|
Coleoptile
Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed. The coleoptile protects the first leaf as well as the growing stem in seedlings and eventually, allows the first leaf to emerge. Coleoptiles have two vascular bundles, one on either side. Unlike the flag leaves rolled up within, the pre-emergent coleoptile does not accumulate significant protochlorophyll or carotenoids, and so it is generally very pale. Some preemergent coleoptiles do, however, accumulate purple anthocyanin pigments. Coleoptiles consist of very similar cells that are all specialised to fast stretch growth. They do not divide, but increase in size as they accumulate more water. Coleoptiles also have water vessels (frequently two) along the axis to provide a water supply. When a coleoptile reaches the surface, it stops growing and the flag leaves penetrate its top, continuing to grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoptile
Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed. The coleoptile protects the first leaf as well as the growing stem in seedlings and eventually, allows the first leaf to emerge. Coleoptiles have two vascular bundles, one on either side. Unlike the flag leaves rolled up within, the pre-emergent coleoptile does not accumulate significant protochlorophyll or carotenoids, and so it is generally very pale. Some preemergent coleoptiles do, however, accumulate purple anthocyanin pigments. Coleoptiles consist of very similar cells that are all specialised to fast stretch growth. They do not divide, but increase in size as they accumulate more water. Coleoptiles also have water vessels (frequently two) along the axis to provide a water supply. When a coleoptile reaches the surface, it stops growing and the flag leaves penetrate its top, continuing to grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
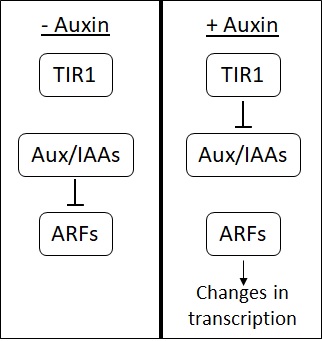
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholodny–Went Model
In botany, the Cholodny–Went model, proposed in 1927, is an early model describing tropism in emerging shoots of monocotyledons, including the tendencies for the shoot to grow towards the light ( phototropism) and the roots to grow downward (gravitropism). In both cases the directional growth is considered to be due to asymmetrical distribution of auxin, a plant growth hormone. Although the model has been criticized and continues to be refined, it has largely stood the test of time. Basic model The model was independently proposed by the Russian scientist Nikolai Cholodny of the University of Kyiv in 1927 and by Frits Warmolt Went of the California Institute of Technology in 1928, both based on work they had done in 1926. The basic elements of the theory are that auxin is the sole hormone that controls growth in gravitropism and phototropism; the rate of growth depends on the concentration of auxin; and both gravity and unidirectional light affect the movement of auxin. The or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototropism
Phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. The cells on the plant that are farthest from the light contain a hormone called auxin that reacts when phototropism occurs. This causes the plant to have elongated cells on the furthest side from the light. Phototropism is one of the many plant tropisms or movements which respond to external stimuli. Growth towards a light source is called positive phototropism, while growth away from light is called negative phototropism. Negative phototropism is not to be confused with skototropism which is defined as the growth towards darkness, whereas negative phototropism can refer to either the growth away from a light source or towards the darkness. Most plant shoots exhibit positive phototropism, and rearrange their chloroplasts in the leaves to maximize photosynthetic energy and promote growth.Goyal, A., Szarzyns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Cholodny
Mykola Hryhorovych Kholodny ( ukr, Микола Григорович Холодний ; 22 June 1882 – 4 May 1953) was an influential microbiologist who worked at the University of Kyiv, Ukraine in the USSR during the 1930s. He is known for the Cholodny–Went model, which he developed independently with Frits Warmolt Went of the California Institute of Technology. Despite being associated with the same theory, the two men never actually met. Cholodny worked in the A.V. Fomin Botanical Garden, attached to the University of Kyiv. He was one of the pioneers of the concept that microbes adhere to surfaces, using the technique of first placing glass slides in earth for a measured time period, then using a microscope to examine the slides. The Prokaryote ''Leptothrix cholodnii'' is named after him. In 1927 Cholodny proposed that the cells of the coleoptile Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Darwin
Sir Francis "Frank" Darwin (16 August 1848 – 19 September 1925) was a British botanist. He was the third son of the naturalist and scientist Charles Darwin. Biography Francis Darwin was born in Down House, Downe, Kent in 1848. He was the third son and seventh child of Charles Darwin and his wife Emma Wedgwood. He was educated at Clapham Grammar School. He then went to Trinity College, Cambridge, first studying mathematics, then changing to natural sciences, graduating in 1870. He then went to study medicine at St George's Medical School, London, earning an MB in 1875, but did not practise medicine. Darwin was married three times and widowed twice. First he married Amy Richenda Ruck in 1874, but she died in 1876 four days after the birth of their son Bernard Darwin, who was later to become a golf writer. In September 1883 he married Ellen Wordsworth Crofts (1856–1903) and they had a daughter Frances Crofts Darwin (1886–1960), a poet who married the poet Francis Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotropism
Gravitropism (also known as geotropism) is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general feature of all higher and many lower plants as well as other organisms. Charles Darwin was one of the first to scientifically document that roots show ''positive gravitropism'' and stems show ''negative gravitropism''. That is, roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull (i.e., downward) and stems grow in the opposite direction (i.e., upwards). This behavior can be easily demonstrated with any potted plant. When laid onto its side, the growing parts of the stem begin to display negative gravitropism, growing (biologists say, turning; see tropism) upwards. Herbaceous (non-woody) stems are capable of a degree of actual bending, but most of the redirected movement occurs as a consequence of root or stem growth outside. The mechanism is base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses ( Poaceae), which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frits Warmolt Went
Frits Warmolt Went (May 18, 1903 – May 1, 1990) was a Dutch biologist whose 1928 experiment demonstrated the existence of auxin in plants. Went's father was the prominent Dutch botanist F.A.F.C. Went. After graduating from the University of Utrecht, Holland in 1927 with a dissertation on the effects of the plant hormone auxin, Went then worked as a plant pathologist in the research labs of the Royal Botanical Garden in Buitenzorg, Dutch East Indies (now Bogor, Indonesia) from 1927 to 1933. He then took a position at Caltech in Pasadena, California, first researching plant hormones. His interest gradually shifted to environmental influences on plant growth. At Caltech he was among the first to demonstrate the importance of hormones in plant growth and development. He played an important role in the development of synthetic plant hormones, which then became the basis of much of the agricultural chemical industry. Frees is known for the Cholodny–Went model, named after Went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitropism
Gravitropism (also known as geotropism) is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general feature of all higher and many lower plants as well as other organisms. Charles Darwin was one of the first to scientifically document that roots show ''positive gravitropism'' and stems show ''negative gravitropism''. That is, roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull (i.e., downward) and stems grow in the opposite direction (i.e., upwards). This behavior can be easily demonstrated with any potted plant. When laid onto its side, the growing parts of the stem begin to display negative gravitropism, growing (biologists say, turning; see tropism) upwards. Herbaceous (non-woody) stems are capable of a degree of actual bending, but most of the redirected movement occurs as a consequence of root or stem growth outside. The mechanism is bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocotyledons
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses (Poaceae), which are ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |