|
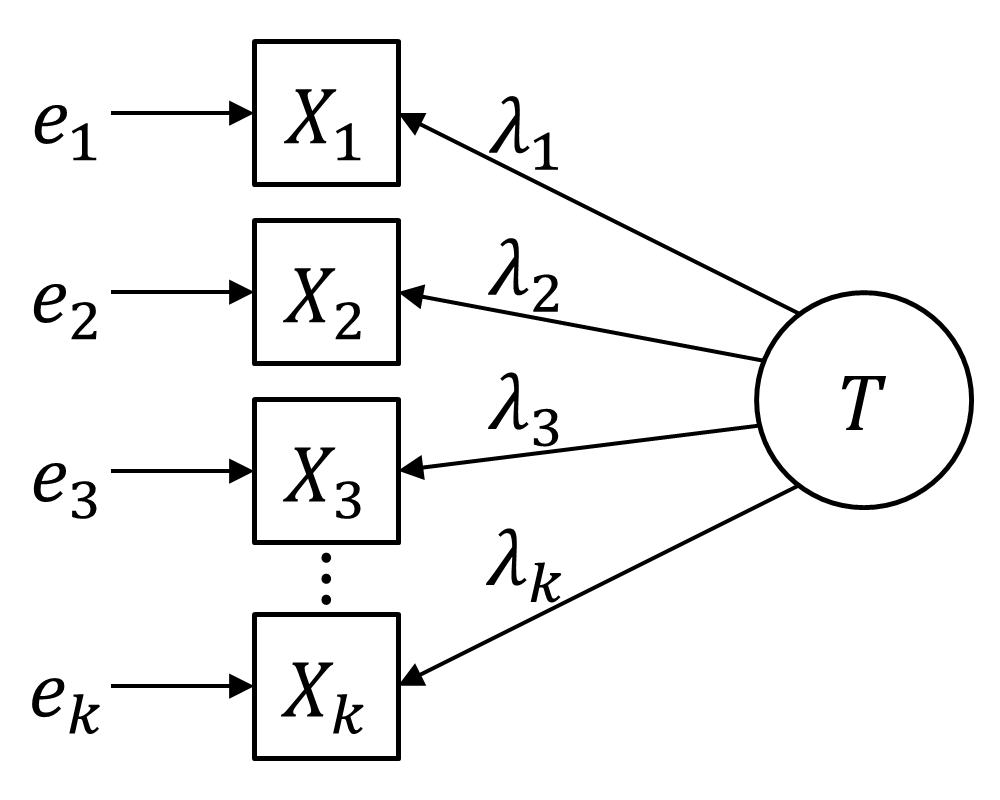
Congeneric Reliability
In statistical models applied to psychometrics, congeneric reliability \rho_C ("rho C")Cho, E. (2016). Making reliability reliable: A systematic approach to reliability coefficients. Organizational Research Methods, 19(4), 651–682. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428116656239 a single-administration test score reliability (i.e., the reliability of persons over items holding occasion fixed coefficient, commonly referred to as composite reliability, construct reliability, and coefficient omega. \rho_C is a structural equation model(SEM)-based reliability coefficients and is obtained from on a unidimensional model. \rho_C is the second most commonly used reliability factor after tau-equivalent reliability(\rho_T), and is often recommended as its alternative. Formula and calculation Systematic and conventional formula Let X_i denote the observed score of item i and X(=X_1 + X_2 + \cdots + X_k) denote the sum of all items in a test consisting of k items. It is assumed that each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau-equivalent Reliability
Cronbach's alpha (Cronbach's \alpha), also known as tau-equivalent reliability (\rho_T) or coefficient alpha (coefficient \alpha), is a reliability coefficient that provides a method of measuring internal consistency of tests and measures. Numerous studies warn against using it unconditionally, and note that reliability coefficients based on structural equation modeling (SEM) are in many cases a suitable alternative.Sijtsma, K. (2009). On the use, the misuse, and the very limited usefulness of Cronbach's alpha. Psychometrika, 74(1), 107–120. Green, S. B., & Yang, Y. (2009). Commentary on coefficient alpha: A cautionary tale. Psychometrika, 74(1), 121–135. Revelle, W., & Zinbarg, R. E. (2009). Coefficients alpha, beta, omega, and the glb: Comments on Sijtsma. Psychometrika, 74(1), 145–154. Cho, E., & Kim, S. (2015). Cronbach's coefficient alpha: Well known but poorly understood. Organizational Research Methods, 18(2), 207–230. Raykov, T., & Marcoulides, G. A. (2017). Thanks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congeneric Measurement Model
Congener may refer to: * A thing or person of the same kind as another, or of the same group. * Congener (biology), organisms within the same genus. * Congener (chemistry), related chemicals, e.g., elements in the same group of the periodic table. * Congener (beverages), a substance other than ethanol produced during the fermentation of alcoholic beverages. Species * ''Agabus congener'', a beetle in the family Dytiscidae. * ''Amata congener'', a moth in the family Erebidae. * ''Amyema congener'', a flowering plant in the family Loranthaceae. * ''Arthroplea congener'', a mayfly in the family Arthropleidae. * ''Elaphropus congener'', a ground beetle in the family Carabidae. * ''Gemmula congener'', a sea snail in the family Turridae. * ''Heterachthes congener'', a beetle in the family Cerambycidae. * ''Lestes congener'', a damselfly in the family Lestidae. * ''Megacyllene congener'', a beetle in the family Cerambycidae. * '' Potamarcha congener'', a dragonfly in the family Libellulid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Loading
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, persona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, persona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Variance Extracted
In statistics (classical test theory), average variance extracted (AVE) is a measure of the amount of variance that is captured by a construct in relation to the amount of variance due to measurement error.Fornell & Larcker (1981), https://www.jstor.org/stable/3151312 History The average variance extracted was first proposed by Fornell & Larcker (1981). Calculation The average variance extracted can be calculated as follows: : \text = \frac Here, k is the number of items, \lambda_i the factor loading of item i and \operatorname( e_i ) the variance of the error of item i. Role for assessing discriminant validity The average variance extracted has often been used to assess discriminant validity based on the following "rule of thumb": the positive square root of the AVE for each of the latent variables should be higher than the highest correlation with any other latent variable. If that is the case, discriminant validity is established at the construct level. This rule i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Assessments
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and in the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |