|
Cornea Plana 2
Cornea plana 2 (CNA2) is a congenital disorder that causes the cornea to flatten and the angle between the sclera and cornea to shrink. This could result in the early development of arcus lipoides, hazy corneal limbus, and hyperopia. There is evidence that cornea plana 2 is caused by mutations in KERA (gene), KERA gene encoding ''keratocan''. Cornea plana 2 is an autosomal recessive disorder. Signs and symptoms Cornea plana commonly presents as a flat cornea, early-onset Arcus senilis, arcus lipoides, low Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber depth, and an indistinct border between the sclera and cornea due to a decreased angle between the two. Although a small corneal diameter is anticipated, measuring it can be challenging because the scleral tissue overlaps the cornea by a few millimeters. In the patients who have cornea plana, the Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber depth has been found to vary from 0.8 to 2.1 mm. Moreover, high hyperopia, strabismus, mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism. This is why it is especially important for this disorder to be treated in children at a young age, before it can interfere with vision development. The term is from Greek 'fall, falling'. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms typically seen in this condition include: * The eyelid(s) may appear to droop. * Droopy eyelids can give the face a false appearance of being fatigued, disinterested, or even sinister. * The eyelid may not protect the eye as effectively, allowing it to dry out. * Sagging upper eyelids can partially block the person's field of view. * Obstructed vision may cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Diseases
This is a partial list of human eye diseases and disorders. The World Health Organization publishes a classification of known diseases and injuries, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, or ICD-10. This list uses that classification. H00-H06 Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit * (H02.1) Ectropion * (H02.2) Lagophthalmos * (H02.3) Blepharochalasis * (H02.4) Ptosis * (H02.5) Stye, an acne type infection of the sebaceous glands on or near the eyelid. * (H02.6) Xanthelasma of eyelid * (H03.0*) Parasitic infestation of eyelid in diseases classified elsewhere ** Dermatitis of eyelid due to Demodex species ( B88.0+ ) ** Parasitic infestation of eyelid in: *** leishmaniasis ( B55.-+ ) *** loiasis ( B74.3+ ) *** onchocerciasis ( B73+ ) *** phthiriasis ( B85.3+ ) * (H03.1*) Involvement of eyelid in other infectious diseases classified elsewhere ** Involvement of eyelid in: *** herpesviral (herpes simplex) infection ( B00.5+ ) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratoglobus
Keratoglobus (from Greek: ''kerato-'' horn, cornea; and Latin: ''globus'' round) is a degenerative non- inflammatory disorder of the eye in which structural changes within the cornea cause it to become extremely thin and change to a more globular shape than its normal gradual curve. It causes corneal thinning, primarily at the margins, resulting in a spherical, slightly enlarged eye. It is sometimes equated with "megalocornea". Pathophysiology Keratoglobus is a little-understood disease with an uncertain cause, and its progression following diagnosis is unpredictable. If afflicting both eyes, the deterioration in vision can affect the patient's ability to drive a car or read normal print. It does not however lead to blindness. Treatment Treatment includes the use of protective eye glasses. A number of surgical options are also available. Further progression of the disease usually leads to a need for corneal transplantation because of extreme thinning of the cornea. Primarily, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea Plana 1
Cornea plana 1 (CNA1) is a congenital disorder that causes the cornea to flatten and the angle between the sclera and cornea to shrink. This could result in the early development of arcus lipoides, hazy corneal limbus, and hyperopia. Cornea plana 1 is an autosomal dominant disorder. Signs and symptoms Cornea plana commonly presents as a flat cornea, early-onset arcus lipoides, low anterior chamber depth, and an indistinct border between the sclera and cornea due to a decreased angle between the two. Although a small corneal diameter is anticipated, measuring it can be challenging because the scleral tissue overlaps the cornea by a few millimeters. In the patients who have been described, the anterior chamber depth has been found to vary from 0.8 to 2.1 mm. Moreover, high hyperopia, strabismus, microcornea, posterior embryotoxon, iridocorneal adhesions, iris lumps, iris wasting, and pupillary abnormalities can all be present. Instead of hyperopia, myopia has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromal Cell
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa (endometrium), prostate, bone marrow, lymph node and the ovary. They are cells that support the function of the parenchymal cells of that organ. The most common stromal cells include fibroblasts and pericytes. The term ''stromal'' comes from Latin , "bed covering", and Ancient Greek , , "bed". Stromal cells are an important part of the body's immune response and modulate inflammation through multiple pathways. They also aid in differentiation of hematopoietic cells and forming necessary blood elements. The interaction between stromal cells and tumor cells is known to play a major role in cancer growth and progression. In addition, by regulating local cytokine networks (e.g. M-CSF, LIF), bone marrow stromal cells have been described to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowman's Membrane
The Bowman layer (Bowman's membrane, anterior limiting lamina, anterior elastic lamina) is a smooth, acellular, nonregenerating layer, located between the superficial epithelium and the stroma in the cornea of the eye. It is composed of strong, randomly oriented collagen fibrils in which the smooth anterior surface faces the epithelial basement membrane and the posterior surface merges with the collagen lamellae of the corneal stroma proper. In adult humans, Bowman layer is 8-12 μm thick. With ageing, this layer becomes thinner. The function of the Bowman layer remains unclear and appears to have no critical function in corneal physiology. Recently, it is postulated that the layer may act as a physical barrier to protect the subepithelial nerve plexus and thereby hastens epithelial innervation and sensory recovery. Moreover, it may also serve as a barrier that prevents direct traumatic contact with the corneal stroma and hence it is highly involved in stromal wound healing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthosis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneal Pachymetry
Corneal pachymetry is the process of measuring the thickness of the cornea. A pachymeter is a medical device used to measure the thickness of the eye's cornea. It is used to perform corneal pachymetry prior to refractive surgery, for Keratoconus screening, LRI surgery and is useful in screening for patients suspected of developing glaucoma among other uses. Process It can be done using either ultrasonic or optical methods . The contact methods, such as ultrasound and optical such as confocal microscopy (CONFOSCAN), or noncontact methods such as optical biometry with a single Scheimpflug camera (such as SIRIUS or PENTACAM), or a Dual Scheimpflug camera (such as GALILEI), or Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT, such as Visante) and online Optical Coherence Pachymetry (OCP, such as ORBSCAN). Corneal Pachymetry is essential prior to a refractive surgery procedure for ensuring sufficient corneal thickness to prevent abnormal bulging of the cornea, a side effect known as ectasia. Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
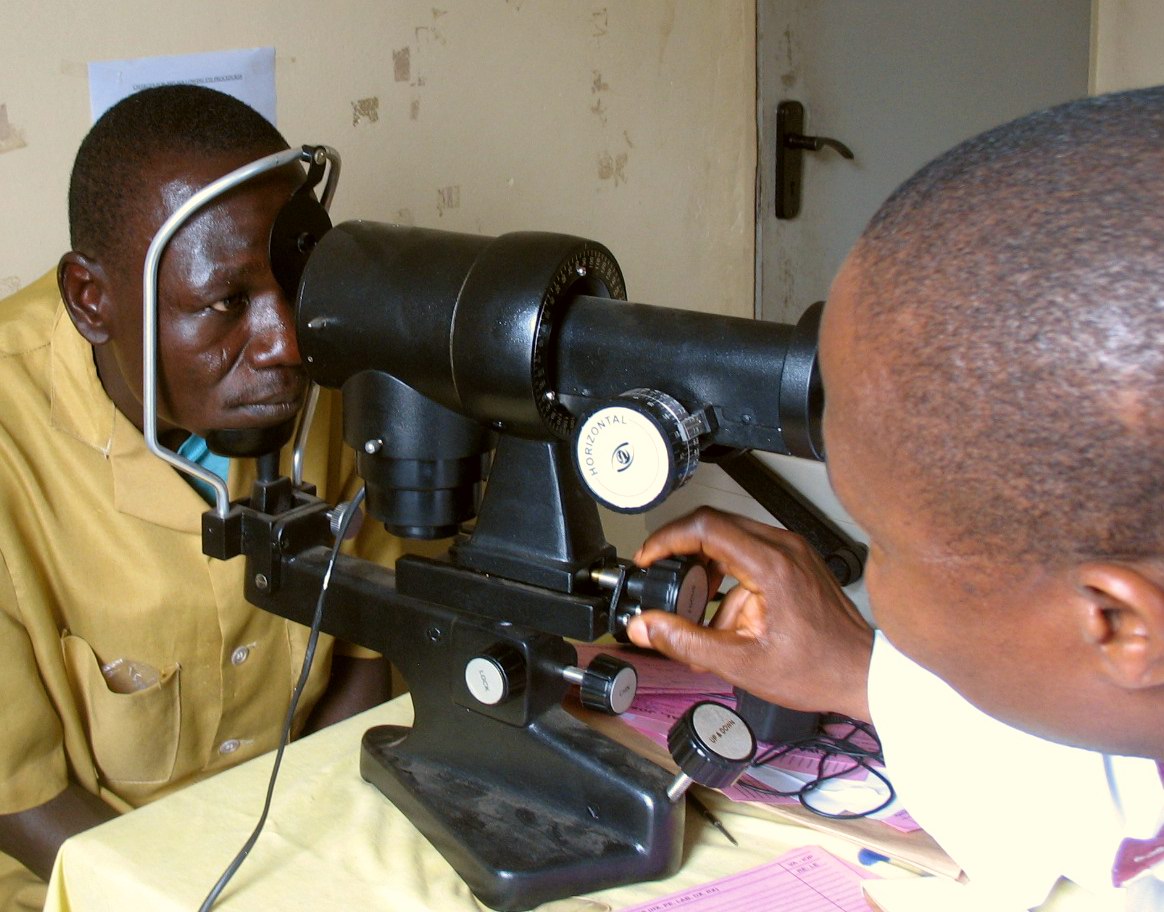
Keratometer
A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea, particularly for assessing the extent and axis of astigmatism. It was invented by the German physiologist Hermann von Helmholtz in 1851, although an earlier model was developed in 1796 by Jesse Ramsden and Everard Home. A keratometer uses the relationship between object size (O), image size (I), the distance between the reflective surface and the object (d), and the radius of the reflective surface (R). If three of these variables are known (or fixed), the fourth can be calculated using the formula :R = 2d \frac{O} There are two distinct variants of determining R; Javal-Schiotz type keratometers have a fixed image size and are typically 'two position', whereas Bausch and Lomb type keratometers have a fixed object size and are usually 'one position'. Javal-Schiotz Principles The Javal-Schiotz keratometer is a two position instrument whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |