|
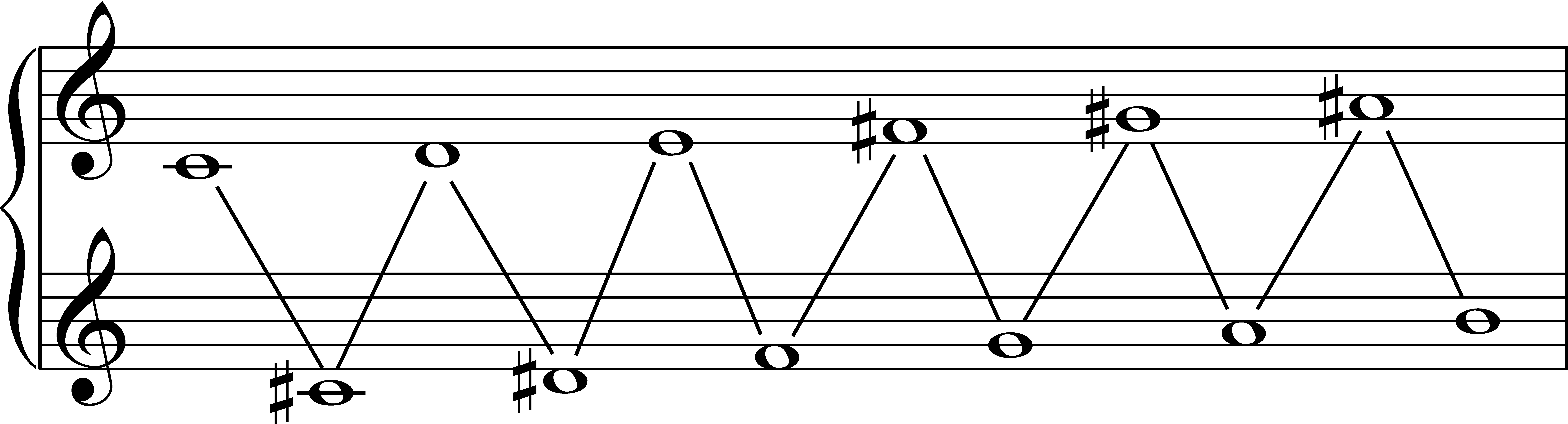
Common Tone (scale)
In music, a common tone is a pitch class that is a member of, or common to (shared by) two or more scales or sets. Common tone theorem A common tone is a pitch class that is a member of, or common to, a musical scale and a transposition of that scale, as in modulation. Six of seven possible common tones are shared by closely related keys, though keys may also be thought of as more or less closely related according to their number of common tones. "Obviously, tonal distance is in some sense a function of the extent of intersection between diatonic PC collections of tonal systems". In diatonic set theory the common tone theorem explains that scales possessing the deep scale property share a different number of common tones, not counting enharmonic equivalents (for example, C and C have no common tones with C major), for every different transposition of the scale. However many times an interval class occurs in a diatonic scale is the number of tones common both to the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Tone Example
Common may refer to: As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin. Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (1841–1903), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (1889–1953), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (1850–1919), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy McGove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common Chord (music)
Common chord may refer to: * Common chord (geometry), the secant line that joins the intersection points of two curves * Common chord (music), a chord shared by two musical keys * '' The Common Chord'', a 1947 short story collection by Frank O'Connor * ''Common Chord'' (album), a 1993 album by David Grisman * Common Chord (organization), nonprofit community music organization in Davenport, Iowa {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Approach Chord
{{disambiguation ...
Approach may refer to: Aviation *Visual approach *Instrument approach * Final approach Music * ''Approach'' (album), by Von Hertzen Brothers * ''The Approach'', an album by I:Scintilla Other uses *Approach Beach, a gazetted beach in Ting Kau, Hong Kong *Approach shot (other) *Lotus Approach, a database *Bridge approach * Approaches to scientific method *Bowling action in the sport of cricket * Flirting See also *Capability approach, in economic theory *Final approach (other) In aeronautics, the final approach (also called the final leg and final approach leg) is the last leg in an aircraft's approach to landing, when the aircraft is lined up with the runway and Descent (aeronautics), descending for landing.Crane, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Whole Tone Scale
In music, a whole-tone scale is a scale (music), scale in which each Musical note, note is separated from its neighbors by the interval (music), interval of a whole tone. In twelve-tone equal temperament, there are only two Complement (music)#Aggregate complementation, complementary whole-tone scales, both six-note or ''Hexatonic scale, hexatonic'' scales. A single whole-tone scale can also be thought of as a "six-tone equal temperament". : : The whole-tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, [and] the scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasised by the fact that triad (music), triads built on such scale tones are all augmented triads. Indeed, all six tones of a whole-tone scale can be played simply with two augmented triads whose roots are a major second apart. Since they are symmetric scale, symmetrical, whole-tone scales do not give a strong impression of the tonic ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
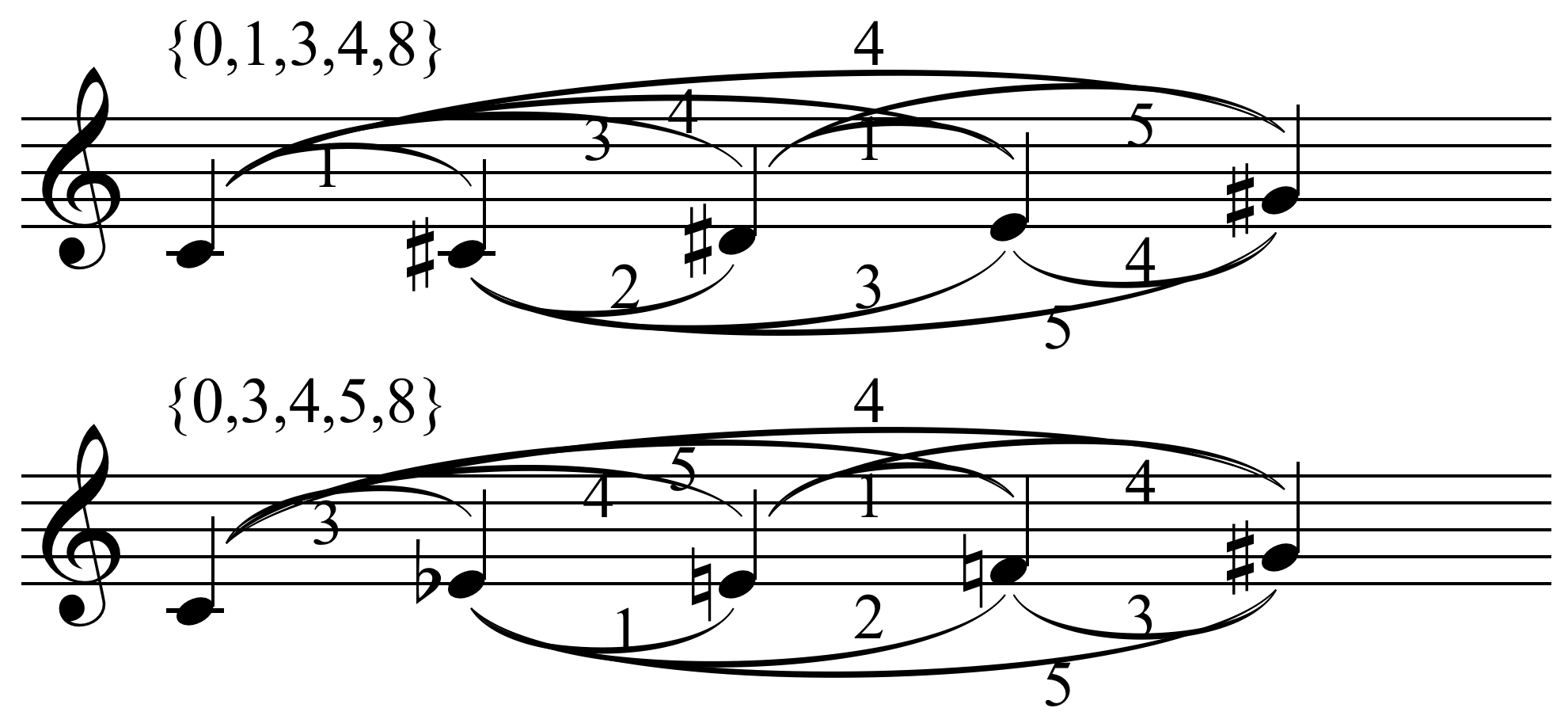
Interval Vector
In musical set theory, an interval vector is an array of natural numbers which summarize the intervals present in a set of pitch classes. (That is, a set of pitches where octaves are disregarded.) Other names include: ic vector (or interval-class vector), PIC vector (or pitch-class interval vector) and APIC vector (or absolute pitch-class interval vector, which Michiel Schuijer states is more proper.) While primarily an analytic tool, interval vectors can also be useful for composers, as they quickly show the sound qualities that are created by different collections of pitch class. That is, sets with high concentrations of conventionally dissonant intervals (i.e., seconds and sevenths) sound more dissonant, while sets with higher numbers of conventionally consonant intervals (i.e., thirds and sixths) sound more consonant. While the actual perception of consonance and dissonance involves many contextual factors, such as register, an interval vector can nevertheless be a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Generated Collection
In music theory, a generated collection is a collection or scale formed by repeatedly adding a constant interval in integer notation, the generator, also known as an interval cycle, around the chromatic circle until a complete collection or scale is formed. All scales with the deep scale property can be generated by any interval coprime with the number of notes per octave. (Johnson, 2003, p. 83) The C major diatonic collection can be generated by adding a cycle of perfect fifths (C7) starting at F: F-C-G-D-A-E-B = C-D-E-F-G-A-B. Using integer notation and 12-tone equal temperament, the standard tuning of Western music: 5 + 7 = 0, 0 + 7 = 7, 7 + 7 = 2, 2 + 7 = 9, 9 + 7 = 4, 4 + 7 = 11. The C major scale could also be generated using cycle of perfect fourths (C5), as 12 minus any coprime of twelve is also coprime with twelve: 12 − 7&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields Pitch (music), pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2, (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western world, Western countries the term ''equal temperamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Musical Mode
In music theory, the term mode or ''modus'' is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context. Its most common use may be described as a type of musical scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic and harmonic behaviors. It is applied to major and minor keys as well as the seven diatonic modes (including the former as Ionian and Aeolian) which are defined by their starting note or tonic. ( Olivier Messiaen's modes of limited transposition are strictly a scale type.) Related to the diatonic modes are the eight church modes or Gregorian modes, in which authentic and plagal forms of scales are distinguished by ambitus and tenor or reciting tone. Although both diatonic and Gregorian modes borrow terminology from ancient Greece, the Greek ''tonoi'' do not otherwise resemble their medieval/modern counterparts. Previously, in the Middle Ages the term modus was used to describe intervals, individual notes, and rhythms (see ). Modal rhythm was an essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Minor Scale
In Classical_music, Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three Scale (music), scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending). These scales contain all three notes of a minor triad: the root (chord), root, a minor third (rather than the major third, as in a Major chord, major triad or major scale), and a perfect fifth (rather than the tritone, diminished fifth, as in a diminished scale or half diminished scale). Minor scale is also used to refer to other scales with this property, such as the Dorian mode or the Pentatonic Scale#Minor pentatonic scale, minor pentatonic scale (see #Other minor scales, other minor scales below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth Degree (music), degree of its relative major, relative major scale. For instance, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
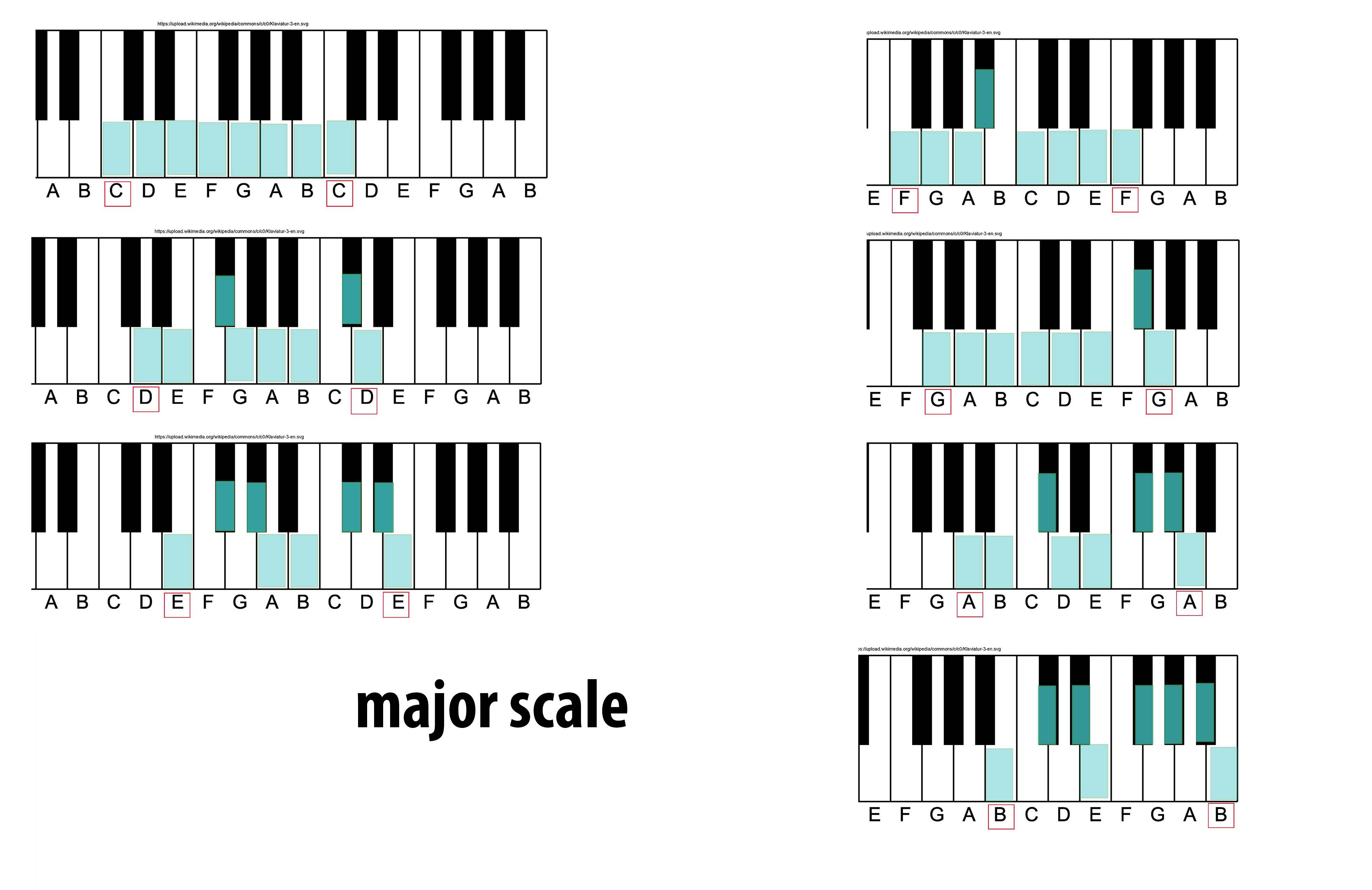
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diatonic Scale
In music theory a diatonic scale is a heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven-note) scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps. In other words, the half steps are maximally separated from each other. The seven pitch (music), pitches of any diatonic scale can also be obtained by using a Interval cycle, chain of six perfect fifths. For instance, the seven natural (music), natural pitch classes that form the C-major scale can be obtained from a stack of perfect fifths starting from F: :F–C–G–D–A–E–B. Any sequence of seven successive natural notes, such as C–D–E–F–G–A–B, and any Transposition (music), transposition thereof, is a diatonic scale. Modern musical keyboards are designed so that the white-key notes form a diatonic scale, though transpositions of this diatonic scale require one or more black keys. A diaton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |