|
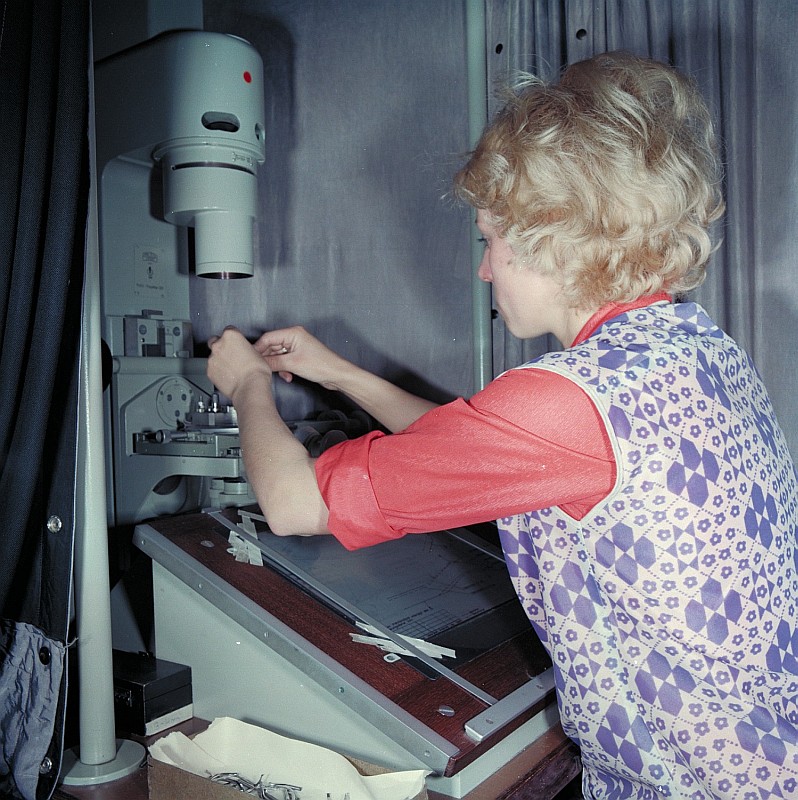
Dissolution Testing
In the pharmaceutical industry, drug ''dissolution testing'' is routinely used to provide critical in vitro drug release information for both quality control purposes, i.e., to assess batch-to-batch consistency of solid oral dosage forms such as tablets, and drug development, i.e., to predict in vivo drug release profiles.Bai, G., Wang, Y., Armenante, P. M., "Velocity profiles and shear strain rate variability in the USP Dissolution Testing Apparatus 2 at Different Impeller Agitation Speeds, " International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 403 (1-2), Pages 1–14, 2011 There are three typical situations where dissolution testing plays a vital role: (i) formulation and optimization decisions: during product development, for products where dissolution performance is a critical quality attribute, both the product formulation and the manufacturing process are optimized based on achieving specific dissolution targets. (ii) Equivalence decisions: during generic product development, and also when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution Units
Dissolution may refer to: Arts and entertainment Books * ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers * ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music * Dissolution, in music, is a specific type of section (music). * ''Dissolution'' (Olivia Block album), 2016 * ''Dissolution'' (The Pineapple Thief album), 2018 Politics and law * Dissolution (politics) is when a state, institution, nation, or administrative region ceases to exist, usually separating into two or more entities. * Dissolution (law), in law, means to end a legal entity or agreement such as a marriage, adoption, or corporation, or unions. * Dissolution of parliament, in politics, the dismissal of a legislature so that elections can be held. **Dissolution of the Parliament of the United Kingdom * Dissolution of the Monasteries, in British history, the formal process during the English Reformation by which Henry VIII confiscated the property of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic or brand medications and medical devices. They are subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern the patenting, testing, safety, efficacy using drug testing and marketing of drugs. The global pharmaceuticals market produced treatments worth $1,228.45 billion in 2020 and showed a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.8%. History Mid-1800s – 1945: From botanicals to the first synthetic drugs The modern era of pharmaceutical industry began with local apothecaries that expanded from their traditional role of distributing botanical drugs such as morphine and quinine to wholesale manufacture in the mid-1800s, and from discoveries resulting from applied research. Intentional drug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet–visible Spectroscopy
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications. The only requirement is that the sample absorb in the UV-Vis region, i.e. be a chromophore. Absorption spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy. Parameters of interest, besides the wavelength of measurement, are absorbance (A) or transmittance (%T) or reflectance (%R), and its change with time. Optical transitions Most molecules and ions absorb energy in the ultraviolet or visible range, i.e., they are chromophores. The absorbed photon excites an electron in the chromophore to higher energy molecular orbitals, giving rise to an excited state. For organic chromophores, four possible types of transitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material. Each component in the sample interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent material, causing different flow rates for the different components and leading to the separation of the components as they flow out of the column. HPLC has been used for manufacturing (''e.g.'', during the production process of pharmaceutical and biological products), legal (''e.g.'', detecting performance enhancement drugs in urine), research (''e.g.'', separating the components of a complex biological sample, or of similar synthetic chemicals from each other), and medical (''e.g.'', detecting vitamin D levels in blood serum) purposes. Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College, and was affiliated with the Reformed Church in America, Dutch Reformed Church. It is the eighth-oldest college in the United States, the second-oldest in New Jersey (after Princeton University), and one of the nine U.S. colonial colleges that were chartered before the American Revolution.Stoeckel, Althea"Presidents, professors, and politics: the colonial colleges and the American revolution", ''Conspectus of History'' (1976) 1(3):45–56. In 1825, Queen's College was renamed Rutgers College in honor of Colonel Henry Rutgers, whose substantial gift to the school had stabilized its finances during a period of uncertainty. For most of its existence, Rutgers was a Private university, private liberal arts college but it has evolved int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid ( liquids and gases) with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed analytical or empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for comparison. A final validation is often performed using full-scale testing, such as flight tests. CFD is applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Pharmacopeia
The ''United States Pharmacopeia'' (''USP'') is a pharmacopeia (compendium of drug information) for the United States published annually by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (usually also called the USP), a nonprofit organization that owns the trademark and also owns the copyright on the pharmacopeia itself. The ''USP'' is published in a combined volume with the ''National Formulary'' (a formulary) as the USP-NF. If a drug ingredient or drug product has an applicable ''USP'' quality standard (in the form of a ''USP-NF'' monograph), it must conform in order to use the designation "USP" or "NF". Drugs subject to ''USP'' standards include both human drugs ( prescription, over-the-counter, or otherwise) and animal drugs. ''USP-NF'' standards also have a role in US federal law; a drug or drug ingredient with a name recognized in ''USP-NF'' is considered adulterated if it does not satisfy compendial standards for strength, quality or purity. USP also sets standards for diet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproducible
Reproducibility, also known as replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a statistical analysis of a data set should be achieved again with a high degree of reliability when the study is replicated. There are different kinds of replication but typically replication studies involve different researchers using the same methodology. Only after one or several such successful replications should a result be recognized as scientific knowledge. With a narrower scope, ''reproducibility'' has been introduced in computational sciences: Any results should be documented by making all data and code available in such a way that the computations can be executed again with identical results. In recent decades, there has been a rising concern that many published scientific results fail the test of reproducibility, evoking a rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements". This approach places emphasis on three aspects (enshrined in standards such as ISO 9001): # Elements such as controls, job management, defined and well managed processes, performance and integrity criteria, and identification of records # Competence, such as knowledge, skills, experience, and qualifications # Soft elements, such as personnel, integrity, confidence, organizational culture, motivation, team spirit, and quality relationships. Inspection is a major component of quality control, where physical product is examined visually (or the end results of a service are analyzed). Product inspectors will be provided with lists and descriptions of unacceptable product defects such as cracks or surface blemishes for example. History and introduction Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accurate
Accuracy and precision are two measures of '' observational error''. ''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements ( observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other. In other words, ''precision'' is a description of '' random errors'', a measure of statistical variability. ''Accuracy'' has two definitions: # More commonly, it is a description of only '' systematic errors'', a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this ''trueness''. # Alternatively, ISO defines accuracy as describing a combination of both types of observational error (random and systematic), so high accuracy requires both high precision and high trueness. In the first, more common definition of "accuracy" above, the concept is independent of "precision", so a particular set of data can be said to be accurate, precise, both, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as ''effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a pragmatic clinical trial#Efficacy versus effectiveness, distinction is now often made between efficacy and effectiveness. The word ''efficacy'' is used in pharmacology and medicine to refer both to the maximum response achievable from a pharmaceutical drug in research settings, and to the capacity for sufficient therapeutic effect or beneficial change in clinical settings. Pharmacology In pharmacology, efficacy () is the maximum response achievable from an applied or dosed agent, for instance, a small molecule drug. Intrinsic activity is a relative term for a drug's efficacy relative to a drug with the highest observed efficacy. It is a purely descriptive term that has little or no mechanistic interpretation. In order for a drug to have an effect, it needs to bind to its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(6982162417).jpg)