|
Direct Insolation
Direct insolation is the insolation measured at a given location on Earth with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun's rays, excluding diffuse insolation (the solar radiation that is scattered or reflected by atmospheric components in the sky). Direct insolation is equal to the solar irradiance above the atmosphere minus the atmospheric losses due to absorption and scattering. While the solar irradiance above the atmosphere varies with the Earth–Sun distance and solar cycles, the losses depend on the time of day (length of light's path through the atmosphere depending on the solar elevation angle), cloud cover, humidity, and other impurities. Simplified formula A simple formula gives the approximate level of direct insolation when there are no clouds: :I_D=1.353\text^2\times 0.7^ where ''AM'' is the airmass given by :AM=\frac 1 with θ being the zenith angle (90° minus the altitude) of the sun. For the sun at the zenith, this gives 947 W/m2. However, ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insolation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units. Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation. Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.Michael Boxwell, ''Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy'' (2012), p. 41–42. Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuring surface, the height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Cover
Cloud cover (also known as cloudiness, cloudage, or cloud amount) refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud cover is correlated to the sunshine duration as the least cloudy locales are the sunniest ones while the cloudiest areas are the least sunny places, as clouds can block sunlight, especially on sunrise and sunset where sunlight is already limited. The global cloud cover averages around 0.68 when analyzing clouds with optical depth larger than 0.1. This value is lower (0.56) when considering clouds with an optical depth larger than 2, and higher when counting subvisible cirrus clouds. Particularly over the oceans cloud cover is persistent with an average 72% of cloud cover. Role in the climate system Clouds play multiple critical roles in the climate system and diurnal cycle. In particular, being bright objects in the visible part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and '' fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then intended to refer to what was sometimes known as pea soup fog, a familiar and serious problem in London from the 19th century to the mid-20th century. This kind of visible air pollution is composed of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxide, ozone, smoke and other particulates. Man-made smog is derived from coal combustion emissions, vehicular emissions, industrial emissions, forest and agricultural fires and photochemical reactions of these emissions. Smog is often categorized as being either summer smog or winter smog. Summer smog is primarily associated with the photochemical formation of ozone. During the summer season when the temperatures are warmer and there is more sunlight present, photochemical smog is the dominant type of smog formation. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Sunlight
Direct may refer to: Mathematics * Directed set, in order theory * Direct limit of (pre), sheaves * Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces Computing * Direct access (other), a method of accessing data in a database * Direct connect (other), various methods of telecommunications and computer networking * Direct memory access, access to memory by hardware subsystems independently of the CPU Entertainment * ''Direct'' (Tower of Power album) * ''Direct'' (Vangelis album) * ''Direct'' (EP), by The 77s Other uses * Nintendo Direct, an online presentation frequently held by Nintendo * Mars Direct, a proposal for a crewed mission to Mars * DIRECT, a proposed space shuttle-derived launch vehicle * DirectX, a proprietary dynamic media platform * Direct current, a direct flow of electricity * Direct examination, the in-trial questioning of a witness by the party who has called him or her to testify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenith
The zenith (, ) is an imaginary point directly "above" a particular location, on the celestial sphere. "Above" means in the vertical direction (plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere. Origin The word "zenith" derives from an inaccurate reading of the Arabic expression (), meaning "direction of the head" or "path above the head", by Medieval Latin scribes in the Middle Ages (during the 14th century), possibly through Old Spanish. It was reduced to "samt" ("direction") and miswritten as "senit"/"cenit", the "m" being misread as "ni". Through the Old French "cenith", "zenith" first appeared in the 17th century. Relevance and use The term ''zenith'' sometimes means the highest point, way, or level reached by a celestial body on its daily apparent path around a given point of observation. This sense of the word is often used to describe the position of the Sun ("The sun reached its zenit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude (astronomy)
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles: altitude and azimuth. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called as the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth. Definition This celestial coordinate system divides the sky into two hemispheres: The upper hemisphere, where objects are above the horizon and are visible, and the lower hemisphere, where objects are below the horizon and cannot be seen, since the Earth obstructs views of them. The great circle separating the hemispheres is called the celestial horizon, which is defined as the great circle on the celestial sphere whose plane is normal to the local gravity vector. In practice, the horizon can be defined as the plane tangent to a quiet, liquid surface, such as a pool of mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airmass
In astronomy, air mass or airmass is a measure of the amount of air along the line of sight when observing a star or other celestial source from below Earth's atmosphere ( Green 1992). It is formulated as the integral of air density along the light ray. As it penetrates the atmosphere, light is attenuated by scattering and absorption; the thicker atmosphere through which it passes, the greater the attenuation. Consequently, celestial bodies when nearer the horizon appear less bright than when nearer the zenith. This attenuation, known as atmospheric extinction, is described quantitatively by the Beer–Lambert law. "Air mass" normally indicates ''relative air mass'', the ratio of absolute air masses (as defined above) at oblique incidence relative to that at zenith. So, by definition, the relative air mass at the zenith is 1. Air mass increases as the angle between the source and the zenith increases, reaching a value of approximately 38 at the horizon. Air mass can be less than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at , but only 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at . Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: absolute, relative, and specific. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
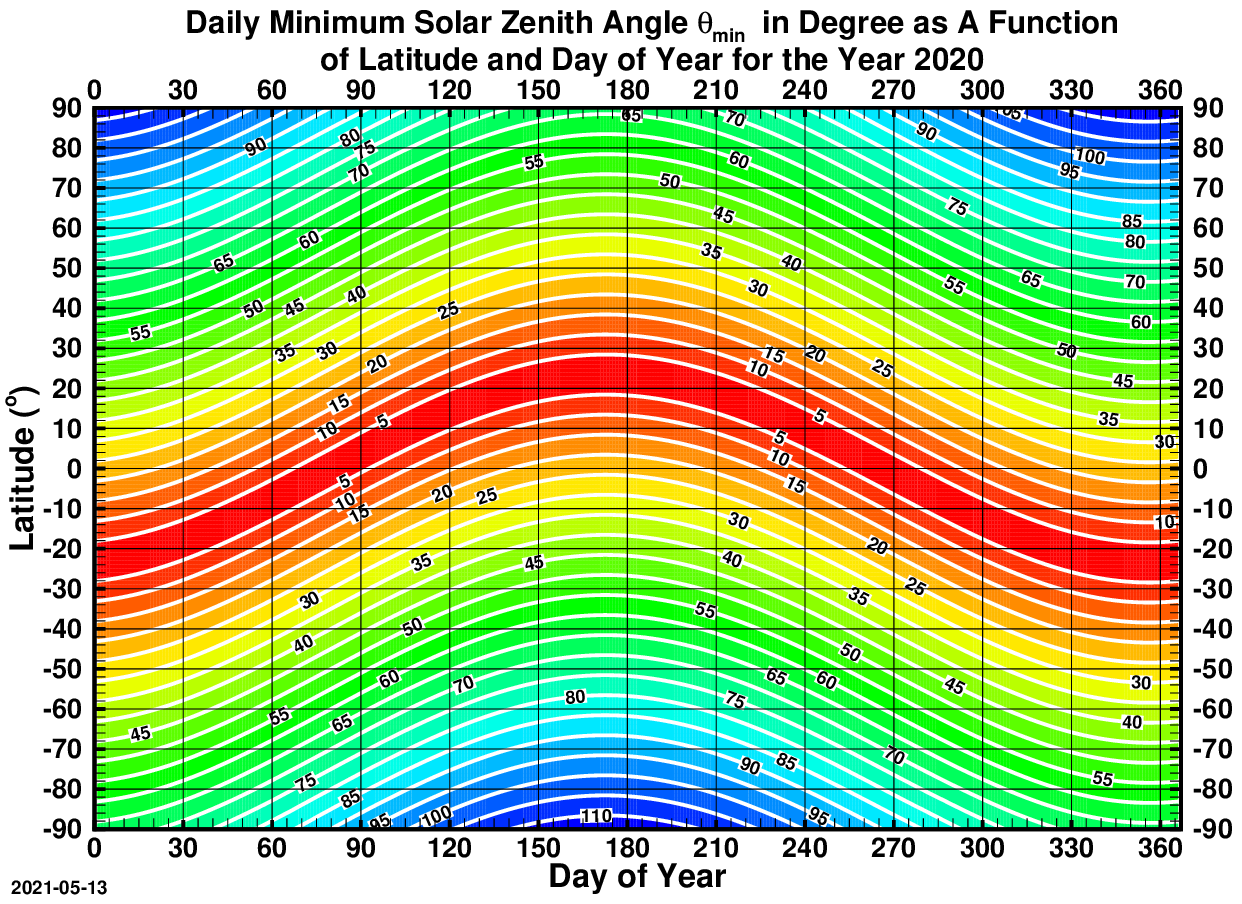
Solar Elevation Angle
The solar zenith angle is the zenith angle of the sun, i.e., the angle between the sun’s rays and the vertical direction. It is the complement to the solar altitude or solar elevation, which is the altitude angle or elevation angle between the sun’s rays and a horizontal plane. At solar noon, the zenith angle is at a minimum and is equal to latitude minus solar declination angle. This is the basis by which ancient mariners navigated the oceans. Solar zenith angle is normally used in combination with the solar azimuth angle to determine the position of the Sun as observed from a given location on the surface of the Earth. Formula : \cos \theta_s = \sin \alpha_s = \sin \Phi \sin \delta + \cos \Phi \cos \delta \cos h where * \theta_s is the ''solar zenith angle'' * \alpha_s is the ''solar altitude angle'', \alpha_s = 90° – \theta_s * h is the hour angle, in the local solar time. * \delta is the current declination of the Sun * \Phi is the local latitude. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a period of minimum activity to a period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified until 1843. Solar activity, driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |