|
Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL) or diagnostic peritoneal aspiration (DPA) is a surgical diagnostic procedure to determine if there is free floating fluid (most often blood) in the abdominal cavity. Indications This procedure is performed when intra-abdominal bleeding (hemoperitoneum), usually secondary to trauma, is suspected. In a hemodynamically unstable patient with high-risk mechanism of injury, peritoneal lavage is a means of rapidly diagnosing intra-abdominal injury requiring laparotomy, but has largely been replaced in trauma care by the use of a focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST scan) due to its repeatability, non-invasiveness and non-interference with subsequent computed tomography (CT scan). Abdominal CT and contrast duodenography may complement lavage in stable patients, but in an unstable or uncooperative persons, these studies are too time-consuming or require ill-advised sedation. Magnetic resonance imaging is extremely accurate for the anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis. Structure Organs Organs of the abdominal cavity include the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, kidneys, large intestine, and adrenal glands. Peritoneum The abdominal cavity is lined with a protective membrane termed the peritoneum. The inside wall is covered by the parietal peritoneum. The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, in the retroperitoneum, outside the abdominal cavity. The viscera are also covered by visceral peritoneum. Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity, which is a potential space. It contains a serous fluid called peritoneal fluid tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linea Alba (abdomen)
The linea alba ( la, white line) is a fibrous structure that runs down the midline of the abdomen in humans and other vertebrates. Structure In humans, the linea alba runs from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis down the midline of the abdomen. The name means ''white line'' as it is composed mostly of collagen connective tissue, which has a white appearance. It is formed by the fusion of the aponeuroses of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. It separates the left and right rectus abdominis muscles. In muscular individuals, its presence can be seen on the skin, forming the depression between the left and right halves of a " six pack". Function The Linea alba stabilizes the anterior abdominal wall, as it balances contractile forces from the muscles attached to it. Clinical significance A median incision through the linea alba is a common surgical approach for abdominal surgery. This is because it consists of mostly connective tissue, and does not contain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneal Washing
Peritoneal washing is a procedure used to look for malignant cells, i.e. cancer, in the peritoneum. Peritoneal washes are routinely done to stage abdominal and pelvic tumours, e.g. ovarian cancer. See also * Peritoneal lavage Additional images Image:Mesothelium peritoneal wash high mag.jpg , Benign mesothelium. Image:Serous carcinoma cytology.jpg , Serous carcinoma A serous tumour is a neoplasm that typically has papillary to solid formations of tumor cells with crowded nuclei, and which typically arises on the modified Mullerian-derived serous membranes that surround the ovaries in females. Such ovarian t .... References {{reflist External linksPeritoneal washing Pathology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile) and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum. The composition of hepatic bile is (97–98)% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About 400 to 800 millilitres of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. Bile salt anions are hydrophilic on one side and hydrophobic on the other side; consequently, they tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have cell nucleus, nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell division, cell lineage (myelocyte, myeloid cells or lymphocyte, lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called "subp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
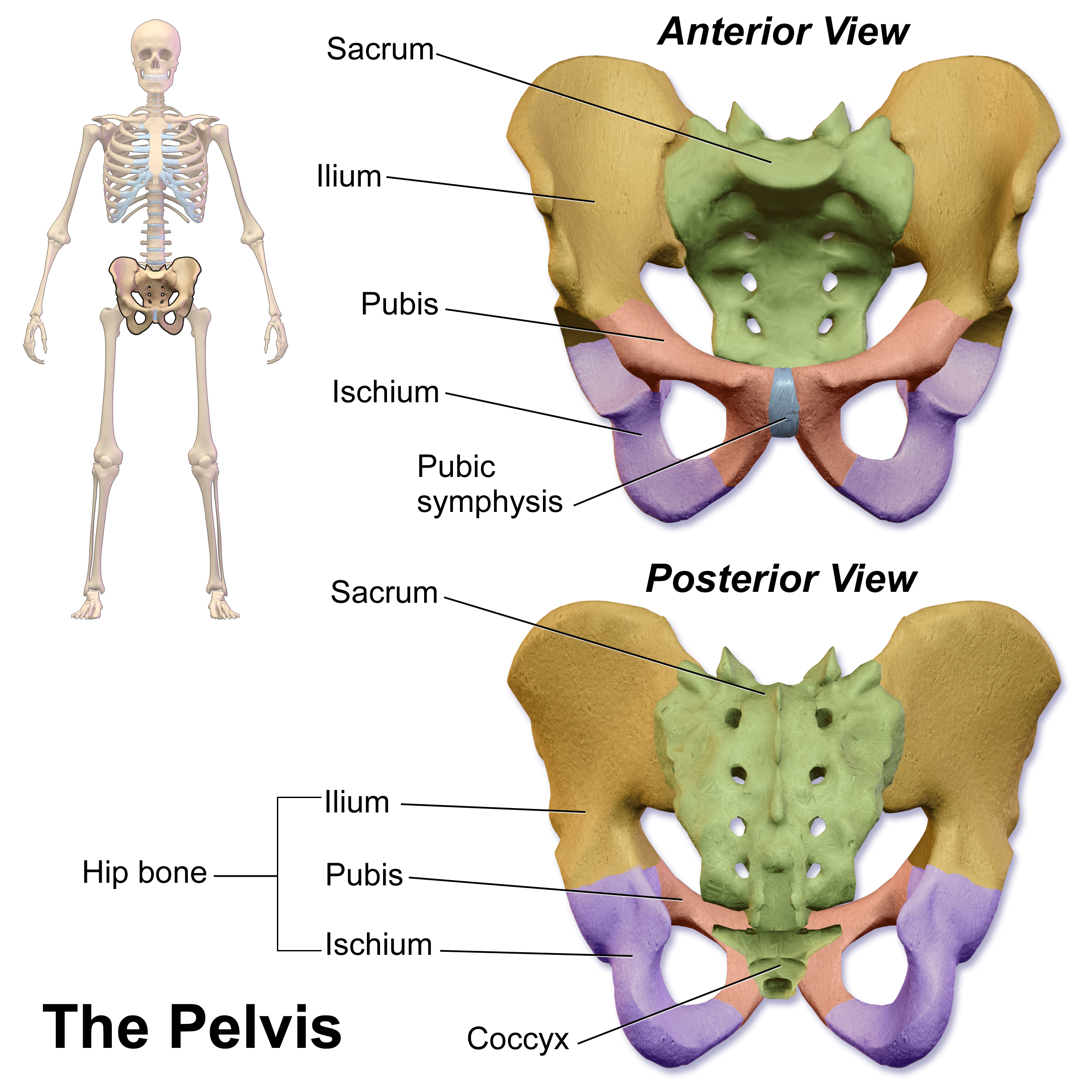
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoperitoneum
Hemoperitoneum (also haemoperitoneum, sometimes also hematoperitoneum) is the presence of blood in the peritoneal cavity. The blood accumulates in the space between the inner lining of the abdominal wall and the internal abdominal organs. Hemoperitoneum is generally classified as a surgical emergency; in most cases, urgent laparotomy is needed to identify and control the source of the bleeding. In selected cases, careful observation may be permissible. The abdominal cavity is highly distensible and may easily hold greater than five liters of blood, or more than the entire circulating blood volume for an average-sized individual. Therefore, large-scale or rapid blood loss into the abdomen will reliably induce hemorrhagic shock and, if untreated, may rapidly lead to death. Causes Causes of hemoperitoneum include: * Penetrating trauma * Blunt trauma, most commonly injuries to solid organs such as the liver and spleen. * Vascular accidents, such as rupture of an abdominal aortic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus, commonly known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals have a navel, although it is generally more conspicuous in humans. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, that is, local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It allows patients to undergo surgical and dental procedures with reduced pain and distress. In many situations, such as cesarean section, it is safer and therefore superior to general anesthesia. The following terms are often used interchangeably: * ''Local anesthesia'', in a strict sense, is anesthesia of a small part of the body such as a tooth or an area of skin. * ''Regional anesthesia'' is aimed at anesthetizing a larger part of the body such as a leg or arm. * ''Conduction anesthesia'' encompasses a great variety of local and regional anesthetic techniques. Medical A local anesthetic is a drug that causes reversible local anesthesia and a loss of nociception. When it is used on specific nerve pathways (nerve block), effects such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |