|
Discoid
Discoid may refer to: * Disk (mathematics), the region in a plane enclosed by a circle Medicine * Furosemide, a medication sold under the trade name Discoid * Discoid meniscus, a human anatomical variant * Discoid lupus erythematosus, a chronic skin condition in humans ** Canine discoid lupus erythematosus, the equivalent condition in dogs * Nummular dermatitis, also known as discoid eczema Biology * Discoid head, a type of floret arrangement in Asteraceae flower heads * Discoidal cleavage, a type of partial cleavage in embryos * Discoidin domain, a protein domain of many blood coagulation factors * ''Blaberus discoidalis'', the discoid cockroach * ''Dictyostelium discoideum'', a slime mold Other * Discoidal stele, a funerary stele type found in Basque country See also * Disc (other) Disk or disc may refer to: * Disk (mathematics), a geometric shape * Disk storage Music * Disc (band), an American experimental music band * ''Disk'' (album), a 1995 EP by Mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyostelium Discoideum
''Dictyostelium discoideum'' is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, ''D. discoideum'' is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual lifecycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The lifecycle of ''D. discoideum'' is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the lifecycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its lifecycle makes ''D. discoideum'' a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms. Natural habitat and diet In the wild, ''D. discoideum'' can be found in soil and moist leaf litter. Its primary diet consists of bacteria, such as ''Escherichia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common type of chronic cutaneous lupus (CCLE), an autoimmune skin condition on the lupus erythematosus spectrum of illnesses. It presents with red, painful, inflamed and coin-shaped patches of skin with a scaly and crusty appearance, most often on the scalp, cheeks, and ears. Hair loss may occur if the lesions are on the scalp.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.) Saunders. Chapter 8. . The lesions can then develop severe scarring, and the centre areas may appear lighter in color with a rim darker than the normal skin. These lesions can last for years without treatment. Patients with systemic lupus erythematous develop discoid lupus lesions with some frequency. However, patients who present initially with discoid lupus infrequently develop systemic lupus. Discoid lupus can be divided into localized, generalized, and childhood discoid lupus. The lesions are d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaberus Discoidalis
''Blaberus discoidalis'', commonly known as the discoid cockroach, tropical cockroach, West Indian leaf cockroach, false death's head cockroach, Haitian cockroach, and drummer, is a cockroach native to Central America of the “giant cockroach” family, Blaberidae. The adult is around in length, and is tan with a dark brown to black patch on its pronotum. The juvenile is brown with tan speckles, and matures to adulthood in 4–5 months. Adults have wings but are not active fliers, and they can not climb smooth vertical surfaces, simplifying their care in captivity. ''Blaberus discoidalis'' is called the false death's head cockroach because of its superficial resemblance to the death's head cockroach, ''Blaberus craniifer''. Distribution ''Blaberus discoidalis'' is found in Jamaica, Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico (Vieques Island), Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago, and Florida. Locomotion The movement of ''B. discoidalis'' runs relatively ineffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoid Meniscus
Discoid meniscus is a rare human anatomic variant that usually affects the lateral meniscus of the knee. Usually a person with this anomaly has no complaints; however, it may present as pain, swelling, or a snapping sound heard from the affected knee. Strong suggestive findings on magnetic resonance imaging includes a thickened meniscal body seen on more than two contiguous sagittal slices. Description The Watanabe classification of discoid lateral meniscus is: (A) Incomplete, (B) Complete, and C) Wrisberg-ligament variant Normally, the meniscus is a thin crescent-shaped piece of cartilage that lies between the weight bearing joint surfaces of the femur and the tibia. It is attached to the lining of the knee joint along its periphery and serves to absorb about a third of the impact load that the joint cartilage surface sees and also provides some degree of stabilization for the knee. There are two menisci in the knee joint, with one on the outside (away from midline) being the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is an uncommon autoimmune disease of the basal cell layer of the skin. It occurs in humans and cats, more frequently occurring in dogs. It was first described in dogs by Griffin and colleagues in 1979. DLE is one form of cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). DLE occurs in dogs in two forms: a classical facial predominant form or generalized with other areas of the body affected. Other non-discoid variants of CLE include vesicular CLE, exfoliative CLE and mucocutaenous CLE. It does not progress to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in dogs. SLE can also have skin symptoms, but it appears that the two are either separate diseases. DLE in dogs differs from SLE in humans in that plasma cells predominate histologically instead of T lymphocytes. Because worsening of symptoms occurs with increased ultraviolet light exposure, sun exposure most likely plays a role in DLE, although certain breeds (see below) are predisposed. After pemphigus foliaceus, DLE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoidin Domain
Discoidin domain (also known as F5/8 type C domain, or C2-like domain) is major protein domain of many blood coagulation factors. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII contain a C-terminal, twice repeated, domain of about 150 amino acids, which is often called "C2-like domain" (that is unrelated to the C2 domain). In the ''Dictyostelium discoideum'' (Slime mold) cell adhesion protein discoidin, a related domain, named discoidin I-like domain, DLD, or DS, has been found which shares a common C-terminal region of about 110 amino acids with the FA58C domain, but whose N-terminal 40 amino acids are much less conserved. Similar domains have been detected in other extracellular and membrane proteins. In coagulation factors V and VIII the repeated domains compose part of a larger functional domain which promotes binding to anionic phospholipids on the surface of platelets and endothelial cells. The C-terminal domain of the second FA58C repeat (C2) of coagulation factor VIII has been sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoidal Cleavage
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula, or of the blastocyst in mammals. Depending mostly on the concentration of yolk in the egg, the cleavage can be holoblastic (total or entire cleavage) or meroblastic (partial cleavage). The pole of the egg with the highest concentration of yolk is referred to as the vegetal pole while the opposite is referred to as the animal pole. Cleavage differs from other forms of cell division in that it increases the number of cells and nuclear mass without increasing the cytoplasmic mass. This means that with each successive subdivision, there is roughly half the cyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nummular Dermatitis
Nummular dermatitis is one of the many forms of dermatitis. it is characterized by round or oval-shaped itchy lesions. The name comes from the Latin word "nummus," which means "coin." Signs and symptoms Nummular dermatitis is characterized by chronic or relapsing itchy coin-sized ovoid-shaped red plaques. They can occur on the trunk, limbs, face, and hands. Causes Many contact sensitizers or irritants are known to cause contact dermatitis superimposed on nummular dermatitis. Studies have implicated nickel, cobalt, chromate, and fragrance as likely culprits. Xerosis, or dehydration of skin is also a likely cause. Infection with ''Staphylococcus aureus'' bacteria or ''Candida albicans'' may also play a role. Diagnosis Diagnosis of nummular dermatitis is largely via clinical observation. Biopsies are typically not necessary, and cannot be used to rule out other atopic dermatitis or other eczemas. However, patch testing may be employed to rule out irritants (contact dermatitis) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoid Head
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae were first described in the year 1740. The number of species in Asteraceae is rivaled only by the Orchidaceae, and which is the larger family is unclear as the quantity of extant species in each family is unknown. Most species of Asteraceae are annual, biennial, or perennial herbaceous plants, but there are also shrubs, vines, and trees. The family has a widespread distribution, from subpolar to tropical regions in a wide variety of habitats. Most occur in hot desert and cold or hot semi-desert climates, and they are found on every continent but Antarctica. The primary common characteristic is the existence of sometimes hundreds of tiny individual florets which are held together by protective involucres in flower heads, or more technically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk (mathematics)
In geometry, a disk (also spelled disc). is the region in a plane bounded by a circle. A disk is said to be ''closed'' if it contains the circle that constitutes its boundary, and ''open'' if it does not. For a radius, r, an open disk is usually denoted as D_r and a closed disk is \overline. However in the field of topology the closed disk is usually denoted as D^2 while the open disk is \operatorname D^2. Formulas In Cartesian coordinates, the ''open disk'' of center (a, b) and radius ''R'' is given by the formula :D=\ while the ''closed disk'' of the same center and radius is given by :\overline=\. The area of a closed or open disk of radius ''R'' is π''R''2 (see area of a disk). Properties The disk has circular symmetry. The open disk and the closed disk are not topologically equivalent (that is, they are not homeomorphic), as they have different topological properties from each other. For instance, every closed disk is compact whereas every open disk is not compact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
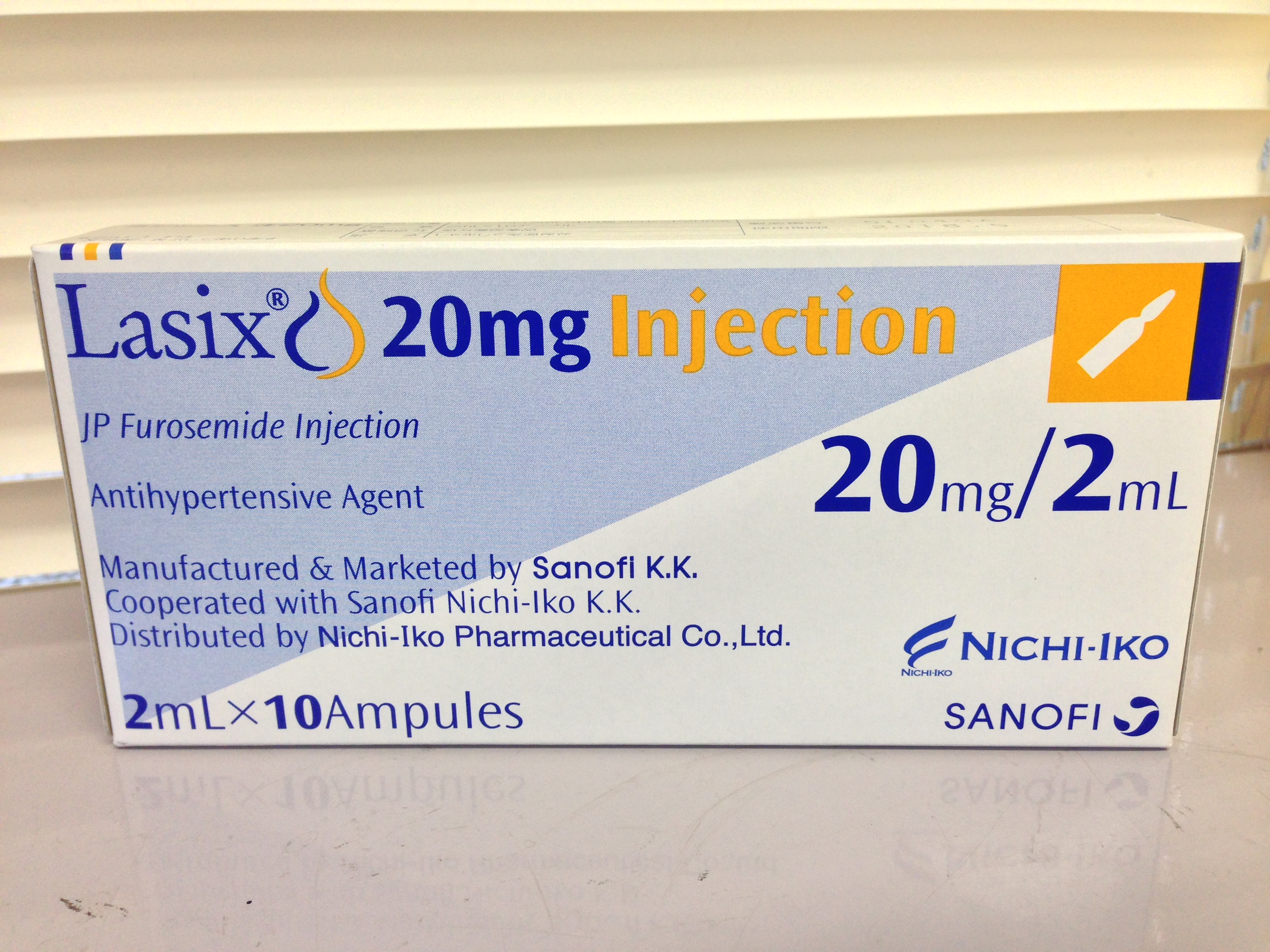
Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes. Common side effects include feeling lightheaded while standing, ringing in the ears, and sensitivity to light. Potentially serious side effects include electrolyte abnormalities, low blood pressure, and hearing loss. Blood tests are recommended regularly for those on treatment. Furosemide is a type of loop diuretic that works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Common side effects of furosemide injection include hypokalemia (low potassium level), hypotension (low blood pressure), and dizziness. Furosemide was patented in 1959 and approved for medical use in 1964. It is on the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoidal Stele
Hilarri (from Basque ''hil'' 'dead' and ''harri'' 'stone') is the name given to disk-shaped funerary steles that are typical of the Basque Country. These funerary steles present a disc-shaped head facing the rising sun on a trapezoidal stand. They belong to an old tradition throughout all of the Western Mediterranean, which includes parts of Europe and North Africa, but today they are mainly found in the Basque Country. Examples Image:Hilarri-4symb.jpg, A cross and a rosette by sector. Image:Hilarri_PawCross.jpg, A cross pattée and text 'our grave'. Image:Orhoitzapena.jpg, A lauburu and text 'Memory'. Image:Hilarri_Stars.jpg, A cross and many kinds of stars. Ornamentation Typology The disc may be decorated by: # geometric symbols, generally organizing the disc into four or eight circle sectors (marked or implicit), a structuring of space that recalls the coat of arms of Navarre; # a single rosette; # a lauburu or other figures that indicate a rotation; # more spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |