|
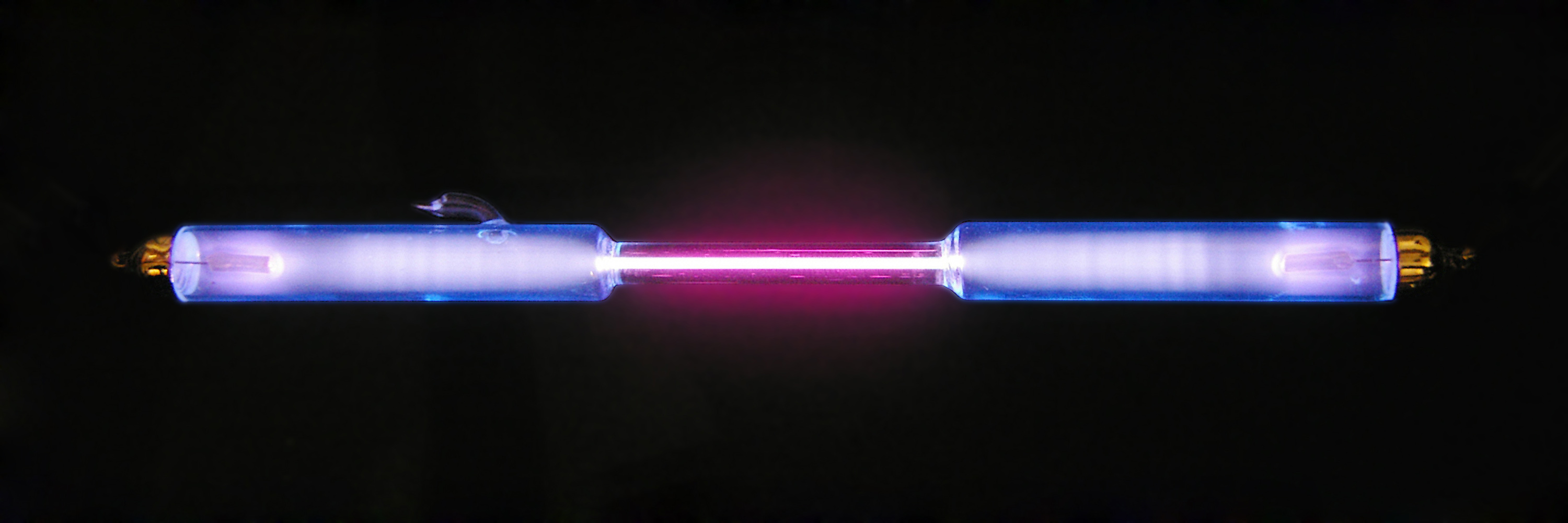
Deuterium Exchange Measurement
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). ( Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Nuclides
A table or chart of nuclides is a two-dimensional graph of isotopes of the elements, in which one axis represents the number of neutrons (symbol ''N'') and the other represents the number of protons (atomic number, symbol ''Z'') in the atomic nucleus. Each point plotted on the graph thus represents a nuclide of a known or hypothetical chemical element. This system of ordering nuclides can offer a greater insight into the characteristics of isotopes than the better-known periodic table, which shows only elements and not their isotopes. The chart of the nuclides is also known as the Segrè chart, after the Italian physicist Emilio Segrè. Description and utility A chart or table of nuclides maps the nuclear, or radioactive, behavior of nuclides, as it distinguishes the isotopes of an element. It contrasts with a periodic table, which only maps their chemical behavior, since isotopes (nuclides which are variants of the same element) do not differ chemically to any significant deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |