|
Covariation
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when the greater values of one variable mainly correspond to the lesser values of the other, (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The sign of the covariance therefore shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. The magnitude of the covariance is not easy to interpret because it is not normalized and hence depends on the magnitudes of the variables. The normalized version of the covariance, the correlation coefficient, however, shows by its magnitude the strength of the linear relation. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of two random ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance Trends
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when the greater values of one variable mainly correspond to the lesser values of the other, (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The sign of the covariance therefore shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. The magnitude of the covariance is not easy to interpret because it is not normalized and hence depends on the magnitudes of the variables. The normalized version of the covariance, the correlation coefficient, however, shows by its magnitude the strength of the linear relation. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of two ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catastrophic Cancellation
In numerical analysis, catastrophic cancellation is the phenomenon that subtracting good approximations to two nearby numbers may yield a very bad approximation to the difference of the original numbers. For example, if there are two studs, one L_1 = 254.5\,\text long and the other L_2 = 253.5\,\text long, and they are measured with a ruler that is good only to the centimeter, then the approximations could come out to be \tilde L_1 = 255\,\text and \tilde L_2 = 253\,\text. These may be good approximations, in relative error, to the true lengths: the approximations are in error by less than 2% of the true lengths, , L_1 - \tilde L_1, /, L_1, < 2\%. However, if the ''approximate'' lengths are subtracted, the difference will be , even though the true difference between the lengths is . The difference of the approximations, |
Normally Distributed And Uncorrelated Does Not Imply Independent
In probability theory, although simple examples illustrate that linear uncorrelatedness of two random variables does not in general imply their independence, it is sometimes mistakenly thought that it does imply that when the two random variables are normally distributed. This article demonstrates that assumption of normal distributions does not have that consequence, although the multivariate normal distribution, including the bivariate normal distribution, does. To say that the pair (X,Y) of random variables has a bivariate normal distribution means that every linear combination aX+bY of X and Y for constant (i.e. not random) coefficients a and b (not both equal to zero) has a univariate normal distribution. In that case, if X and Y are uncorrelated then they are independent. However, it is possible for two random variables X and Y to be so distributed jointly that each one alone is marginally normally distributed, and they are uncorrelated, but they are not independent; example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the multivariate normal distribution, multivariate Gaussian distribution, or joint normal distribution is a generalization of the one-dimensional (univariate) normal distribution to higher dimensions. One definition is that a random vector is said to be ''k''-variate normally distributed if every linear combination of its ''k'' components has a univariate normal distribution. Its importance derives mainly from the multivariate central limit theorem. The multivariate normal distribution is often used to describe, at least approximately, any set of (possibly) correlated real-valued random variables each of which clusters around a mean value. Definitions Notation and parameterization The multivariate normal distribution of a ''k''-dimensional random vector \mathbf = (X_1,\ldots,X_k)^ can be written in the following notation: : \mathbf\ \sim\ \mathcal(\boldsymbol\mu,\, \boldsymbol\Sigma), or to make it explicitly known that ''X'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Independence
Independence is a fundamental notion in probability theory, as in statistics and the theory of stochastic processes. Two events are independent, statistically independent, or stochastically independent if, informally speaking, the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other or, equivalently, does not affect the odds. Similarly, two random variables are independent if the realization of one does not affect the probability distribution of the other. When dealing with collections of more than two events, two notions of independence need to be distinguished. The events are called pairwise independent if any two events in the collection are independent of each other, while mutual independence (or collective independence) of events means, informally speaking, that each event is independent of any combination of other events in the collection. A similar notion exists for collections of random variables. Mutual independence implies pairwise independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance Matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix (also known as auto-covariance matrix, dispersion matrix, variance matrix, or variance–covariance matrix) is a square matrix giving the covariance between each pair of elements of a given random vector. Any covariance matrix is symmetric and positive semi-definite and its main diagonal contains variances (i.e., the covariance of each element with itself). Intuitively, the covariance matrix generalizes the notion of variance to multiple dimensions. As an example, the variation in a collection of random points in two-dimensional space cannot be characterized fully by a single number, nor would the variances in the x and y directions contain all of the necessary information; a 2 \times 2 matrix would be necessary to fully characterize the two-dimensional variation. The covariance matrix of a random vector \mathbf is typically denoted by \operatorname_ or \Sigma. Definition Throughout this article, boldfaced unsubsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncorrelated
In probability theory and statistics, two real-valued random variables, X, Y, are said to be uncorrelated if their covariance, \operatorname ,Y= \operatorname Y- \operatorname \operatorname /math>, is zero. If two variables are uncorrelated, there is no linear relationship between them. Uncorrelated random variables have a Pearson correlation coefficient, when it exists, of zero, except in the trivial case when either variable has zero variance (is a constant). In this case the correlation is undefined. In general, uncorrelatedness is not the same as orthogonality, except in the special case where at least one of the two random variables has an expected value of 0. In this case, the covariance is the expectation of the product, and X and Y are uncorrelated if and only if \operatorname Y= 0. If X and Y are independent, with finite second moments, then they are uncorrelated. However, not all uncorrelated variables are independent. Definition Definition for two real random varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. It gives the probabilities of various values of the variables in the subset without reference to the values of the other variables. This contrasts with a conditional distribution, which gives the probabilities contingent upon the values of the other variables. Marginal variables are those variables in the subset of variables being retained. These concepts are "marginal" because they can be found by summing values in a table along rows or columns, and writing the sum in the margins of the table. The distribution of the marginal variables (the marginal distribution) is obtained by marginalizing (that is, focusing on the sums in the margin) over the distribution of the variables being discarded, and the discarded variables are said to have been marginalized out. The context here is that the theoretical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covariance Geometric Visualisation
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the lesser values (that is, the variables tend to show similar behavior), the covariance is positive. In the opposite case, when the greater values of one variable mainly correspond to the lesser values of the other, (that is, the variables tend to show opposite behavior), the covariance is negative. The sign of the covariance therefore shows the tendency in the linear relationship between the variables. The magnitude of the covariance is not easy to interpret because it is not normalized and hence depends on the magnitudes of the variables. The normalized version of the covariance, the correlation coefficient, however, shows by its magnitude the strength of the linear relation. A distinction must be made between (1) the covariance of two rand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-covariance
In probability theory and statistics, complex random variables are a generalization of real-valued random variables to complex numbers, i.e. the possible values a complex random variable may take are complex numbers. Complex random variables can always be considered as pairs of real random variables: their real and imaginary parts. Therefore, the distribution of one complex random variable may be interpreted as the joint distribution of two real random variables. Some concepts of real random variables have a straightforward generalization to complex random variables—e.g., the definition of the mean of a complex random variable. Other concepts are unique to complex random variables. Applications of complex random variables are found in digital signal processing, quadrature amplitude modulation and information theory. Definition A complex random variable Z on the probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,P) is a function Z \colon \Omega \rightarrow \mathbb such that both its real part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
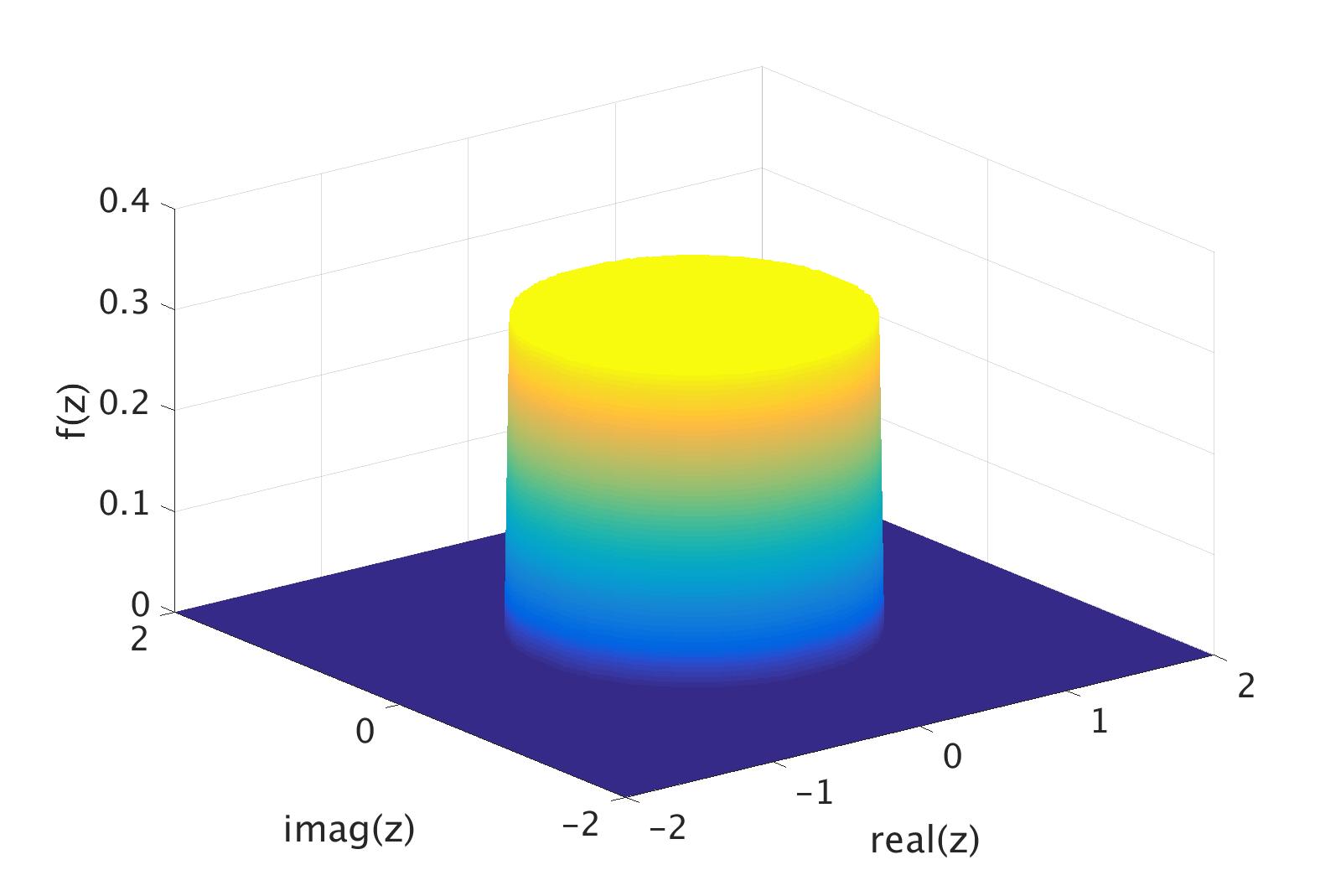
Complex Random Variable
In probability theory and statistics, complex random variables are a generalization of real-valued random variables to complex numbers, i.e. the possible values a complex random variable may take are complex numbers. Complex random variables can always be considered as pairs of real random variables: their real and imaginary parts. Therefore, the distribution of one complex random variable may be interpreted as the joint distribution of two real random variables. Some concepts of real random variables have a straightforward generalization to complex random variables—e.g., the definition of the mean of a complex random variable. Other concepts are unique to complex random variables. Applications of complex random variables are found in digital signal processing, quadrature amplitude modulation and information theory. Definition A complex random variable Z on the probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,P) is a function Z \colon \Omega \rightarrow \mathbb such that both its real part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Number
A dimensionless quantity (also known as a bare quantity, pure quantity, or scalar quantity as well as quantity of dimension one) is a quantity to which no physical dimension is assigned, with a corresponding SI unit of measurement of one (or 1), ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. which is not explicitly shown. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in many fields, such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering, and economics. Dimensionless quantities are distinct from quantities that have associated dimensions, such as time (measured in seconds). Dimensionless units are dimensionless values that serve as units of measurement for expressing other quantities, such as radians (rad) or steradians (sr) for plane angles and solid angles, respectively. For example, optical extent is defined as having units of metres multiplied by steradians. History Quantities having dimension one, ''dimensionless quantities'', regularly occur in sciences, and are formally treated within the field of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |