|
Diminished Fourth
In classical music from Western culture, a diminished fourth () is an interval produced by narrowing a perfect fourth by a chromatic semitone.Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . Specific example of an d4 not given but general example of perfect intervals described. For example, the interval from C to F is a perfect fourth, five semitones wide, and both the intervals from C to F, and from C to F are diminished fourths, spanning four semitones. Being diminished, it is considered a dissonant interval. A diminished fourth is enharmonically equivalent to a major third; that is, it spans the same number of semitones, and they are physically the same pitch in twelve-tone equal temperament. For example, B–D is a major third; but if the same pitches are spelled B and E, as occurs in the C harmonic minor scale, the interval is instead a diminished fourth. In other tunings, however, they are not necessarily identical. For example, in 31 equal tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Fifth
In classical music from Western culture, an augmented fifth () is an interval produced by widening a perfect fifth by a chromatic semitone.Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . For instance, the interval from C to G is a perfect fifth, seven semitones wide, and both the intervals from C to G, and from C to G are augmented fifths, spanning eight semitones. Being augmented, it is considered a dissonant interval. Its inversion is the diminished fourth, and its enharmonic equivalent is the minor sixth. The augmented fifth only began to make an appearance at the beginning of the common practice period of music as a consequence of composers seeking to strengthen the normally weak seventh degree when composing music in minor modes. This was achieved by chromatically raising the seventh degree (or subtonic) to match that of the unstable seventh degree (or leading tone) of the major mode (an increasingly widespread practice that led to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonically Equivalent
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schismatic Temperament
A schismatic temperament is a musical tuning system that results from tempering the schisma of 32805:32768 (1.9537 cents) to a unison. It is also called the schismic temperament, Helmholtz temperament, or quasi-Pythagorean temperament. Construction In Pythagorean tuning all notes are tuned as a number of perfect fifths (701.96 cents ). The major third above C, E, is considered four fifths above C. This causes the Pythagorean major third, E (407.82 cents ), to differ from the just major third, E (386.31 cents ): the Pythagorean third is sharper than the just third by 21.51 cents (a syntonic comma ). C — G — D — A — E Ellis's "skhismic temperament". instead uses the note eight fifths ''below'' C, F (384.36 cents ), the Pythagorean diminished fourth or schismatic major third. Though spelled "incorrectly" for a major third, this note is only 1.95 cents (a schisma) flat of E, and thus more in tune than the Pythagorean major third. As Ellis puts it, "the Fifths should be p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimal Major Third
In music, the septimal major third , also called the supermajor third (by Hermann von Helmholtz among others Hermann L. F. von Helmholtz (2007). ''Sensations of Tone'', p. 187. .) and sometimes '' Bohlen–Pierce third'' is the musical interval exactly or approximately equal to a just 9:7 ratioAndrew Horner, Lydia Ayres (2002). ''Cooking with Csound: Woodwind and Brass Recipes'', p. 131. . "Super-Major Second". of frequencies, or alternately 14:11. It is equal to 435 cents, sharper than a just major third (5:4) by the septimal quarter tone (36:35) (). In 24-TET the septimal major third is approximated by 9 quarter tones, or 450 cents (). Both 24 and 19 equal temperament map the septimal major third and the septimal narrow fourth (21:16) to the same interval. The septimal major third has a characteristic brassy sound which is much less sweet than a pure major third, but is classed as a 9-limit consonance. Together with the root 1:1 and the perfect fifth of 3:2, it makes up the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
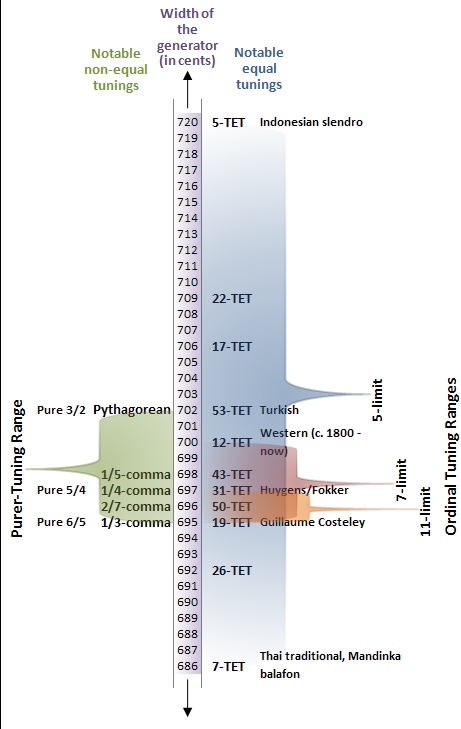
31 Equal Temperament
In music, 31 equal temperament, 31-ET, which can also be abbreviated 31-TET (31 tone ET) or 31-EDO (equal division of the octave), also known as tricesimoprimal, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 31 equal-sized steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 38.71 cents (). 31-ET is a very good approximation of quarter-comma meantone temperament. More generally, it is a regular diatonic tuning in which the tempered perfect fifth is equal to 696.77 cents, as shown in Figure 1. On an isomorphic keyboard, the fingering of music composed in 31-ET is precisely the same as it is in any other syntonic tuning (such as 12-ET), so long as the notes are spelled properly — that is, with no assumption of enharmonicity. History and use Division of the octave into 31 steps arose naturally out of Renaissance music theory; the lesser diesis — the ratio of an octave to three major thirds, 128:125 or 41.06 cents — was approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Minor Scale
In music theory, the minor scale is three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending) – rather than just two as with the major scale, which also has a harmonic form but lacks a melodic form. In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifth scale degrees form a minor triad (rather than a major triad, as in a major scale). In some contexts, ''minor scale'' is used to refer to any heptatonic scale with this property (see Related modes below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relative minor'' of C major. Every major key has a relative minor, which star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Third
In classical music, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four semitones. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept and Practice'', p.8. Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. Third edition . "A large 3rd, or ''major 3rd'' (M3) encompassing four half steps." Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is qualified as ''major'' because it is the larger of the two: the major third spans four semitones, the minor third three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished and augmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five). The major third may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the fourth and fifth harmonics. The maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonance And Dissonance
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unpleasantness, or unacceptability, although there is broad acknowledgement that this depends also on familiarity and musical expertise. The terms form a structural dichotomy in which they define each other by mutual exclusion: a consonance is what is not dissonant, and a dissonance is what is not consonant. However, a finer consideration shows that the distinction forms a gradation, from the most consonant to the most dissonant. In casual discourse, as German composer and music theorist Paul Hindemith stressed, "The two concepts have never been completely explained, and for a thousand years the definitions have varied". The term ''sonance'' has been proposed to encompass or refer indistinctly to the terms ''consonance'' and ''dissonance''. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Fourth On C
Diminished may refer to: *Diminution In Western music and music theory, diminution (from Medieval Latin ''diminutio'', alteration of Latin ''deminutio'', decrease) has four distinct meanings. Diminution may be a form of embellishment in which a long note is divided into a series ... in music * "Diminished" (R.E.M. song), from the 1998 album ''Up'' {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Semitone
In modern Western tonal music theory an augmented unison or augmented prime is the interval between two notes on the same staff position, or denoted by the same note letter, whose alterations cause them, in ordinary equal temperament, to be one semitone apart. In other words, it is a unison where one note has been altered by a half-step, such as B and B or C and C. The interval is often described as a chromatic semitone. The term, in its French form ''unisson superflu'', appears to have been coined by Jean-Philippe Rameau in 1722, who also called this interval a minor semitone (''semiton mineur'').Gene Henry Anderson, "Musical Terminology in J.-P. Rameau's ''Traité de l'harmonie'': A Study and Glossary Based on an Index". PhD diss. (Iowa City: University of Iowa, 1981): 196. Historically, this interval, like the tritone, is described as being "mi contra fa", and therefore is the "diabolus in musica" (the Devil in music). In 12-tone equal temperament, it is the enharmonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Fourth
A fourth is a musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending interval from C to the next F is a perfect fourth, because the note F is the fifth semitone above C, and there are four staff positions between C and F. Diminished and augmented fourths span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (four and six, respectively). The perfect fourth may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the third and fourth harmonics. The term ''perfect'' identifies this interval as belonging to the group of perfect intervals, so called because they are neither major nor minor. A perfect fourth in just intonation corresponds to a pitch ratio of 4:3, or about 498 cents (), while in equal temperament a perfect fourth is equal to five semitones, or 500 cents (see additive synth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |