|
Cognitive Reflection Test
The cognitive reflection test (CRT) is a task designed to measure a person's tendency to override an incorrect "gut" response and engage in further reflection to find a correct answer; however, the validity of the assessment as a measure of "cognitive reflection" or "intuitive thinking" is under question. It was first described in 2005 by psychologist Shane Frederick. The CRT has a moderate positive correlation with measures of intelligence, such as the Intelligence Quotient test, and it correlates highly with various measures of mental heuristics. Some research argue that the CRT is actually measuring cognitive abilities (colloquially known as intelligence). Later research showed that the CRT is a multifaceted construct: many start their response with the correct answer, while others fail to solve the test even if they reflect on their intuitive first answer. It has also been argued that suppression of the first answer is not the only factor behind the successful performance on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shane Frederick
Shane Frederick is a tenured professor at the Yale School of Management. He earlier worked at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is the creator of the cognitive reflection test, which has been found to be "predictive of the types of choices that feature prominently in tests of decision-making theories, like expected utility theory and prospect theory. People who score high on the CRT are less vulnerable to various biases, and show more patience in intertemporal choice tasks. His specialties are decision-making and intertemporal choice, time preferences and Discount function, discount functions, and has authored papers with, among others, George Loewenstein of Carnegie Mellon University and Nobel laureate Daniel Kahneman, emeritus of Princeton University. Frederick was born in Park Falls, Wisconsin, and graduated from the University of Wisconsin with a B.A. in Zoology, from Simon Fraser University with an M.S. in Resource Management, and from Carnegie Mellon University wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. Intelligence is most often studied in humans but has also been observed in both non-human animals and in plants despite controversy as to whether some of these forms of life exhibit intelligence. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns '' intelligentia'' or '' intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb '' intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In the Middle Ages, the word ''intellectus'' became the scholarly technical term for understanding, and a translation f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thinking, Fast And Slow
''Thinking, Fast and Slow'' is a 2011 book by psychologist Daniel Kahneman. The book's main thesis is a differentiation between two modes of thought: "System 1" is fast, instinctive and emotional; "System 2" is slower, more deliberative, and more logical. The book delineates rational and non-rational motivations or triggers associated with each type of thinking process, and how they complement each other, starting with Kahneman's own research on loss aversion. From framing choices to people's tendency to replace a difficult question with one which is easy to answer, the book summarizes several decades of research to suggest that people have too much confidence in human judgement. Kahneman performed his own research, often in collaboration with Amos Tversky, which enriched his experience to write the book. It covers different phases of his career: his early work concerning cognitive biases, his work on prospect theory and happiness, and with the Israel Defense Forces. The book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Process Theory
In psychology, a dual process theory provides an account of how thought can arise in two different ways, or as a result of two different processes. Often, the two processes consist of an implicit (automatic), unconscious process and an explicit (controlled), conscious process. Verbalized explicit processes or attitudes and actions may change with persuasion or education; though implicit process or attitudes usually take a long amount of time to change with the forming of new habits. Dual process theories can be found in social, personality, cognitive, and clinical psychology. It has also been linked with economics via prospect theory and behavioral economics, and increasingly in sociology through cultural analysis. History The foundations of dual process theory likely comes from William James. He believed that there were two different kinds of thinking: associative and true reasoning. James theorized that empirical thought was used for things like art and design work. For James, im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council On Measurement In Education
The National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME) is a U.S. based professional organization for assessment, evaluation, testing, and other aspects of educational measurement. NCME was launched in 1938 and previously operated under the name National Council on Measurements Used in Education. NCME professionals work in evaluation, testing, program evaluation, and, more generally, educational and psychological measurement. Members come from universities, test development organizations, and industry. A goal of the organization is to ensure that assessment is fair and equitable for all students. NCME's Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice journal is accessible for all NCME members. See also * Psychometrics Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Psychological Association
The American Psychological Association (APA) is the largest scientific and professional organization of psychologists in the United States, with over 133,000 members, including scientists, educators, clinicians, consultants, and students. It has 54 divisions—interest groups for different subspecialties of psychology or topical areas. The APA has an annual budget of around $115 million. Profile The APA has task forces that issue policy statements on various matters of social importance, including abortion, human rights, the welfare of detainees, human trafficking, the rights of the mentally ill, IQ testing, sexual orientation change efforts, and gender equality. Governance APA is a corporation chartered in the District of Columbia. APA's bylaws describe structural components that serve as a system of checks and balances to ensure democratic process. The organizational entities include: * APA President. The APA's president is elected by the membership. The president chairs th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Educational Research Association
The American Educational Research Association (AERA, pronounced "A-E-R-A") is a professional organization representing education researchers in the United States and around the world. AERA's mission is to advance knowledge about education and promote the use of research in educational practice. Organization and membership AERA is led by an Executive Director (Felice J. Levine in 2020) and a President ( H. Richard Milner, IV from Vanderbilt University in 2022–23). AERA's governance structure includes the Council, Executive Board, standing committees, and award committees. Temporary committees, task forces, and working groups are initiated for other specific needs. AERA has 25,000 members, including scientists, teachers, students, administrators, state and local agencies, counselors, and evaluators. The range of disciplines represented by the membership includes education, psychology, statistics, sociology, history, economics, philosophy, anthropology, and political science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standards For Educational And Psychological Testing
''The Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing'' is a set of testing Standards organization, standards developed jointly by the American Educational Research Association (AERA), American Psychological Association (APA), and the National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME). The new edition of ''The Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing'' was released in July 2014. Five areas received particular attention in the 2014 revision: 1. Examining accountability issues associated with the uses of tests in educational policy 2. Broadening the concept of accessibility of tests for all examinees 3. Representing more comprehensively the role of tests in the workplace 4. Taking into account the expanding role of technology in testing 5. Improving the structure of the book for better communication of the standards Previous versions It was published on 1985, the 1999 ''Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing'' has more in-depth background material in ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychometrics
Psychometrics is a field of study within psychology concerned with the theory and technique of measurement. Psychometrics generally refers to specialized fields within psychology and education devoted to testing, measurement, assessment, and related activities. Psychometrics is concerned with the objective measurement of latent constructs that cannot be directly observed. Examples of latent constructs include intelligence, introversion, mental disorders, and educational achievement. The levels of individuals on nonobservable latent variables are inferred through mathematical modeling based on what is observed from individuals' responses to items on tests and scales. Practitioners are described as psychometricians, although not all who engage in psychometric research go by this title. Psychometricians usually possess specific qualifications such as degrees or certifications, and most are psychologists with advanced graduate training in psychometrics and measurement theory. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Validity (statistics)
Validity is the main extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and likely corresponds accurately to the real world. The word "valid" is derived from the Latin validus, meaning strong. The validity of a measurement tool (for example, a test in education) is the degree to which the tool measures what it claims to measure. Validity is based on the strength of a collection of different types of evidence (e.g. face validity, construct validity, etc.) described in greater detail below. In psychometrics, validity has a particular application known as test validity: "the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores" ("as entailed by proposed uses of tests"). It is generally accepted that the concept of scientific validity addresses the nature of reality in terms of statistical measures and as such is an epistemological and philosophical issue as well as a question of measurement. The use of the term in logic is narrower, relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
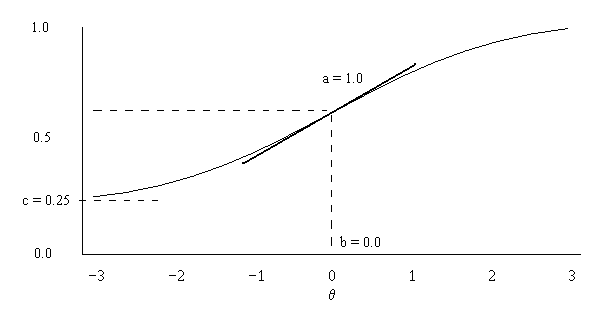
Item Response Theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) (also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments".A. van Alphen, R. Halfens, A. Hasman and T. Imbos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be described as the ability to perceive or infer information, and to retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context. Intelligence is most often studied in humans but has also been observed in both non-human animals and in plants despite controversy as to whether some of these forms of life exhibit intelligence. Intelligence in computers or other machines is called artificial intelligence. Etymology The word ''intelligence'' derives from the Latin nouns '' intelligentia'' or '' intellēctus'', which in turn stem from the verb '' intelligere'', to comprehend or perceive. In the Middle Ages, the word ''intellectus'' became the scholarly technical term for understanding, and a translation f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |