|
Cottonclad
Cottonclads were a classification of steam-powered warships where a wooden ship was protected from enemy fire by bales of cotton lining its sides. Cottonclads were prevalent during the American Civil War, particularly in the Confederate States Navy for riverine and coastal service such as in the battles of Memphis, Galveston, and Sabine Pass. Confederate tactics generally had cottonclads, which were outgunned by Union warships, steam at full speed towards enemy vessels, relying on the cotton to absorb fire. Once they were within firing range, they would open fire, and, if possible, ram or board the enemy. Conversion Around 1863, Confederate Commander John B. Magruder realized that Texas did not possess the funding and resources—such as iron mills—to produce impressive and potent vessels such as the ironclad CSS Virginia, thus inspiring the development of a new type of warship, later classified as a cottonclad warship. Cottonclads were various kinds of steamboats transformed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Memphis
The First Battle of Memphis was a naval battle fought on the Mississippi River immediately North of the city of Memphis, Tennessee on June 6, 1862, during the American Civil War. The engagement was witnessed by many of the citizens of Memphis. It resulted in a crushing defeat for the Confederate forces, and marked the virtual eradication of a Confederate naval presence on the river. Despite the lopsided outcome, the Union Army failed to grasp its strategic significance. Its primary historical importance is that it was the last time civilians with no prior military experience were permitted to command ships in combat. As such, it is a milestone in the development of professionalism in the United States Navy. Background The defending Confederates closely matched the advancing federal force in raw numbers, with eight rebel vessels opposing nine Union gunboats and rams, but the fighting qualities of the former were far inferior. Each was armed with only one or two guns, of a light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS General Sterling Price
''Laurent Millaudon'' was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS ''General Sterling Price''. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS ''General Price'' and served until the end of the war. (''Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships'', 1968, p. 525) CSS ''General Sterling Price'' CSS ''General Sterling Price'', often referred to as ''General Price'' or ''Price'', was built as ''Laurent Millaudon'', (or ''L. Millandon'' or ''Milledon'') at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856. She was acquired for Confederate service and fitted out at New Orleans, Louisiana, for the River Defense Fleet (See DANFS appendix II) and was renamed after the Confederate general Sterling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Stonewall Jackson
CSS ''Stonewall Jackson'' was a cotton-clad sidewheel ram of the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. ''Stonewall Jackson'' was selected in January 1862, by Capt. James E. Montgomery to be part of his River Defense Fleet at New Orleans. On 25 January Montgomery began to convert her into a cottonclad ram by placing a oak sheath with iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads fitted with compressed cotton bales. Service history ''Stonewall Jackson''s conversion was completed on 16 March 1862. Under Capt. G. M. Phillips she was detached from Montgomery's main force and sent to Forts Jackson and St. Philip on the lower Mississippi to cooperate in the Confederate defense of New Orleans. There, with five other vessels of Montgomery's fleet, all under Capt. J. A. Stevenson, she joined the force under Capt. J. K. Mitchell, CSN, commanding Confederate naval forces in the lower Mississippi. On 24 April 1862 a Union fleet under Flag Officer David F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Governor Moore
LSNS ''Governor Moore'' was a schooner-rigged steamer in the Confederate States Navy. ''Governor Moore'' had been Southern S. S. Company's ''Charles Morgan'', named for the firm's founder and built at New York in 1854 as a schooner-rigged, low pressure, walking beam-engined, seagoing steamer. She was seized at New Orleans, Louisiana by Brigadier General Mansfield Lovell, CSA, in mid-January 1862 "for the public service." As a gunboat, renamed for Louisiana's Governor Thomas Overton Moore, her stem was reinforced for ramming by two strips of flat railroad iron at the waterline, strapped and bolted in place, with pine lumber and cotton-bale barricades to protect her boilers, but the ''Governor Moore'' was never commissioned as a ship in the Confederate States Navy. The larger of two similar cotton-clads owned and operated by the State of Louisiana, ''Governor Moore'' was commanded for some time by Lieutenant Beverly Kennon, CSN, then serving as Commander in the Louisiana Provis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS General Bragg (1851)
USS ''General Bragg'' was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America. Service history ''General Bragg'' was originally the 1043-ton side-wheel river steamer ''Mexico'' and was built in New York City in 1851. She was owned by the Southern Steamship Co. at the start of the American Civil War. ''Mexico'' was pressed into Confederate service as CSS ''General Bragg'' at New Orleans, Louisiana 15 January 1862. She was converted to a "cottonclad" ram and renamed for General Braxton Bragg, a western theater commander. As part of the River Defense Fleet, she took part in the defenses of Memphis, Tennessee, and the surrounding area. In an action off Fort Pillow on 10 May 1862 she helped sink the Union Navy ironclad (later raised and refitted) and was put out of action herself. On 6 June, she w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulwark (nautical)
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin ''nauticus'', from Greek ''nautikos'', from ''nautēs'': "sailor", from ''naus'': "ship". Further information on nautical terminology may also be found at Nautical metaphors in English, and additional military terms are listed in the Multiservice tactical brevity code article. Terms used in other fields associated with bodies of water can be found at Glossary of fishery terms, Glossary of underwater diving terminology, Glossary of rowing terms, and Glossary of meteorology. This glossary is split into two articles: * terms starting with the letters A to L are at Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) * terms starting with the letters M to Z are at Glossary of nautical terms (M-Z). __NO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
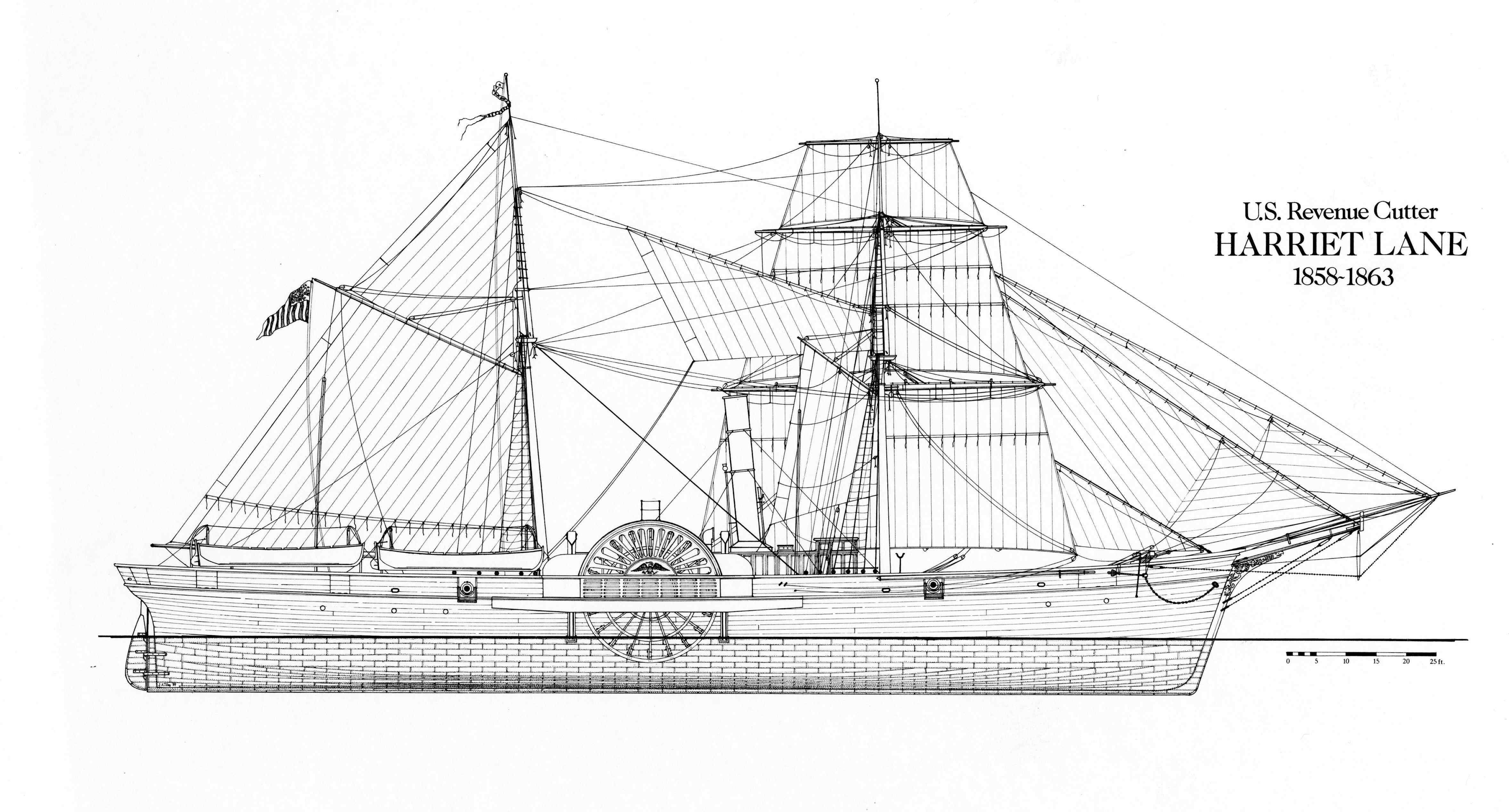
USRC Harriet Lane (1857)
''Harriet Lane'' was a revenue cutter of the United States Revenue Cutter Service and, on the outbreak of the American Civil War, a ship of the United States Navy and later Confederate States Navy. The craft was named after the niece of senator and later United States President, James Buchanan; during his presidency, she acted as First Lady. The cutter was christened and entered the water for the Revenue Service in 1859 out of New York City, and saw action during the Civil War at Fort Sumter, New Orleans, Galveston, Texas, and Virginia Point. The Confederates captured her in 1863, whereupon she was converted to mercantile service. Union forces recaptured her at the end of war. The U.S. Navy declared her unfit for service and sold her. New owners out of Philadelphia renamed her ''Elliot Ritchie''. Her crew abandoned her at sea in 1881. Layout of the ship ''Harriet Lane'' measured 177.5 feet long, 30.5 feet wide and 12 feet from the bottom of the hull to the main deck. Her pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Smith (naval Commander)
Leonidas R. Smith (1829 – December 26, 1869) was an American steamboat captain and soldier. In the American Civil War he served the Confederate States of America as a volunteer; he was named Commander of the Texas Marine Department under General John B. Magruder. Smith was involved in most major conflicts along the Texas coast during the war, and was described by war-time governor of Texas Francis Lubbock as "undoubtedly the ablest Confederate naval commander in the Gulf waters". Personal life and family Smith was born in Portsmouth, New Hampshire in 1829. He was a Freemason, and according to some wartime and post-war reports, Caleb Blood Smith, a cabinet member under President Lincoln, was his half-brother. New York Times, 23 Feb 1863 Smith was married, and had a son, named Leon B. Smith. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Galveston
The Battle of Galveston was a naval and land battle of the American Civil War, when Confederate forces under Major Gen. John B. Magruder expelled occupying Union troops from the city of Galveston, Texas on January 1, 1863. After the loss of the cutter , the Union Fleet Commander William B. Renshaw blew up the stranded vessel to save it from falling into enemy hands. Union troops on shore thought the fleet was surrendering, and laid down their arms. The battle is sometimes called the Second Battle of Galveston, as the Battle of Galveston Harbor (October 1862) is sometimes called the First Battle of Galveston. Battle Two Confederate cottonclads, and the commanded by Leon Smith, sailed from Houston to Galveston in an effort to engage the Union Fleet in Galveston Harbor, which consisted of , , , , and . Outnumbered six to two by the Northern ships, ''Neptune'' was severely damaged by the Union Fleet and eventually sank. While ''Neptune'' was quickly disabled, ''Bayou City' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Little Rebel (1859)
''Little Rebel'' was a cotton-clad ram that had been converted from a Mississippi River steamer to serve as the flagship of the Confederate River Defense Fleet in the American Civil War. Sent from New Orleans to defend against the Federal descent of the Mississippi, she was among the force that engaged vessels of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla at the Battle of Plum Point Bend on May 10, 1862. On June 6, she again was involved in an action with the Federal gunboats, this time at the Battle of Memphis. In the battle, a shot from a Federal gun pierced her boiler, disabling her, and she was then pushed aground by the Federal ram and captured. Subsequently repaired and taken into the Union Navy, she served through the remainder of the war, seeing only limited action. After the war, she was deemed surplus by the Navy Department. Sold, she reentered the merchant service, where she remained until 1874. Confederate service ''Little Rebel'' was built as ''R. E. and A. N. Watso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships came into practical usage during the early 1800s; however, there were exceptions that came before. Steamships usually use the prefix designations of "PS" for ''paddle steamer'' or "SS" for ''screw steamer'' (using a propeller or screw). As paddle steamers became less common, "SS" is assumed by many to stand for "steamship". Ships powered by internal combustion engines use a prefix such as "MV" for ''motor vessel'', so it is not correct to use "SS" for most modern vessels. As steamships were less dependent on wind patterns, new trade routes opened up. The steamship has been described as a "major driver of the first wave of trade globalization (1870–1913)" and contributor to "an increase in international trade that was unprecedented in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)