|
Comma (music)
In music theory, a comma is a very small interval, the difference resulting from tuning one note two different ways. Strictly speaking, there are only two kinds of comma, the syntonic comma, "the difference between a just major 3rd and four just perfect 5ths less two octaves", and the Pythagorean comma, "the difference between twelve 5ths and seven octaves". The word ''comma'' used without qualification refers to the syntonic comma, which can be defined, for instance, as the difference between an F tuned using the D-based Pythagorean tuning system, and another F tuned using the D-based quarter-comma meantone tuning system. Intervals separated by the ratio 81:80 are considered the same note because the 12-note Western chromatic scale does not distinguish Pythagorean intervals from 5-limit intervals in its notation. Other intervals are considered commas because of the enharmonic equivalences of a tuning system. For example, in 53TET, B and A are both approximated by the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntonic Comma On C
In music theory, the syntonic comma, also known as the chromatic diesis, the Didymean comma, the Ptolemaic comma, or the diatonic comma is a small comma type interval between two musical notes, equal to the frequency ratio 81:80 (= 1.0125) (around 21.51 cents). Two notes that differ by this interval would sound different from each other even to untrained ears, , ''BBC''. but would be close enough that they would be more likely interpreted as out-of-tune versions of the same note than as different notes. The comma is also referred to as a Didymean comma because it is the amount by which Didymus corrected the |
Enharmonically Equivalent
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cent (music)
The cent is a logarithmic unit of measure used for musical intervals. Twelve-tone equal temperament divides the octave into 12 semitones of 100 cents each. Typically, cents are used to express small intervals, or to compare the sizes of comparable intervals in different tuning systems, and in fact the interval of one cent is too small to be perceived between successive notes. Cents, as described by Alexander John Ellis, follow a tradition of measuring intervals by logarithms that began with Juan Caramuel y Lobkowitz in the 17th century. Ellis chose to base his measures on the hundredth part of a semitone, , at Robert Holford Macdowell Bosanquet's suggestion. He made extensive measurements of musical instruments from around the world, using cents extensively to report and compare the scales employed, and further described and employed the system in his 1875 edition of Hermann von Helmholtz's ''On the Sensations of Tone''. It has become the standard method of representin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-limit Tuning
Five-limit tuning, 5-limit tuning, or 5-prime-limit tuning (not to be confused with 5-odd-limit tuning), is any system for tuning a musical instrument that obtains the frequency of each note by multiplying the frequency of a given reference note (the base note) by products of integer powers of 2, 3, or 5 (prime numbers limited to 5 or lower), such as . Powers of 2 represent intervallic movements by octaves. Powers of 3 represent movements by intervals of perfect fifths (plus one octave, which can be removed by multiplying by 1/2, i.e., 2−1). Powers of 5 represent intervals of major thirds (plus two octaves, removable by multiplying by 1/4, i.e., 2−2). Thus, 5-limit tunings are constructed entirely from stacking of three basic purely-tuned intervals (octaves, thirds and fifths). Since the perception of consonance seems related to low numbers in the harmonic series, and 5-limit tuning relies on the three lowest primes, 5-limit tuning should be capable of producing very consona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
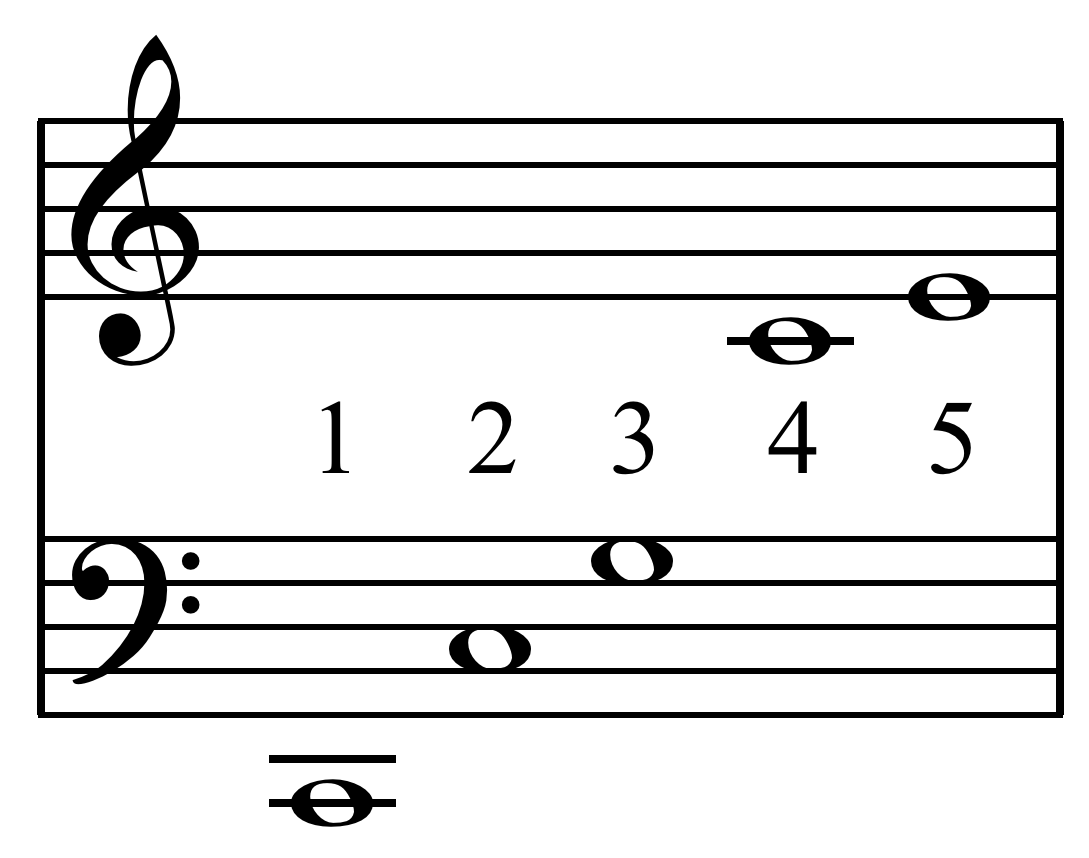
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth. In Western musical practice, instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire for different keys to have identical intervals in Western music makes this impractical. Some instruments of fixed pitch, such as electric pianos, are commonly tuned using equal temperament, in which all intervals other than octaves consist of irrational-number freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Comma (difference A1-m2)
In musical tuning, the Pythagorean comma (or ditonic comma), named after the ancient mathematician and philosopher Pythagoras, is the small interval (or comma) existing in Pythagorean tuning between two enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and B (), or D and C. It is equal to the frequency ratio = ≈ 1.01364, or about 23.46 cents, roughly a quarter of a semitone (in between 75:74 and 74:73). The comma that musical temperaments often refer to tempering is the Pythagorean comma. The Pythagorean comma can be also defined as the difference between a Pythagorean apotome and a Pythagorean limma (i.e., between a chromatic and a diatonic semitone, as determined in Pythagorean tuning), or the difference between twelve just perfect fifths and seven octaves, or the difference between three Pythagorean ditones and one octave (this is the reason why the Pythagorean comma is also called a ''ditonic comma''). The diminished second, in Pythagorean tuning, is defined as the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Diesis (difference M2-A1)
In classical music from Western culture, a diesis ( , plural dieses ( , "difference"; Greek: δίεσις "leak" or "escape"Benson, Dave (2006). ''Music: A Mathematical Offering'', p.171. . Based on the technique of playing the aulos, where pitch is raised a small amount by slightly raising the finger on the lowest closed hole, letting a small amount of air "escape".) is either an accidental (see sharp), or a very small musical interval, usually defined as the difference between an octave (in the ratio 2:1) and three justly tuned major thirds (tuned in the ratio 5:4), equal to 128:125 or about 41.06 cents. In 12-tone equal temperament (on a piano for example) three major thirds in a row equal an octave, but three justly-tuned major thirds fall quite a bit narrow of an octave, and the diesis describes the amount by which they are short. For instance, an octave (2:1) spans from C to C', and three justly tuned major thirds (5:4) span from C to B (namely, from C, to E, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the chromatic scale, while other instruments capable of continuously variable pitch, such as the trombone and violin, can also produce microtones, or notes between those available on a piano. Most music uses subsets of the chromatic scale such as diatonic scales. While the chromatic scale is fundamental in western music theory, it is seldom directly used in its entirety in musical compositions or improvisation. Definition The chromatic scale is a musical scale with twelve pitches, each a semitone, also known as a half-step, above or below its adjacent pitches. As a result, in 12-tone equal temperament (the most common tuning in Western music), the chromatic scale covers all 12 of the available pitches. Thus, there is only one chromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meantone Temperament
Meantone temperament is a musical temperament, that is a tuning system, obtained by narrowing the fifths so that their ratio is slightly less than 3:2 (making them ''narrower'' than a perfect fifth), in order to push the thirds closer to pure. Meantone temperaments are constructed the same way as Pythagorean tuning, as a stack of equal fifths, but it is a ''temperament'' in that the fifths are not pure. Notable meantone temperaments Equal temperament, obtained by making all semitones the same size, each equal to one-twelfth of an octave (with ratio the 12th root of 2 to one (:1), narrows the fifths by about 2 cents or 1/12 of a Pythagorean comma, and produces thirds that are only slightly better than in Pythagorean tuning. Equal temperament is roughly the same as 1/11 comma meantone tuning. Quarter-comma meantone, which tempers the fifths by 1/4 of a syntonic comma, is the best known type of meantone temperament, and the term ''meantone temperament'' is often used to refer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitone
A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones. In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. from C to C). These are enharmonically equivalent when twelve-tone equal temperament is used, but are not the same thing in meantone te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesis
In classical music from Western culture, a diesis ( , plural dieses ( , "difference"; Greek: δίεσις "leak" or "escape"Benson, Dave (2006). ''Music: A Mathematical Offering'', p.171. . Based on the technique of playing the aulos, where pitch is raised a small amount by slightly raising the finger on the lowest closed hole, letting a small amount of air "escape".) is either an accidental (see sharp), or a very small musical interval, usually defined as the difference between an octave (in the ratio 2:1) and three justly tuned major thirds (tuned in the ratio 5:4), equal to 128:125 or about 41.06 cents. In 12-tone equal temperament (on a piano for example) three major thirds in a row equal an octave, but three justly-tuned major thirds fall quite a bit narrow of an octave, and the diesis describes the amount by which they are short. For instance, an octave (2:1) spans from C to C', and three justly tuned major thirds (5:4) span from C to B (namely, from C, to E, to G, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |