|
Deltopectoral Lymph Nodes
One or two deltopectoral lymph nodes (or infraclavicular nodes) are found beside the cephalic vein, between the pectoralis major and deltoideus, immediately below the clavicle The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the rig .... They are situated in the course of the external collecting trunks of the arm. Additional images File:Gray606.png, The superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of the upper extremity. References External links Lymphatics of the upper limb {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Lymph Nodes
An apical (or medial or subclavicular) group of six to twelve glands is situated partly posterior to the upper portion of the Pectoralis minor and partly above the upper border of this muscle. Its only direct territorial afferents are those that accompany the cephalic vein, and one that drains the upper peripheral part of the mamma. However, it receives the efferents of all the other axillary glands. The efferent vessels of the subclavicular group unite to form the subclavian trunk, which opens either directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins or into the jugular lymphatic trunk; on the left side it may end in the thoracic duct. A few efferents from the subclavicular glands usually pass to the inferior deep cervical glands The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes extend beyond the posterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid muscle into the subclavian triangle, where they are closely related to the brachial plexus and subclavian vein The subclavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein is a superficial vein in the arm. It originates from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein. Anatomy The cephalic vein is situated within the superficial fascia along the anterolateral surface of the biceps. Origin The cephalic vein forms over the anatomical snuffbox at the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand. Course and relations From its origin, it ascends ascends up the lateral aspect of the radius. Near the shoulder, the cephalic vein passes between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles (deltopectoral groove) and through the clavipectoral triangle, where it empties into the axillary vein. Anastomoses It communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein at the elbow. Clinical significance The cephalic vein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoralis Major
The pectoralis major () is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor, a thin, triangular muscle. The pectoralis major's primary functions are flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of the humerus. The pectoral major may colloquially be referred to as "pecs", "pectoral muscle", or "chest muscle", because it is the largest and most superficial muscle in the chest area. Structure It arises from the anterior surface of the sternal half of the clavicle from breadth of the half of the anterior surface of the sternum, as low down as the attachment of the cartilage of the sixth or seventh rib; from the cartilages of all the true ribs, with the exception, frequently, of the first or seventh, and from the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. From this extensive origin the fibers converge toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoideus
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek capital letter delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further shortened in slang as "delt". A study of 30 shoulders revealed an average mass of in humans, ranging from to . Structure Previous studies showed that the insertions of the tendons of the delto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
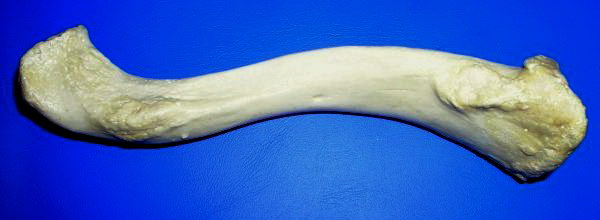
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |