|
Diple (textual Symbol)
Diple ( grc, διπλῆ, meaning double, referring to the two lines in the mark >) was a mark used in the margins of ancient Greek manuscripts to draw attention to something in the text. It is sometimes also called antilambda because the sign resembles a Greek capital letter lambda (Λ) turned upon its side. In some ways its usage was similar to modern day quotation marks; guillemets (« »), used for quotations in French, are derived from it. Isidore remarks in his ''Etymologiae'' (I.21.13) that the diple was used to mark quotations from the Bible. He also talks about ''diple peri strichon'' (or ''sticon''), which was used to draw attention to separate concepts and ''diple periestigmene'' used (like obelos) to mark dubious passages. ''Diple obolismene'' was used according to Isidore to separate sentences in comedies and tragedies, so its usage was similar to that of paragraphos. See also * Usenet quoting * Obelos The obol ( grc-gre, , ''obolos'', also ὀβελό ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comedies
Comedy is a genre of fiction that consists of discourses or works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. The term originated in ancient Greece: in Athenian democracy, the public opinion of voters was influenced by political satire performed by comic poets in theaters. The theatrical genre of Greek comedy can be described as a dramatic performance pitting two groups, ages, genders, or societies against each other in an amusing '' agon'' or conflict. Northrop Frye depicted these two opposing sides as a "Society of Youth" and a "Society of the Old". A revised view characterizes the essential agon of comedy as a struggle between a relatively powerless youth and the societal conventions posing obstacles to his hopes. In this struggle, the youth then becomes constrained by his lack of social authority, and is left with little choice but to resort to ruses wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeography
Palaeography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, UK) or paleography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, US; ultimately from grc-gre, , ''palaiós'', "old", and , ''gráphein'', "to write") is the study of historic writing systems and the deciphering and dating of historical manuscripts, including the analysis of historic handwriting. It is concerned with the forms and processes of writing; not the textual content of documents. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of Scriptorium, scriptoria. The discipline is one of the auxiliary sciences of history. It is important for understanding, authenticating, and dating historic texts. However, it generally cannot be used to pinpoint dates with high precision. Application Palaeography can be an essential skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronis (textual Symbol)
A coronis ( grc, κορωνίς, ''korōnís'', , ''korōnídes'') is a textual symbol found in ancient Greek papyri that was used to mark the end of an entire work or of a major section in poetic and prose texts. The coronis was generally placed in the left-hand margin of the text and was often accompanied by a paragraphos or a forked paragraphos (diple obelismene). The coronis is encoded by Unicode as part of the Supplemental Punctuation block, at . Etymology Liddell and Scott's '' Greek–English Lexicon'' gives the basic meaning of as "crook-beaked" from which a general meaning of "curved" is supposed to have derived. concurs and derives the word from (), "crow", assigning the meaning of the epithet's use in reference to the textual symbol to the same semantic range of "curve". But, given the fact that the earliest coronides actually take the form of birds, there has been debate about whether the name of the textual symbol initially referred to use of a decorativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelism
Obelism is the practice of annotating manuscripts with marks set in the margins. Modern obelisms are used by editors when proofreading a manuscript or typescript. Examples are "stet" (which is Latin for "Let it stand", used in this context to mean "disregard the previous mark") and "dele" (for "Delete"). The obelos symbol (see obelus) gets its name from the spit, or sharp end of a lance in ancient Greek. An obelos was placed by editors on the margins of manuscripts, especially in Homer, to indicate lines that may not have been written by Homer. The system was developed by Aristarchus and notably used later by Origen in his ''Hexapla''. Origen marked spurious words with an opening obelos and a closing metobelos ("end of obelus"). There were many other such shorthand symbols, to indicate corrections, emendations, deletions, additions, and so on. Most used are the editorial coronis, the paragraphos, the forked paragraphos, the reversed forked paragraphos, the hypodiastole, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet Quoting
When Usenet and e-mail users respond to a message, they often want to include some context for the discussion. This is often accomplished by quoting a portion of the original message using Usenet conventions. In essence the convention is to communicate in plain text format (not HTML) and quote with ">" at the beginning of each line, ">>" for a quote of quote, and so on. Most email clients can perform Usenet quoting automatically. Examples Usenet standard quoting refers to the practice of preceding the original message with the ">" (or right-angle bracket) character at the beginning of each line, and then inserting one's responses inline, using no special designator for the author's messages. > hello, how are you? I am fine When a second response is made to the second message, the second message is again quoting with >, perhaps causing parts of the original message to now be designated with >>. Such nested quotations can technically be continued indefinitely, but quickly become c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paragraphos
A paragraphos ( grc, , , from , 'beside', and , 'to write') was a mark in ancient Greek punctuation, marking a division in a text (as between speakers in a dialogue or drama) or drawing the reader's attention to another division mark, such as the two dot punctuation mark . There are many variants of this symbol, sometimes supposed to have developed from Greek gamma (), the first letter of the word . It was usually placed at the beginning of a line and trailing a little way under or over the text. It was referenced by Aristotle, who was dismissive of its use. Unicode encodes multiple versions: * * * See also * Obelus and Obelism, Greek marginal notes * Coronis, the Greek paragraph mark * Pilcrow (¶), the English paragraph mark * Section sign The section sign, §, is a typographical character for referencing individually numbered sections of a document; it is frequently used when citing sections of a legal code. It is also known as the section symbol, section mark, dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragedies
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelism
Obelism is the practice of annotating manuscripts with marks set in the margins. Modern obelisms are used by editors when proofreading a manuscript or typescript. Examples are "stet" (which is Latin for "Let it stand", used in this context to mean "disregard the previous mark") and "dele" (for "Delete"). The obelos symbol (see obelus) gets its name from the spit, or sharp end of a lance in ancient Greek. An obelos was placed by editors on the margins of manuscripts, especially in Homer, to indicate lines that may not have been written by Homer. The system was developed by Aristarchus and notably used later by Origen in his ''Hexapla''. Origen marked spurious words with an opening obelos and a closing metobelos ("end of obelus"). There were many other such shorthand symbols, to indicate corrections, emendations, deletions, additions, and so on. Most used are the editorial coronis, the paragraphos, the forked paragraphos, the reversed forked paragraphos, the hypodiastole, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginalia
Marginalia (or apostils) are marks made in the margins of a book or other document. They may be scribbles, comments, glosses (annotations), critiques, doodles, drolleries, or illuminations. Biblical manuscripts Biblical manuscripts have liturgical notes at the margin, for liturgical use. Numbers of texts' divisions are given at the margin (, Ammonian Sections, Eusebian Canons). There are some scholia, corrections and other notes usually made later by hand in the margin. Marginalia may also be of relevance because many ancient or medieval writers of marginalia may have had access to other relevant texts that, although they may have been widely copied at the time, have since then been lost due to wars, prosecution, or censorship. As such, they might give clues to an earlier, more widely known context of the extant form of the underlying text than is currently appreciated. For this reason, scholars of ancient texts usually try to find as many still existing manuscripts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymologiae
''Etymologiae'' (Latin for "The Etymologies"), also known as the ''Origines'' ("Origins") and usually abbreviated ''Orig.'', is an etymological encyclopedia compiled by Isidore of Seville (c. 560–636) towards the end of his life. Isidore was encouraged to write the book by his friend Braulio, Bishop of Saragossa. ''The Etymologies'' summarized and organized a wealth of knowledge from hundreds of classical sources; three of its books are derived largely from Pliny the Elder's '' Natural History''. Isidore acknowledges Pliny, but not his other principal sources, namely Cassiodorus, Servius and Solinus. The work contains whatever Isidore, an influential Christian bishop, thought worth keeping. ''Etymologiae'' covers an encyclopedic range of topics. Etymology, the origins of words, is prominent, but the work covers among other things: grammar, rhetoric, mathematics, geometry, music, astronomy, medicine, law, the Roman Catholic Church and heretical sects, pagan philosophers, lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



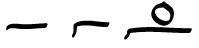


.jpg)
