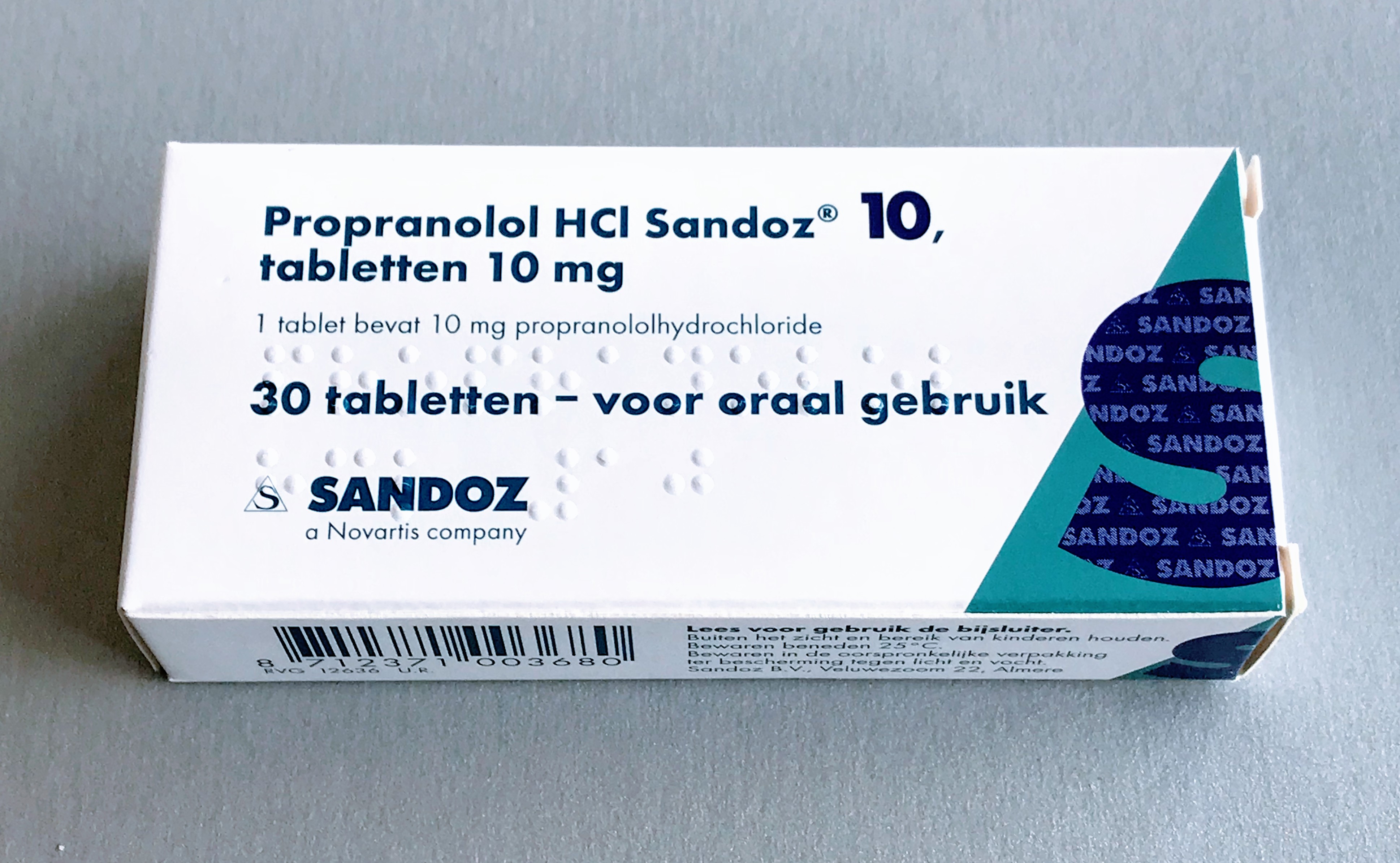
Propranolol
Propranolol, sold under the brand name Inderal among others, is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat high blood pressure, a number of types of irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, performance anxiety, and essential tremors, as well to prevent migraine headaches, and to prevent further heart problems in those with angina or previous heart attacks. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. The formulation that is taken by mouth comes in short-acting and long-acting versions. Propranolol appears in the blood after 30 minutes and has a maximum effect between 60 and 90 minutes when taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea, abdominal pain, and constipation. It should not be used in those with an already slow heart rate and most of those with heart failure. Quickly stopping the medication in those with coronary artery disease may worsen symptoms. It may worsen the symptoms of asthma. Caution is recommended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |